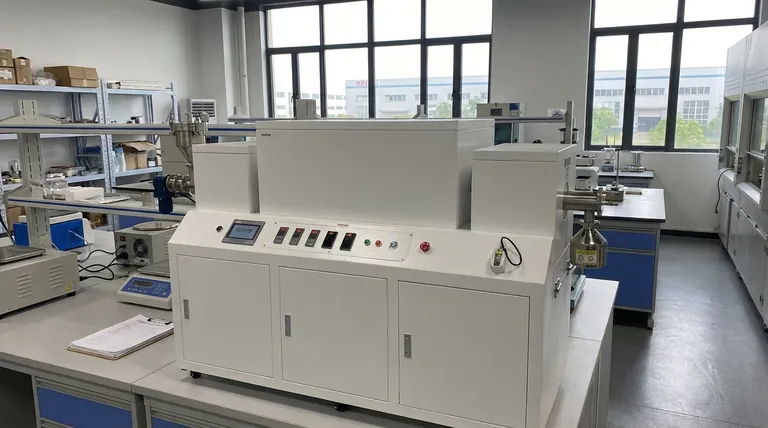
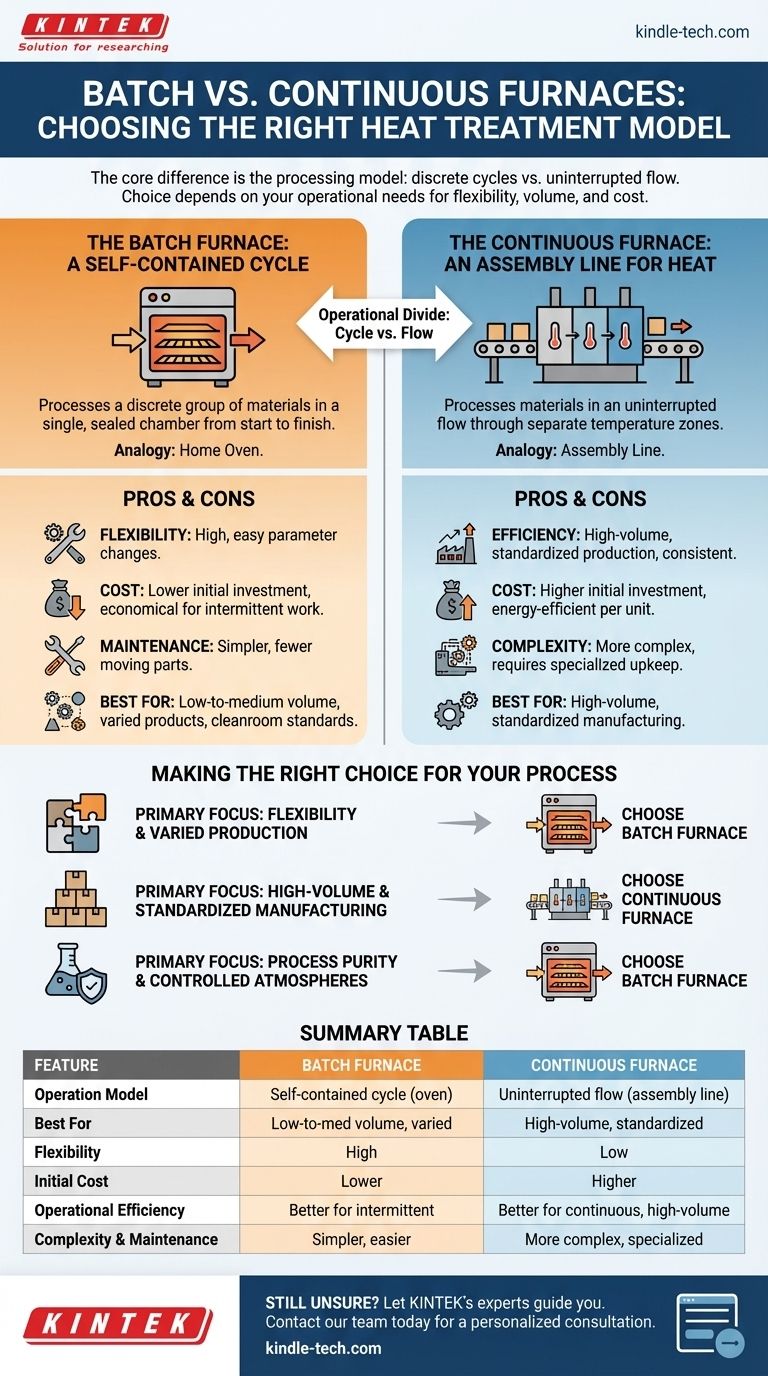
At its core, the difference between a batch and a continuous furnace is their processing model. A batch furnace processes a discrete group, or "batch," of materials in a single, self-contained cycle from start to finish within a closed chamber. In contrast, a continuous furnace processes materials in an uninterrupted flow, with products constantly entering one end, moving through various temperature zones, and exiting the other.
