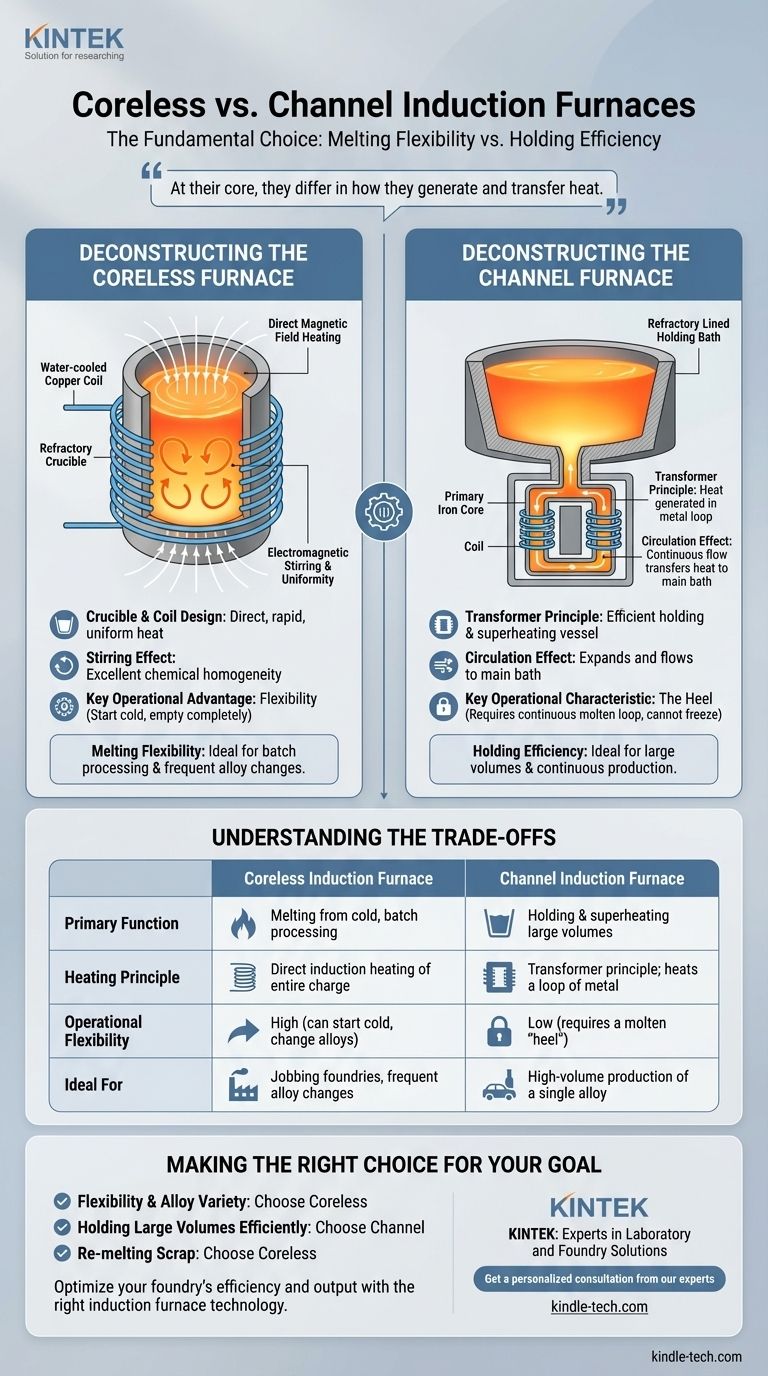
At their core, a coreless induction furnace and a channel induction furnace differ in how they generate and transfer heat. A coreless furnace acts like a large crucible wrapped in a high-power electrical coil, heating the entire metal charge directly. In contrast, a channel furnace functions like a transformer, where the molten metal itself forms a secondary circuit loop that is heated and then circulates to warm a larger bath.
The fundamental choice between these two furnaces is a decision between melting flexibility and holding efficiency. Coreless furnaces offer superior flexibility for melting different materials from a cold state, while channel furnaces excel at efficiently holding and superheating large volumes of a single molten alloy.
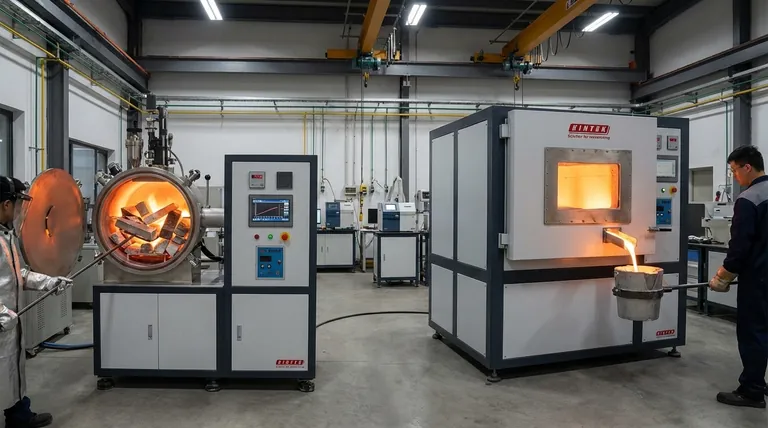

Deconstructing the Coreless Furnace
A coreless induction furnace is defined by its simple and direct heating method, making it a versatile tool for foundries. Its design directly dictates its operational strengths.
