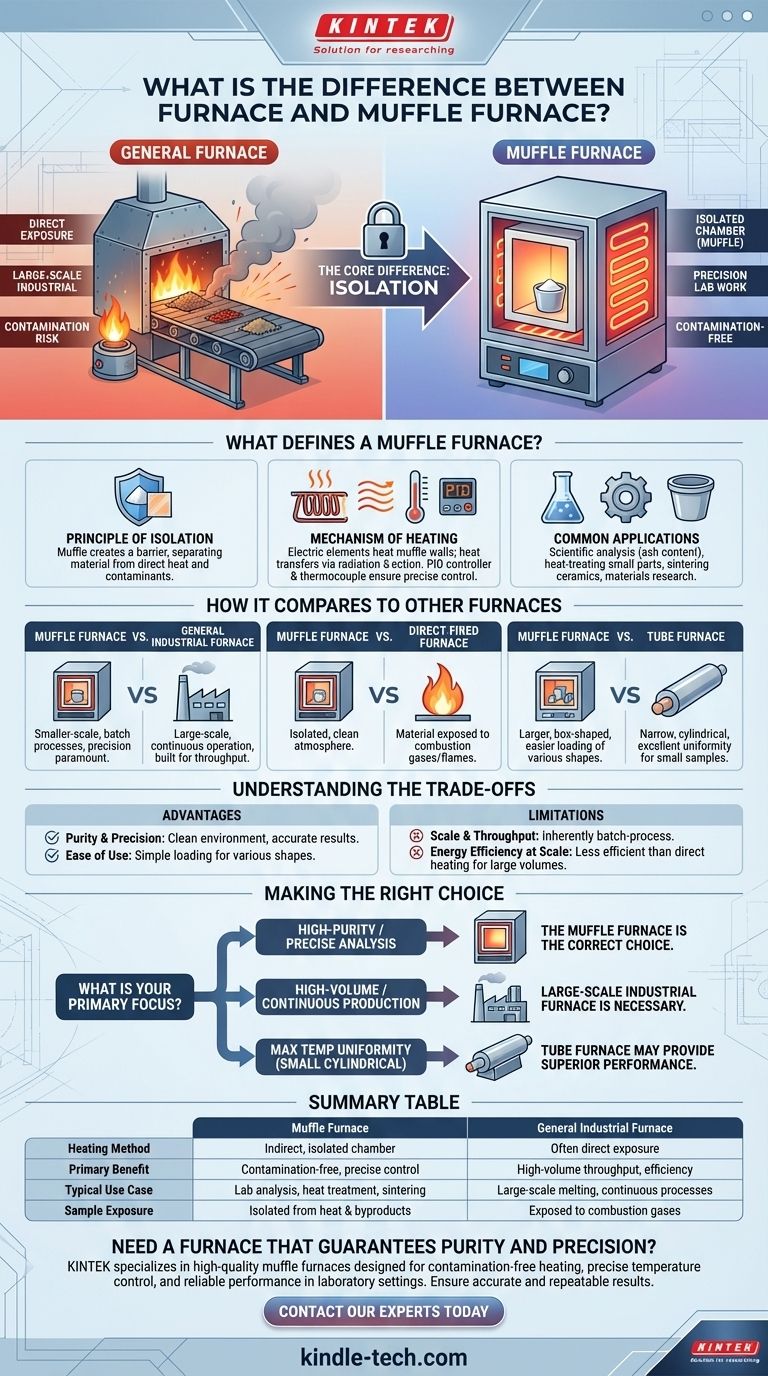
At its core, a muffle furnace is a specific type of furnace distinguished by its method of heating. While the term "furnace" is a broad category for any high-temperature heating device, a "muffle furnace" specifically uses an isolated chamber—the muffle—to separate the material being heated from the direct heat source and any potential contaminants. This design ensures a clean, controlled, and uniform heating environment.
The essential difference is isolation. A muffle furnace heats material inside a sealed chamber to prevent contamination, making it ideal for precise laboratory work. A general furnace is a broader term and may expose the material directly to flames or heating elements, which is common in large-scale industrial processes.
What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
The defining characteristic of this furnace is not its size or temperature range, but its architecture. The name comes from the "muffle," an insulated inner chamber that contains the sample.
The Principle of Isolation
A muffle creates a barrier between the material being heated and the source of that heat.
In traditional fuel-fired furnaces, this prevents the sample from coming into contact with damaging combustion byproducts like gas and soot.
In modern electric furnaces, the muffle chamber separates the sample from direct contact with the heating coils, protecting both the sample and the elements while promoting uniform heat distribution.
The Mechanism of Heating
Modern muffle furnaces are almost exclusively electric. They operate by passing an electric current through high-resistance heating elements, such as nichrome wire.
These elements heat the walls of the insulated muffle chamber. The heat is then transferred to the sample inside the chamber primarily through radiation and convection, not direct conduction from the heat source.
This indirect heating, managed by a PID controller and monitored by a thermocouple, allows for extremely precise and stable temperature control.
Common Applications
Because of their precision and purity, muffle furnaces are staples in environments where contamination would ruin a process.