The choice is not about which furnace type is "better," but which aligns with your operational needs. Batch furnaces offer flexibility and lower cost for varied or smaller-scale work, while continuous furnaces deliver high-volume efficiency and consistency at the cost of higher initial investment and complexity.

The Operational Divide: Cycle vs. Flow
The most fundamental difference lies in how each furnace handles the product. This distinction dictates nearly every other factor, from cost to flexibility.
The Batch Furnace: A Self-Contained Cycle
A batch furnace operates much like a home oven. A specific quantity of product, often held in baskets or racks, is loaded into a single chamber.
The chamber is then sealed, and the entire batch is subjected to a programmed thermal cycle—heating, soaking, and cooling. Once the cycle is complete, the chamber is opened, and the finished batch is removed.
This single-chamber, all-in-one process makes it ideal for applications requiring cleanroom standards or controlled inert atmospheres, as the environment is easily sealed and managed.
The Continuous Furnace: An Assembly Line for Heat
A continuous furnace operates like an assembly line. Products are constantly fed into one end of the furnace, typically on a conveyor belt or pushed by a mechanism.
The material travels through different, physically separate zones within the furnace, each maintained at a constant temperature for a specific part of the process.
This design eliminates the need to heat and cool the entire furnace for each run, creating a highly efficient and consistent process for large quantities of identical products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two models requires a clear understanding of their inherent compromises in cost, flexibility, and efficiency.
Production Volume and Flexibility
Batch furnaces are the clear winner for flexibility. You can easily change the temperature, time, and atmosphere for each new load, making them ideal for low-to-medium volume production or facilities that handle a wide variety of parts and processes.
Continuous furnaces are built for high-volume, standardized production. They are locked into a single thermal profile, offering exceptional consistency but virtually no flexibility without significant downtime and reconfiguration.
Capital and Operational Costs
From an initial investment standpoint, batch furnaces are significantly less expensive. They are less complex, smaller, and easier to install.
Operational cost is more nuanced. A continuous furnace, once running at temperature, is highly energy-efficient on a per-unit basis because it avoids repeated heat-up/cool-down cycles. However, a batch furnace is more economical for intermittent or varied work where a large continuous system would be idle.
Maintenance and Complexity
The simplicity of a batch furnace translates to easier maintenance and lower long-term upkeep costs. They have fewer moving parts and simpler control systems.
Continuous furnaces are mechanically complex systems with conveyors, sensors, and multiple control zones. This complexity demands more frequent and specialized maintenance to ensure reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific production goals will point directly to the correct furnace technology for your application.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and varied production: Choose a batch furnace for its ability to handle different product types and thermal profiles with a lower initial investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized manufacturing: Choose a continuous furnace to maximize throughput and achieve the lowest possible per-unit processing cost.
- If your primary focus is process purity and controlled atmospheres: A batch furnace often provides a more easily sealed and managed environment for applications requiring strict atmospheric control.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's fundamental operating model with your production goals is the key to a sound investment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Model | Self-contained cycle (like an oven) | Uninterrupted flow (like an assembly line) |
| Best For | Low-to-medium volume, varied products | High-volume, standardized production |
| Flexibility | High (easy to change parameters per batch) | Low (locked into a single profile) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Operational Efficiency | Better for intermittent work | Better for continuous, high-volume runs |
| Complexity & Maintenance | Simpler, easier maintenance | More complex, requires specialized upkeep |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application?
Let KINTEK's experts guide you to the perfect solution. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both batch and continuous furnaces, tailored to your specific production volume, flexibility, and budget requirements.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right furnace can optimize your heat treatment process, improve efficiency, and drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results



