The Crucible and Coil Design
The primary feature is a water-cooled copper coil that surrounds a refractory crucible. When alternating current flows through this coil, it generates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field.
This magnetic field directly penetrates the metal charge inside the crucible, inducing strong electrical currents (eddy currents) within the metal itself. The resistance of the metal to these currents generates intense, rapid, and uniform heat throughout the charge.
The Stirring Effect
A significant advantage of this direct induction method is the inherent electromagnetic stirring action it creates within the molten bath. This ensures excellent chemical homogeneity and temperature uniformity, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Key Operational Advantage: Flexibility
Because the entire charge is the target of the heating process, a coreless furnace can be started with a cold, solid charge. It can also be completely emptied after a melt. This makes it ideal for operations that require frequent alloy changes or work in batches.
Deconstructing the Channel Furnace
The channel furnace operates on a fundamentally different principle. It is less of a direct melter and more of a highly efficient holding and superheating vessel.
The Transformer Principle
A channel furnace has a main refractory-lined shell for holding metal, but the heating occurs in a separate, attached induction unit. This unit contains a primary iron core and coil, much like a standard transformer.
A small, closed loop or "channel" of molten metal passes through this induction unit, acting as the secondary winding of the transformer. The current induced in this single loop generates all the heat for the entire furnace.
The Circulation Effect
The intense heat generated in the narrow channel causes the metal within it to expand and flow out into the main bath. This movement draws cooler metal from the main bath into the channel, creating a continuous circulation that transfers heat to the entire volume.
Key Operational Characteristic: The Heel
Because the channel furnace requires a continuous, closed loop of molten metal to function as the secondary circuit, it cannot be allowed to freeze. This means the furnace must always maintain a molten "heel" of metal, making it unsuitable for frequent shutdowns or changes in alloy composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The architectural differences between these furnaces create a clear set of trade-offs in performance, efficiency, and application.
Melting vs. Holding
Coreless furnaces excel at melting solid materials like scrap, ingots, and returns. Their ability to generate heat directly within the charge makes this process fast and efficient.
Channel furnaces excel at holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature for extended periods. Because the heating is concentrated in a small, well-insulated channel, they are often more energy-efficient for this specific task than a coreless furnace.
Operational Flexibility
The coreless furnace is the clear winner in flexibility. Its ability to start from cold and be completely emptied makes it the default choice for jobbing foundries that produce many different alloys in varying batch sizes.
The channel furnace is highly inflexible. The need to maintain a molten heel locks it into a single alloy for long campaigns, making it suitable for large, continuous production environments like automotive foundries.
Refractory Wear and Maintenance
In a channel furnace, the extreme heat density in the inductor throat leads to high, localized refractory wear. This specific area requires careful monitoring and periodic replacement.
In a coreless furnace, the refractory wear is generally more uniform across the crucible walls, but the constant thermal cycling of batch operations can also stress the lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is critical for optimizing your metallurgical process for cost, quality, and throughput.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and alloy variety: A coreless induction furnace is the superior choice for its batch processing and cold-starting capabilities.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single alloy efficiently: A channel induction furnace is the ideal solution for continuous or high-volume pouring operations.
- If your primary focus is re-melting a wide variety of solid scrap: The direct melting power and stirring action of a coreless furnace will provide the best performance.
Ultimately, your choice depends on matching the furnace's fundamental operating principle to the daily demands of your production schedule.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Melting from cold, batch processing | Holding & superheating large volumes |
| Heating Principle | Direct induction heating of entire charge | Transformer principle; heats a loop of metal |
| Operational Flexibility | High (can start cold, change alloys) | Low (requires a molten "heel") |
| Ideal For | Jobbing foundries, frequent alloy changes | High-volume production of a single alloy |
Optimize your foundry's efficiency and output with the right induction furnace technology.
Choosing between a coreless and channel furnace is a critical decision that impacts your operational flexibility, energy costs, and final product quality. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you analyze your specific production needs—whether you're melting diverse alloys or holding large volumes—and recommend the ideal lab equipment solution.
We specialize in providing robust and reliable furnaces for laboratory and foundry applications. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your melting process, reduce costs, and improve your metal quality.
Get a personalized consultation from our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















