In short, a fused bead is a homogenous glass disk created by melting a sample with a flux, while a pressed pellet is a solid wafer made by compressing a powdered sample. The fused bead method chemically dissolves the sample to eliminate physical inconsistencies, offering superior accuracy. The pressed pellet method is a simpler, faster physical process but is more susceptible to analytical errors.
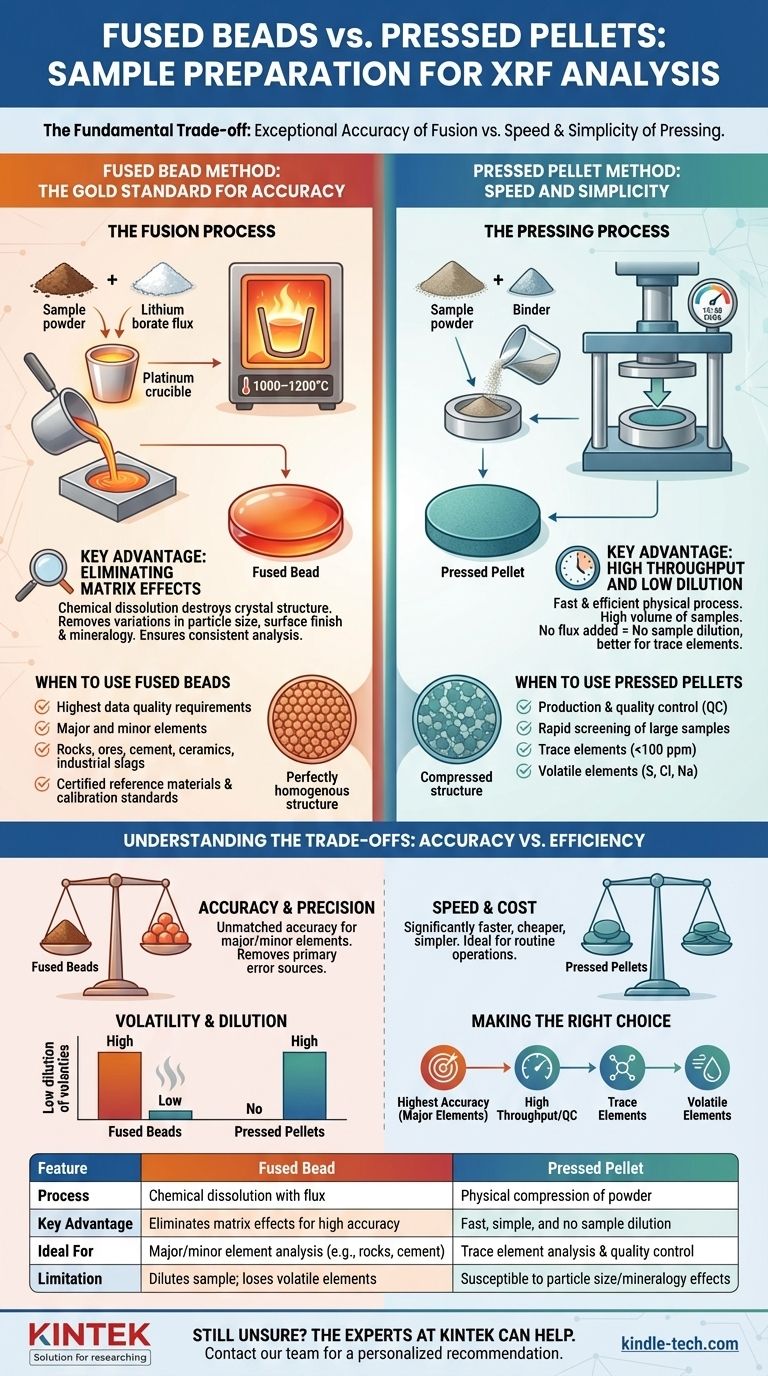
The choice between a fused bead and a pressed pellet is a fundamental trade-off in X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis. You are choosing between the exceptional accuracy of fusion and the speed and simplicity of pressing. Understanding this trade-off is the key to producing reliable results.

The Fused Bead Method: The Gold Standard for Accuracy
A fused bead is the preferred sample preparation method when accuracy is the highest priority. It is a chemical process designed to create a perfectly homogenous sample, ideal for XRF analysis.
The Fusion Process
To create a fused bead, a small, precisely weighed amount of the sample is mixed with a lithium borate flux (such as lithium tetraborate or lithium metaborate). This mixture is heated in a platinum crucible to approximately 1000–1200°C until the sample completely dissolves into the molten flux. The resulting liquid is then cast into a mold and cooled to form a smooth, solid glass disk.
