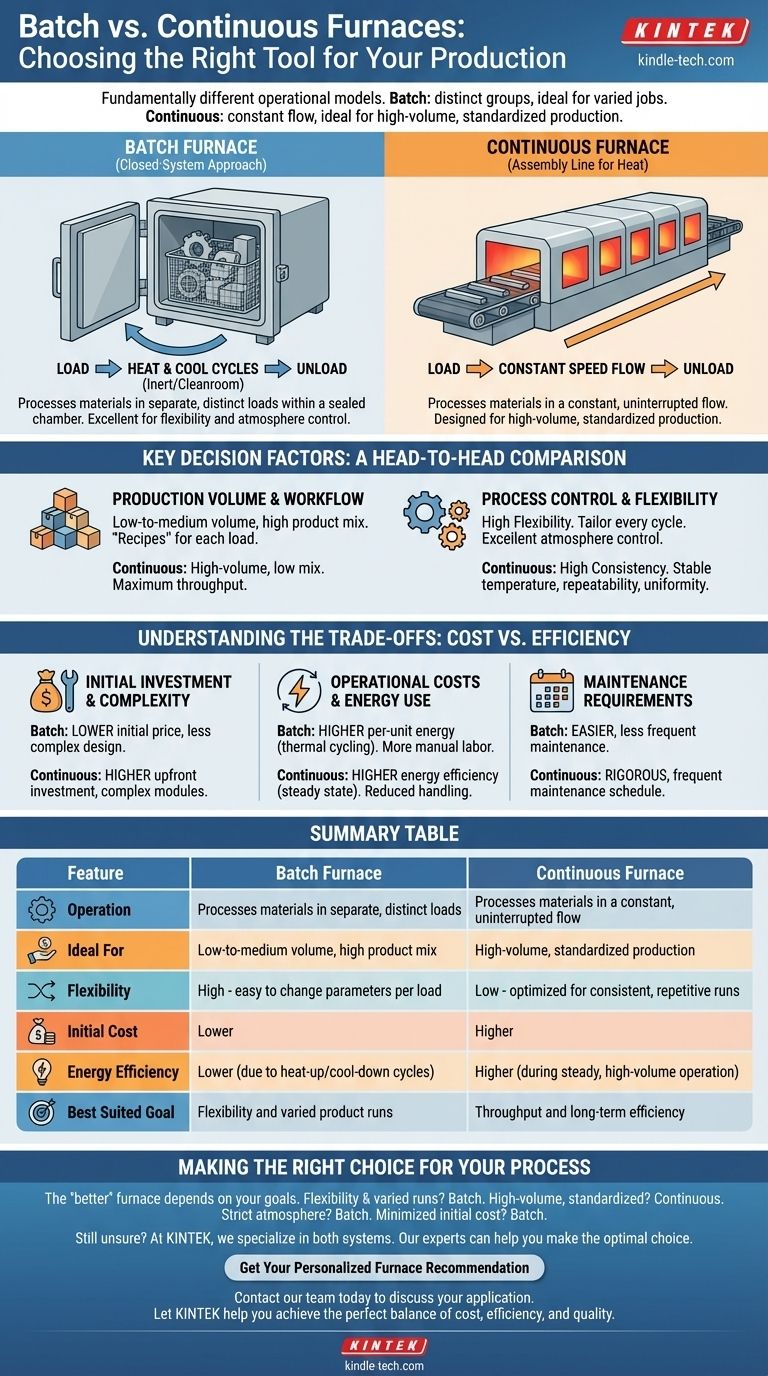
Fundamentally, the difference between a batch furnace and a continuous furnace lies in their operational model for processing materials. A batch furnace treats materials in distinct, separate groups within a closed chamber, ideal for varied jobs. In contrast, a continuous furnace processes materials in a constant, uninterrupted flow, designed for high-volume, standardized production.
Your choice between these two furnace types is a strategic decision about your production philosophy. Batch furnaces offer superior flexibility and lower initial costs for varied, discrete jobs, while continuous furnaces provide unmatched efficiency and consistency for large-scale, repetitive manufacturing.

How Each Furnace Type Operates
To select the right tool, you must first understand its mechanics. The core distinction is the movement—or lack thereof—of the product during the heating process.
