In industrial practice, the terms "pelleting" and "pelletizing" are frequently used to describe the same general outcome: converting fine powders or materials into larger, uniform granules called pellets. However, a technical distinction exists based on the mechanism used and the industry in which the term is applied. Pelleting typically involves high-pressure extrusion, while pelletizing often refers to a process of tumbling agglomeration.
The core difference lies in the method of formation. Pelleting is a high-pressure process that forces material through a die, common for organic materials like animal feed and biomass. Pelletizing is a lower-pressure process that tumbles fine particles with a liquid binder to form spheres, primarily used for minerals like iron ore.

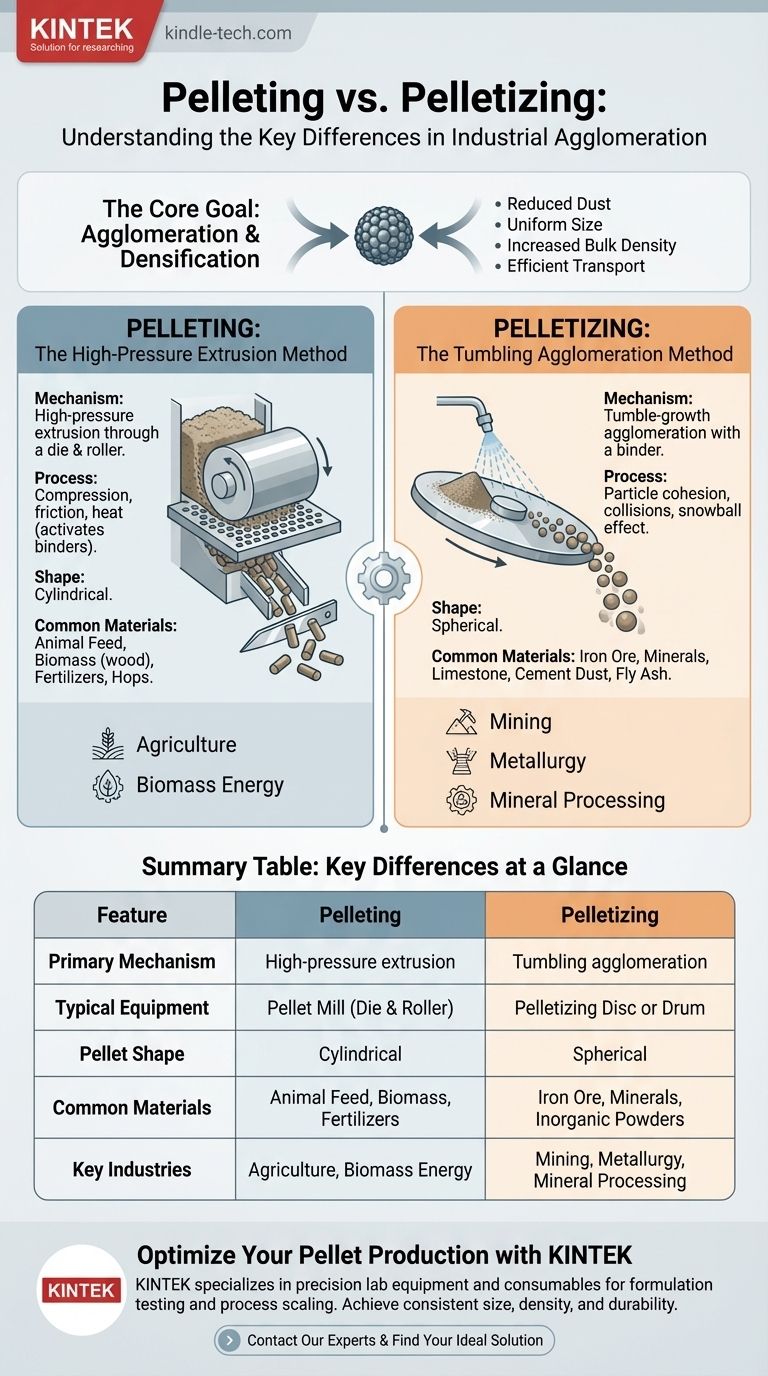
The Core Process: Agglomeration and Densification
Both pelleting and pelletizing are forms of agglomeration. The fundamental goal is to take a fine, dusty, or difficult-to-handle material and transform it into a dense, predictable, and free-flowing product.
