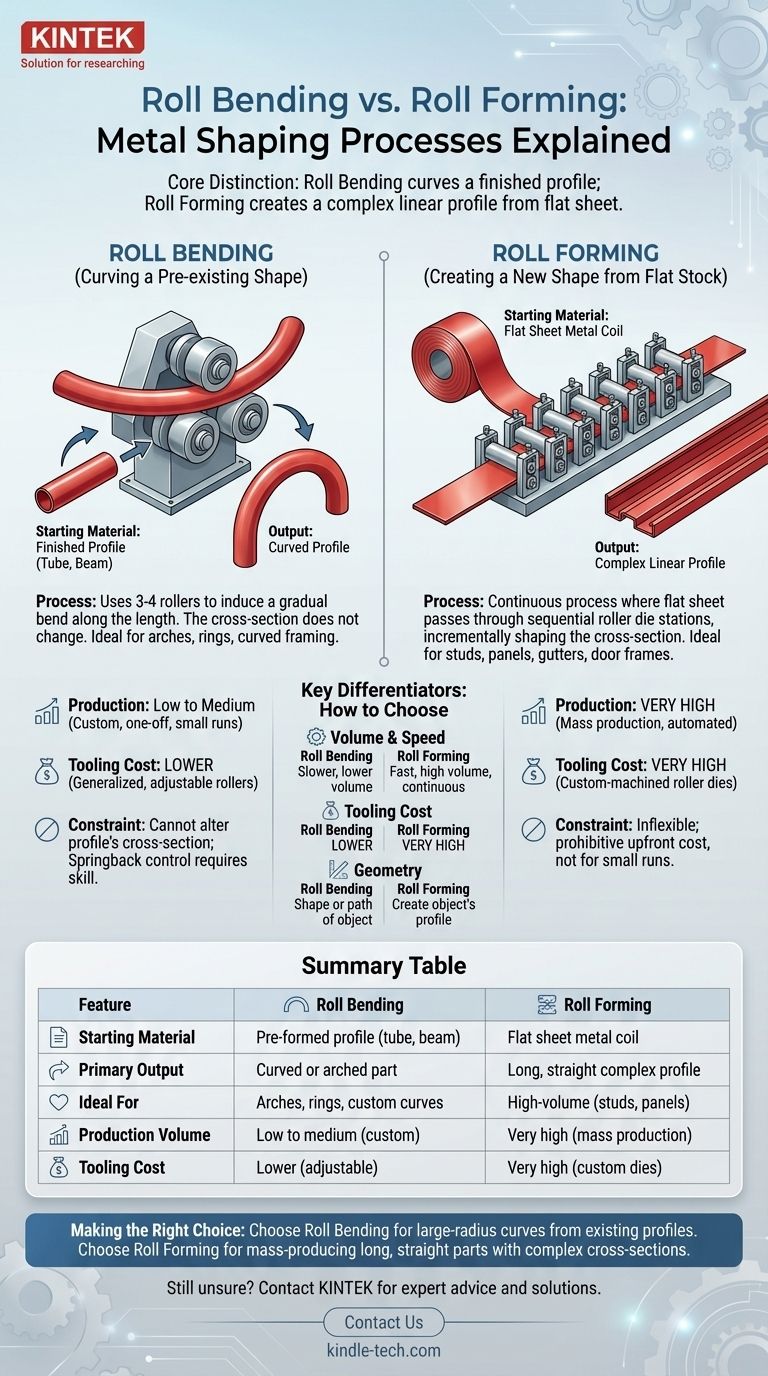
At first glance, roll bending and roll forming appear similar, as both use rollers to shape metal. However, they are fundamentally different manufacturing processes designed for entirely distinct applications. Roll bending takes an existing structural shape—like a tube or an I-beam—and curves it into a large arc, while roll forming takes a flat strip of sheet metal and progressively shapes it into a complex, linear cross-section.
The core distinction lies in the input and the output. Roll bending starts with a finished profile and creates a curve. Roll forming starts with flat sheet metal and creates a complex linear profile.

The Core Process: A Tale of Two Geometries
Understanding the mechanics of each process reveals their unique purposes. The machinery, the material flow, and the final product could not be more different.
Roll Bending: Curving a Pre-existing Shape
Roll bending, also known as section bending or profile bending, uses a set of three or four rollers arranged in a pyramid or pinching configuration.
A pre-formed structural shape, such as a pipe, angle iron, or extruded profile, is fed through these rollers. The pressure and position of the rollers induce a gradual bend along the length of the material.
