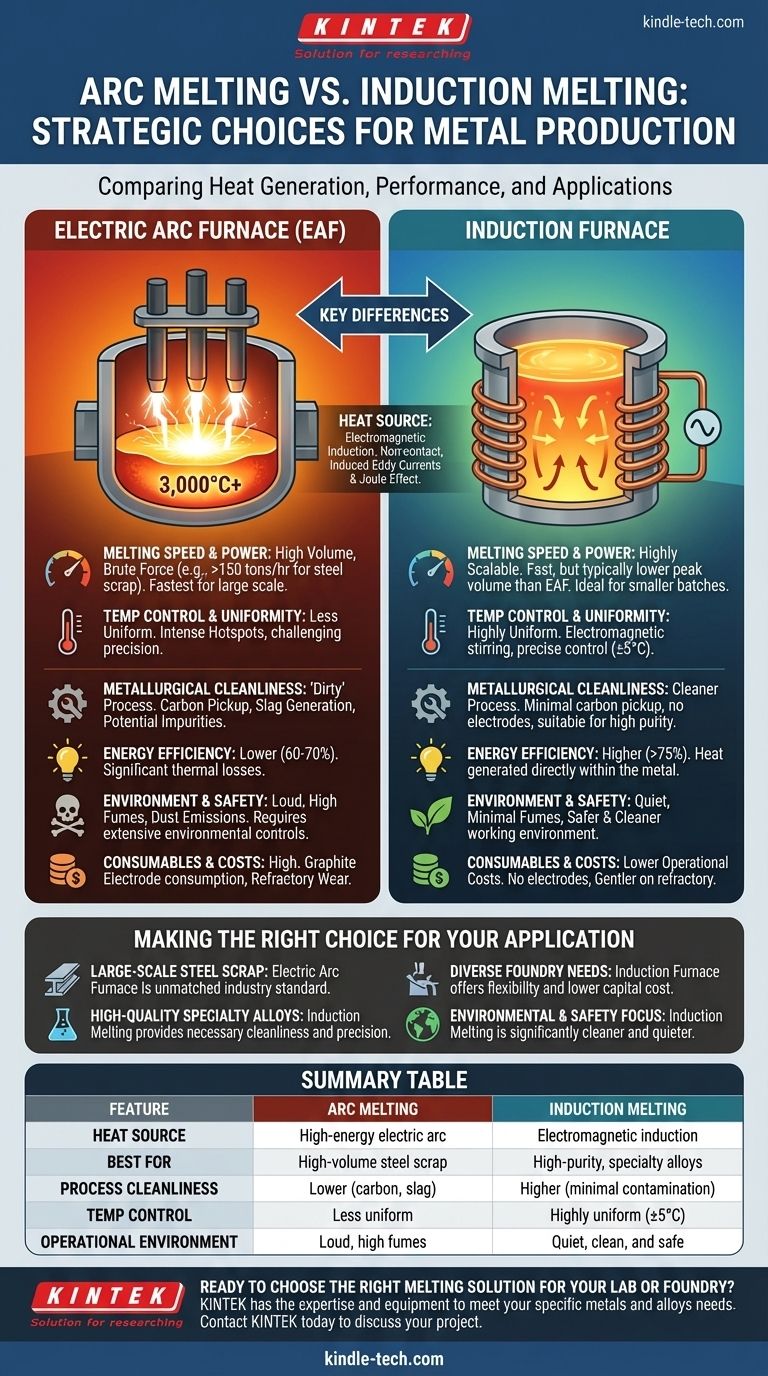
At its core, the primary difference between arc and induction melting lies in the method of heat generation. An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) uses a high-energy electric arc—a controlled lightning strike—that passes from graphite electrodes to the metal, melting it with intense, direct heat. In contrast, an induction furnace uses non-contact electromagnetic fields to generate heat within the metal itself, offering a fundamentally cleaner and more controlled process.
Choosing between arc and induction melting is not a simple preference; it is a strategic decision based on a trade-off between raw power and metallurgical precision. Arc melting excels at high-volume, "brute force" melting of raw materials like steel scrap, while induction melting provides the control and purity required for high-value and specialty alloys.

The Mechanics of Melting: Arc vs. Induction
To understand which technology fits your goals, you must first grasp their fundamentally different operating principles.