The Batch Furnace: A Closed-System Approach
A batch furnace is a self-contained unit where a specific quantity of material is loaded, processed, and then unloaded. The entire process occurs in one chamber, which cycles through heating and cooling stages.
Materials are often held in fixtures like baskets or racks. Because the system is sealed during operation, it provides excellent control over the internal environment, making it ideal for processes requiring a pure, inert atmosphere or cleanroom standards.
The Continuous Furnace: An Assembly Line for Heat
A continuous furnace operates like a manufacturing assembly line. Materials are loaded at one end, travel through various heating and cooling zones at a constant speed, and are unloaded at the other end.
This design is a straight-through system where the central heat chamber often remains hot and under vacuum or a controlled atmosphere. This eliminates the need for fixtures and reduces the thermal cycling common in batch processes, making it highly productive for tasks like annealing, brazing, and hardening.
Key Decision Factors: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Your specific application will dictate which model is more suitable. The choice hinges on volume, product variability, and process control requirements.
Production Volume and Workflow
Batch furnaces excel in low-to-medium volume production or situations with a high mix of different products. They allow you to run different "recipes"—varying temperatures and durations—for each load.
Continuous furnaces are built for high-volume, low-mix production. They are optimized to process a large quantity of the same or similar products with maximum throughput and consistency.
Process Control and Flexibility
The greatest strength of a batch furnace is its flexibility. You can tailor every cycle to the specific needs of the product being processed.
A continuous furnace offers less flexibility once configured. Its strength lies in maintaining a constant, stable temperature and processing speed, which ensures high repeatability and uniformity across thousands of parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Efficiency
The operational differences create a clear set of trade-offs regarding cost, complexity, and long-term energy consumption. Acknowledging these is critical for making an informed investment.
Initial Investment and Complexity
Batch furnaces are generally less complex in their design and construction. This results in a significantly lower initial purchase price and a smaller physical footprint.
Continuous furnaces are more complex machines, often consisting of multiple interconnected modules (e.g., preheat, high heat, quench chambers). This complexity leads to a higher upfront investment.
Operational Costs and Energy Use
While cheaper to buy, batch furnaces can have higher per-unit energy costs due to repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles. They also often require more manual labor for loading and unloading work-in-process groups.
Continuous furnaces, by keeping their core heating zones constantly hot, are often more energy-efficient during steady, high-volume runs. They eliminate the energy waste of thermal cycling and reduce material handling.
Maintenance Requirements
The simpler design of a batch furnace typically translates to easier and less frequent maintenance.
The mechanical complexity of a continuous furnace, with its conveyor systems and multiple chambers, demands a more rigorous and frequent maintenance schedule to ensure reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The "better" furnace does not exist in a vacuum; it is only "better" relative to your specific operational needs and business goals.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and varied product runs: A batch furnace is the superior choice, allowing you to tailor each cycle to unique requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace will deliver the throughput, consistency, and long-term efficiency you need.
- If your primary focus is strict atmosphere control for specialized jobs: A batch furnace's sealed-chamber design provides a more easily controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital expenditure: A batch furnace represents a significantly lower upfront investment.
By aligning the furnace's operational model with your specific production goals, you can ensure an optimal balance of cost, efficiency, and quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Processes materials in separate, distinct loads | Processes materials in a constant, uninterrupted flow |
| Ideal For | Low-to-medium volume, high product mix | High-volume, standardized production |
| Flexibility | High - easy to change parameters per load | Low - optimized for consistent, repetitive runs |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (due to heat-up/cool-down cycles) | Higher (during steady, high-volume operation) |
| Best Suited Goal | Flexibility and varied product runs | Throughput and long-term efficiency |
Still unsure which furnace type is right for your lab's workflow?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment, including both batch and continuous furnaces, to meet your specific production needs. Whether you require the flexibility of a batch system for varied R&D projects or the high-throughput efficiency of a continuous furnace for large-scale processing, our experts can help you make the optimal choice for performance and cost.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK help you achieve the perfect balance of cost, efficiency, and quality in your heat treatment processes.
Get Your Personalized Furnace Recommendation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency



