The key principle is that the cross-section of the profile does not change. The process simply curves the entire part into a desired radius, creating components like structural arches, rings, or curved framing.
Roll Forming: Creating a New Shape from Flat Stock
Roll forming is a continuous process that begins with a long coil of flat sheet metal. This strip is fed through a series of roller die stations arranged in a long line.
Each station has a unique set of rollers that performs a small, incremental part of the total bend. As the metal strip passes through the successive stations, its cross-section is gradually shaped into a final, complex profile.
This method is used to create long, straight parts with a uniform cross-section, such as metal studs, roof panels, gutters, and door frames.
Key Differentiators: How to Choose
The decision between these two processes is rarely ambiguous. Your choice will be dictated by your part's geometry, the required production volume, and your budget for tooling.
Starting Material and Final Geometry
Roll bending starts with dimensionally complete profiles and changes their longitudinal shape from straight to curved. Think of it as shaping the path of an object.
Roll forming starts with a simple flat sheet and creates a complex cross-sectional shape along a straight path. It is about creating the object's profile itself.
Production Volume and Speed
Roll forming is an extremely fast, automated, and continuous process. It is designed for high-volume production where thousands of feet of a specific profile are needed.
Roll bending is a much slower, more deliberate process. It is often used for lower-volume custom fabrication, one-off architectural pieces, or small production runs.
Tooling and Setup Costs
The most significant business difference is the tooling investment. Roll forming requires a long series of custom-machined roller dies, one for each stage of the bend. This results in very high initial tooling costs, often tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Roll bending uses more generalized, often adjustable rollers that can accommodate a range of standard profile sizes. This leads to significantly lower setup and tooling costs, making it accessible for smaller jobs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is universally superior; each comes with clear constraints that define its ideal use case. Objectively evaluating these trade-offs is critical for making a sound manufacturing decision.
The Constraints of Roll Bending
The primary limitation of roll bending is that it cannot create or alter a profile's cross-section. You must start with the shape you want.
Furthermore, controlling material springback—the tendency of the metal to partially return to its original shape—requires significant operator skill and experience to achieve precise radii consistently.
The High Barrier to Entry for Roll Forming
The main drawback of roll forming is the prohibitive upfront tooling cost. This investment is only justifiable with very high production volumes that allow the cost to be amortized over many units.
This process is also inflexible. Once a set of roller dies is created, it can only produce one specific profile. Any design change requires expensive re-tooling. It is completely unsuitable for prototyping or small runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process becomes simple when you focus on your project's primary goal: are you creating a curve or creating a profile?
- If your primary focus is creating large-radius curves, rings, or arches from existing tubes, beams, or extrusions: Roll bending is the correct and most cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing long, straight parts with a consistent, complex cross-section from sheet metal: Roll forming is the only viable process for achieving speed and low per-part cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is creating a low quantity of straight, custom profiles: Neither process is ideal; you should investigate press braking, which offers greater flexibility for small batches.
By understanding the fundamental difference between curving an existing profile and forming a new one, you can confidently select the manufacturing process that aligns perfectly with your design intent and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Roll Bending | Roll Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Material | Pre-formed structural profile (tube, beam) | Flat sheet metal coil |
| Primary Output | Curved or arched part | Long, straight part with complex cross-section |
| Ideal For | Arches, rings, custom curves | High-volume production (e.g., metal studs, panels) |
| Production Volume | Low to medium (custom, one-off) | Very high (mass production) |
| Tooling Cost | Lower (generalized, adjustable rollers) | Very high (custom roller dies) |
Still unsure which metal forming process is right for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right equipment and expert advice for your laboratory and manufacturing needs. Whether you're working with structural profiles or sheet metal, our team can help you select the perfect solution to ensure precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- High Precision Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of a laboratory hydraulic press for sulfide electrolytes? Achieve Maximum Sample Density
- What is the function of the rolling press process in air cathode preparation? Optimize Your Electrode Performance
- What precautions should be taken when using XRF? Essential Safety Protocols for Radiation Protection
- What industries use hydraulic press? Powering Manufacturing, Construction, and R&D
- What is the difference between hydraulic and mechanical press machines? Choose the Right Force for Your Production
- What is the specific application of a laboratory hydraulic press in LNMO cathode fabrication? Enhance Density & Performance
- What are the applications of compression molding? Creating Strong, Heat-Resistant Parts for Demanding Industries
- What is the temperature of a hydraulic system? Maintain Optimal Performance & Prevent Damage



















