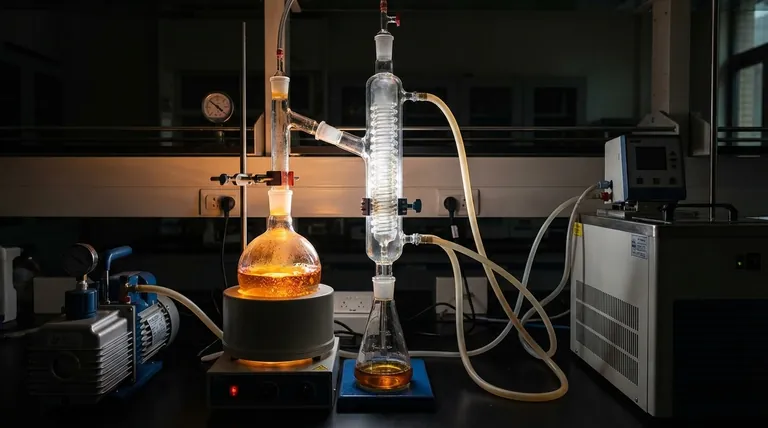
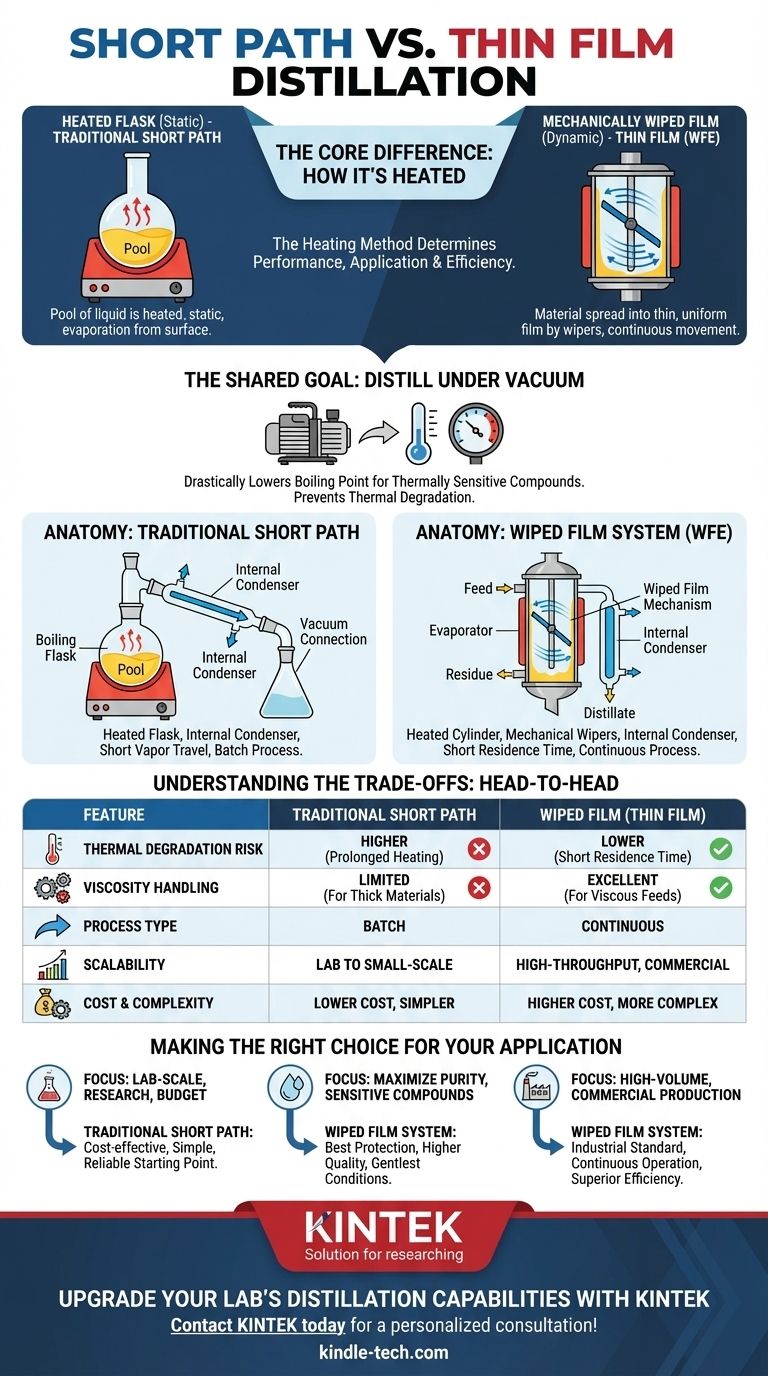
While often used in similar contexts, the core difference between short path and thin film distillation lies in how the material is heated and turned into vapor. A traditional short path system heats a pool of liquid in a flask, while a thin film system uses mechanical wipers to spread the material across a heated surface. This distinction in heating method is the critical factor that determines the performance, application, and efficiency of each technique.
The choice isn't truly "short path vs. thin film," as most modern thin film systems are also a type of short path distillation. The real decision is between a static, heated flask (traditional short path) and a dynamic, mechanically wiped film system. Wiped film offers superior control for highly sensitive or viscous materials, whereas traditional short path is a simpler, more accessible starting point.