Typical uses include scientific analysis (like determining the ash content of coal), heat-treating small metal parts, sintering ceramics, and materials research in laboratory settings.
How it Compares to Other Furnaces
Understanding the muffle furnace is easier when contrasted with other common types. Its design is purpose-built for needs that other furnaces cannot meet.
Muffle Furnace vs. General Industrial Furnace
A muffle furnace is typically used for smaller-scale, batch processes where precision is paramount.
An industrial furnace is often designed for large-scale, continuous operation. These systems are complex, with integrated preheaters and exhaust systems, built for throughput rather than analytical purity.
Muffle Furnace vs. Direct-Fired Furnace
This is the classic distinction. In a direct-fired or reverberatory furnace, the material is intentionally exposed to the hot gases and flames from combustion.
This is efficient for melting large quantities of metal but is completely unsuitable for processes that require a clean atmosphere. The muffle furnace solves this by isolating the sample.
Muffle Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
Both are common in laboratories, but they serve different needs. A tube furnace uses a narrow, cylindrical chamber, which is excellent for heating small samples with exceptional temperature uniformity along its length.
A muffle furnace has a larger, box-shaped chamber. This makes it much easier to load and unload multiple samples or larger, irregularly shaped objects that would not fit in a tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace design is perfect for every task. The muffle furnace's advantages are directly tied to its limitations.
Advantage: Purity and Precision
The isolated chamber is the primary benefit. It guarantees a clean heating environment free from contamination, enabling highly accurate and repeatable scientific and manufacturing processes.
Advantage: Ease of Use
The simple, box-like chamber design allows for straightforward placement and removal of materials, making it a flexible tool for a variety of sample sizes and shapes.
Limitation: Scale and Throughput
Muffle furnaces are inherently batch-process devices. Their design is not suited for the continuous, high-volume workflow required in most large-scale industrial production.
Limitation: Energy Efficiency at Scale
While modern units are well-insulated and energy-efficient for their size, heating an isolated chamber indirectly is less energy-efficient than heating a product directly with flame or gas, especially at an industrial scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing or precise analysis: The muffle furnace is the correct choice because its isolated chamber prevents contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous industrial production: A large-scale industrial furnace designed for throughput is the necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity on a small, cylindrical sample: A tube furnace may provide superior performance for that specific geometry.
Ultimately, choosing a furnace begins by asking whether your process can tolerate exposure to a direct heat source or if absolute isolation is non-negotiable.
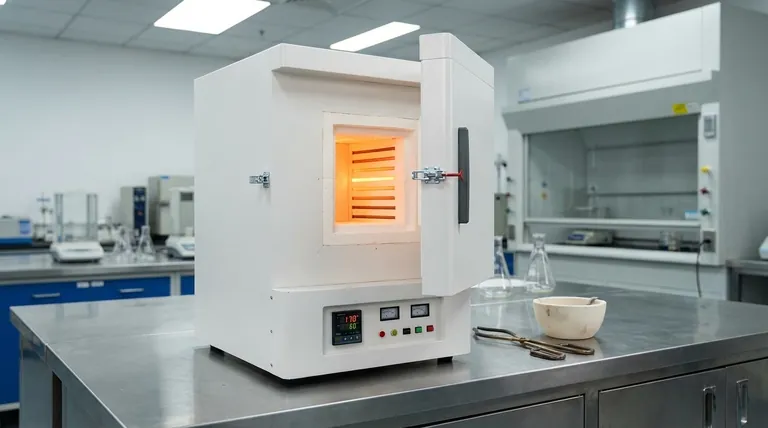

Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | General Industrial Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect, via an isolated chamber (muffle) | Often direct exposure to heat source/flames |
| Primary Benefit | Contamination-free, precise temperature control | High-volume throughput, efficiency at scale |
| Typical Use Case | Laboratory analysis, heat treatment, sintering | Large-scale melting, continuous industrial processes |
| Sample Exposure | Isolated from heat source and byproducts | Exposed to combustion gases/elements |
Need a furnace that guarantees purity and precision for your lab work?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality muffle furnaces designed for contamination-free heating, precise temperature control, and reliable performance in laboratory settings. Whether your application is ash content determination, heat treatment, or materials research, our equipment ensures accurate and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which furnace is used for sintering? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Application
- Why is a laboratory muffle furnace necessary for TiO2 blocking layer preparation? Enhance Photoelectrode Efficiency
- What is the primary function of high-temperature muffle or tube furnaces for ceramic coatings? Ensure Peak Durability
- What core functions does a high-temperature muffle furnace perform in Fe2O3–CeO2 synthesis? Key Roles in Crystallization
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for azide combustion synthesis? Ensure Stability and Purity in Powder Pre-treatment
- How does a high-temperature box resistance furnace study Cr2O3 oxidation? Unlock Precise Kinetics & Defect Analysis
- What is the use of ashing? Isolate and Quantify Total Mineral Content in Your Samples
- What contributes to ash content in food? A Guide to Mineral Content and Food Quality



