How Arc Furnaces Work
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) operates by creating an extremely hot electric arc between graphite electrodes and the metallic charge inside the furnace.
This arc can reach temperatures exceeding 3,000°C (5,400°F), rapidly transferring immense thermal energy to the metal. The process is aggressive, powerful, and designed for melting massive quantities of material quickly.
How Induction Furnaces Work
An induction furnace functions like a high-powered wireless charger for metal. An alternating current is passed through a copper coil, creating a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field.
When conductive metal is placed within this field, the field induces strong electrical eddy currents inside the metal. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates precise, uniform heat throughout the charge via the Joule effect, melting it from the inside out.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in heating mechanisms lead to significant variations in performance, quality, and operational scope.
Melting Speed and Power
Arc furnaces are the undisputed leaders in raw melting power and speed for very large volumes. They are the backbone of "mini-mills" and can melt over 150 tons of steel scrap in under an hour.
Induction furnaces are highly scalable, from small laboratory units to furnaces holding over 60 tons. While very fast, they do not typically match the sheer top-end scale and brute-force speed of the largest arc furnaces.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
The arc in an EAF creates an intense hot spot directly under the electrodes, leading to less uniform temperature distribution throughout the melt. Precise temperature control is more challenging.
The magnetic field in an induction furnace simultaneously heats and stirs the molten bath. This electromagnetic stirring action creates an exceptionally homogeneous and uniform melt, allowing for tight temperature control, often within +/- 5°C.
Metallurgical Cleanliness
Arc melting is an inherently "dirty" process. The graphite electrodes are consumed, introducing carbon into the melt. The process also generates significant slag and allows for greater interaction with the atmosphere, which can introduce impurities.
Induction melting is a far cleaner process. There is no contact with electrodes and no combustion, resulting in minimal carbon pickup and gas contamination. This makes it the superior choice for producing high-purity, clean metals and complex alloys where chemistry is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Costs
Your decision must also weigh the financial and operational realities of each technology.
Energy Efficiency
Induction furnaces are more energy-efficient. Because heat is generated directly within the metal, less energy is lost to the furnace environment. Electrical-to-thermal efficiency can exceed 75%.
Arc furnaces suffer from significant thermal losses due to the open arc and the large volume of fume extraction required. Their efficiency is typically lower, often in the 60-70% range.
Consumables and Refractory Wear
A major operational cost for arc furnaces is the constant consumption of expensive graphite electrodes. Furthermore, the intense, localized heat from the arc is extremely harsh on the refractory lining, leading to more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Induction furnaces have no electrodes, eliminating that cost entirely. The more uniform heating profile is also gentler on the refractory lining, leading to a longer service life and lower maintenance costs.
Environmental and Safety Impact
Arc furnaces are notoriously loud and generate significant dust, fumes, and emissions, requiring extensive and costly environmental control systems (e.g., baghouses).
Induction furnaces are comparatively quiet, produce minimal fumes, and create a much safer and cleaner working environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct melting technology is about aligning the process capabilities with your product requirements and business model.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap: The raw power and massive volume capacity of an Electric Arc Furnace make it the unmatched industry standard.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality specialty alloys, stainless steel, or precious metals: The cleanliness, precision, and tight chemical control of induction melting are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is operating a foundry with diverse metal needs and batch sizes: The flexibility, lower capital cost, and cleaner operation of induction furnaces offer a significant advantage for small-to-medium enterprises.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact and improving workplace safety: Induction melting provides a significantly cleaner, quieter, and safer process by design.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select not just a furnace, but a complete melting strategy aligned with your specific quality, volume, and cost objectives.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Arc Melting | Induction Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | High-energy electric arc | Electromagnetic induction |
| Best For | High-volume steel scrap melting | High-purity, specialty alloys |
| Process Cleanliness | Lower (carbon pickup, slag) | Higher (minimal contamination) |
| Temperature Control | Less uniform | Highly uniform (±5°C) |
| Operational Environment | Loud, high fume/dust emissions | Quiet, clean, and safe |
Ready to choose the right melting solution for your lab or foundry?
Whether your priority is the high-volume power of arc melting or the precision and purity of induction melting, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs. Our range of lab and production furnaces is designed to deliver the performance and reliability required for your specific metals and alloys.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our melting technology can enhance your efficiency, improve your product quality, and support your operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