The Shared Goal: Distilling Under Vacuum
To grasp the difference, we must first understand the problem both methods are designed to solve: distilling thermally sensitive, high-boiling-point compounds like those found in cannabis, essential oils, and pharmaceuticals.
The Problem with Standard Distillation
Standard distillation relies on boiling a liquid at atmospheric pressure. Many valuable organic compounds have extremely high boiling points, and applying that much heat for an extended period would simply burn or thermally degrade them before they could ever turn to vapor.
The Solution: Lowering Pressure and Time
Both short path and thin film distillation operate under a deep vacuum. This drastically lowers the boiling point of the compounds, allowing them to vaporize at much safer, lower temperatures. The "short path" design further minimizes the time a molecule spends in its hot vapor phase.
Anatomy of a Traditional Short Path System
This is the classic setup most people envision when they hear "short path." It's an evolution of standard laboratory glassware, optimized for vacuum operation.
The Heated Flask
The process begins with the crude material in a boiling flask. This flask is heated externally, and the material is typically stirred with a magnetic stir bar to improve heat distribution. Evaporation occurs from the surface of this static pool of liquid.
The Internal Condenser
The key innovation is placing the condenser inside the main body of the still. This creates a very short travel distance—the "short path"—for vapor molecules to travel from the boiling liquid to the cold condensing surface. This minimizes pressure drop and prevents molecules from being lost or reacting on the way.
Anatomy of a Thin Film (Wiped Film) System
A thin film system, often called a Wiped Film Evaporator (WFE), represents a more advanced, industrial approach to the same problem.
The Wiped Film Mechanism
Instead of a static flask, a thin film system uses a vertical, heated cylinder. The feed material is introduced at the top and immediately distributed into a very thin, uniform film on the inner wall by a set of rotating wipers or rollers.
The Internal Condenser
Just like a traditional short path, a thin film system has a condenser located in the center of the evaporation cylinder. Because the vapor molecules only have to travel a few centimeters from the wiped film to the condenser, this is also fundamentally a short path distillation apparatus. This is the source of most confusion.
Dynamic Heat Transfer
The continuously moving film is the game-changer. It ensures the material has a very short residence time on the heated surface—often just a few seconds. This provides extremely efficient and uniform heat transfer while drastically minimizing the risk of thermal degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
The practical differences between a static flask (short path) and a dynamic wiped film system are significant.
Thermal Exposure and Degradation
A traditional short path flask heats a bulk volume of oil for a prolonged period, creating the risk of localized overheating and degradation.
A wiped film system is the clear winner for sensitive materials. The extremely short residence time on the heater provides the gentlest possible thermal conditions, preserving the quality of the final product.
Viscosity Handling
High-viscosity materials are challenging for traditional short path systems. They are difficult to stir effectively and don't evaporate efficiently from a static pool.
The mechanical wipers in a wiped film system excel at handling thick, viscous materials, smearing them effectively to ensure efficient evaporation.
Throughput and Scalability
Traditional short path is primarily a batch process. It's excellent for lab-scale development and smaller production runs but is limited in volume.
Wiped film systems are designed for continuous operation. Once dialed in, they can run for hours or days with a continuous feed, making them the standard for high-throughput, commercial-scale production.
Cost and Complexity
A traditional short path setup is mechanically simple, relying mostly on glassware, heaters, and a vacuum pump. This makes it significantly less expensive and easier to maintain.
A wiped film system is a more complex piece of industrial machinery with motors, rotating seals, and precise engineering. This results in a much higher capital cost and more demanding maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct technology depends entirely on your specific goals, scale, and the material you are processing.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale research or processing lower-viscosity materials on a budget: A traditional short path system offers a cost-effective, simple, and capable solution.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity and yield for highly sensitive compounds: A wiped film system provides the best protection against thermal degradation and delivers a higher-quality product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, commercial production, especially with viscous feeds: A wiped film system is the industrial standard for its continuous operation, superior efficiency, and scalability.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction empowers you to select the right tool based on your material's sensitivity, your production scale, and your financial constraints.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Short Path | Wiped Film (Thin Film) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Static pool in heated flask | Mechanically wiped thin film |
| Thermal Degradation Risk | Higher (prolonged heating) | Lower (short residence time) |
| Viscosity Handling | Limited for thick materials | Excellent for viscous feeds |
| Process Type | Batch | Continuous |
| Scalability | Lab to small-scale | High-throughput, commercial |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler | Higher cost, more complex |
Upgrade Your Lab's Distillation Capabilities with KINTEK
Whether you're processing sensitive cannabinoids, essential oils, or high-value pharmaceuticals, choosing the right distillation system is critical for product purity and yield. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions tailored to your specific needs.
- For R&D and budget-conscious labs: Explore our range of traditional short path distillation kits for reliable, small-scale purification.
- For high-purity, high-volume production: Our wiped film evaporators (WFE) provide superior thermal control and continuous operation.
Let our experts help you select the ideal system to maximize efficiency and protect your valuable compounds. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