### The Purpose of Creating Pellets
This process adds value by improving the material's properties. Key benefits include dramatically reduced dust, uniform size for consistent chemical reactions or dosing, increased bulk density for efficient transport and storage, and prevention of component segregation in a mixture.
Understanding "Pelleting": The Extrusion Method
Pelleting is best understood as a process of compression and extrusion. It creates dense, typically cylindrical pellets.
### The Mechanism: Die and Roller
In a standard pellet mill, loose material is fed into a chamber where heavy rollers press it against the inner surface of a perforated metal ring or plate, known as a die.
The immense pressure forces the material through the holes in the die. The combination of compression and friction generates significant heat, which can help activate natural binders within the material (like lignin in wood).
As the compressed material exits the die, it is cut by knives to a specified length, forming the final pellets.
### Common Industries and Materials
This high-pressure method is the standard for producing highly durable pellets from softer, often organic materials.
Common applications include animal feed, wood biomass fuel, fertilizers, and hops.
Understanding "Pelletizing": The Tumbling Method
Pelletizing is a process of tumble-growth agglomeration. It relies on particle cohesion rather than extreme force and typically produces spherical pellets.
### The Mechanism: Disc or Drum
This method uses a rotating disc or drum set at a precise angle. Fine raw material (like mineral concentrate) is continuously fed onto the disc.
A fine spray of a binding agent, often just water, is applied. As the disc rotates, the moistened particles tumble, collide, and stick together, gradually growing in size layer by layer, much like a snowball rolling downhill.
Once the pellets reach the desired size, they roll off the edge of the disc or out of the end of the drum.
### Common Industries and Materials
This "gentler" method is ideal for forming pellets from very fine, hard, inorganic powders.
The most prominent application is in the steel industry for pelletizing iron ore concentrate before it is fed into a blast furnace. Other uses include limestone, cement kiln dust, and fly ash.
Why the Terms Overlap
While technical experts in specific fields maintain the distinction, the terms often become blurred in general use.
### Colloquial vs. Technical Usage
In everyday conversation, "pelletizing" is often used as a catch-all verb for making any kind of pellet. The plastics industry, for example, uses "pelletizing" to describe cutting extruded polymer strands into pellets—a process mechanically closer to pelleting but using the other term.
### Focus on the Equipment
Often, the terminology simply follows the name of the machine. A pellet mill performs pelleting. A pelletizing disc performs pelletizing. This equipment-based distinction is a reliable way to differentiate the processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To communicate with clarity, select your term based on the material and the underlying mechanical process.
- If your primary focus is on animal feed, biomass, or organic fertilizers: The term "pelleting" is more precise, as it refers to the high-pressure die-and-roller extrusion process common in these fields.
- If your primary focus is on mining, metallurgy, or mineral processing: "Pelletizing" is the correct choice to describe the tumble-growth agglomeration used for materials like iron ore.
- If you are speaking in a general or mixed context: Using "pelletizing" as a broad verb is often acceptable, but be prepared to clarify the specific mechanical process (extrusion vs. tumbling) if precision matters.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between high-pressure extrusion and tumble-growth agglomeration is the key to mastering the subject.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pelleting | Pelletizing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | High-pressure extrusion through a die | Tumbling agglomeration with a binder |
| Typical Equipment | Pellet Mill (Die & Roller) | Pelletizing Disc or Drum |
| Pellet Shape | Cylindrical | Spherical |
| Common Materials | Animal Feed, Biomass, Fertilizers | Iron Ore, Minerals, Inorganic Powders |
| Key Industries | Agriculture, Biomass Energy | Mining, Metallurgy, Mineral Processing |
Ready to Optimize Your Pellet Production Process?
Whether your project involves high-pressure pelleting for organic materials or tumble-growth pelletizing for minerals, selecting the right equipment is critical for efficiency and product quality.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for all your agglomeration needs. We provide the tools and expertise to help you:
- Test and develop the perfect pellet formulation.
- Scale your process from lab to production with confidence.
- Achieve consistent size, density, and durability in your final product.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory or pilot plant.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement



