Key Advantage: Eliminating Matrix Effects
The primary benefit of fusion is the elimination of physical matrix effects. By dissolving the sample, this method destroys the original crystal structure and removes variations in particle size, surface finish, and mineralogy between different samples. This ensures the X-ray spectrometer analyzes a consistent material every time, which dramatically improves accuracy and precision.
When to Use Fused Beads
This method is the benchmark for applications that demand the highest data quality. It is ideal for analyzing major and minor elements in materials like rocks, ores, cement, ceramics, and industrial slags. It is also the required method for creating certified reference materials and primary calibration standards.
The Pressed Pellet Method: Speed and Simplicity
A pressed pellet is a physical preparation method that prioritizes speed and sample throughput. It is often the go-to technique for quality control and process monitoring where rapid results are essential.
The Pressing Process
The sample is first ground into a very fine, uniform powder. This powder is often mixed with a binding agent (like a wax or cellulose) to help the particles adhere. The mixture is then poured into a die and compressed under immense pressure (typically 15-30 tons) to form a dense, stable pellet with a flat, smooth surface for analysis.
Key Advantage: High Throughput and Low Dilution
The main advantage of pressing is its efficiency. The process is fast, uses relatively inexpensive equipment (a grinder and a hydraulic press), and allows for a high volume of samples to be prepared quickly. Furthermore, because no flux is added, there is no sample dilution, making it better for detecting elements at very low concentrations.
When to Use Pressed Pellets
This method is best suited for production and quality control environments. It excels at the rapid screening of large numbers of similar samples, analyzing for trace elements (parts-per-million levels), and measuring volatile elements that would be lost at the high temperatures required for fusion.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Accuracy vs. Efficiency
Neither method is universally superior; the correct choice depends entirely on your analytical requirements.
Accuracy and Precision
Fused beads offer unmatched accuracy for major and minor element concentrations because they remove the primary sources of measurement error. Pressed pellets are more prone to errors from particle size effects and mineralogical effects, where different crystal structures in the sample can alter the X-ray signal.
Element Volatility and Sample Dilution
Fusion's high temperatures can cause volatile elements like sulfur (S), chlorine (Cl), and sodium (Na) to evaporate, leading to inaccurate, low readings. Pressed pellets are prepared at room temperature, making them the required method for these elements. Likewise, the flux in a fused bead dilutes the sample, which can make trace element analysis difficult or impossible as concentrations fall below the instrument's detection limit.
Cost, Time, and Complexity
Fusion is more expensive and time-consuming. It requires a fusion instrument, expensive platinum crucibles, and high-purity fluxes. The process is more complex and requires a higher level of operator skill. Pressing is significantly faster, cheaper, and simpler to execute, making it ideal for routine operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Select your sample preparation method based on your specific analytical goal and the limitations of each technique.
- If your primary focus is the highest accuracy for major elements (e.g., in geological samples or cement): The fused bead method is the only reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening or routine quality control: The speed and simplicity of pressed pellets are ideal.
- If your primary focus is trace element analysis (<100 ppm): Use pressed pellets to avoid sample dilution and maximize signal intensity.
- If your primary focus is analyzing volatile elements (like S, Cl, Br, or Na): You must use pressed pellets to prevent the elements from being lost during preparation.
Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method empowers you to generate data you can trust.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fused Bead | Pressed Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Chemical dissolution with flux | Physical compression of powder |
| Key Advantage | Eliminates matrix effects for high accuracy | Fast, simple, and no sample dilution |
| Ideal For | Major/minor element analysis (e.g., rocks, cement) | Trace element analysis & quality control |
| Limitation | Dilutes sample; loses volatile elements | Susceptible to particle size/mineralogy effects |
Still unsure which method is right for your lab's analysis? The experts at KINTEK can help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for both fused bead and pressed pellet preparation, ensuring you achieve reliable and accurate results.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a personalized recommendation for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed pellet technique? A Guide to Creating Uniform Solid Samples from Powder
- What is a punch tablet press? Precision Tableting for R&D and Small Batches
- What are the two classifications of press machines? Single Punch vs. Rotary Presses Explained
- What are advantages of single punch tablet press machine? Maximize R&D Efficiency with Minimal Material
- What is the difference between single punch and rotary tablet press? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production



















