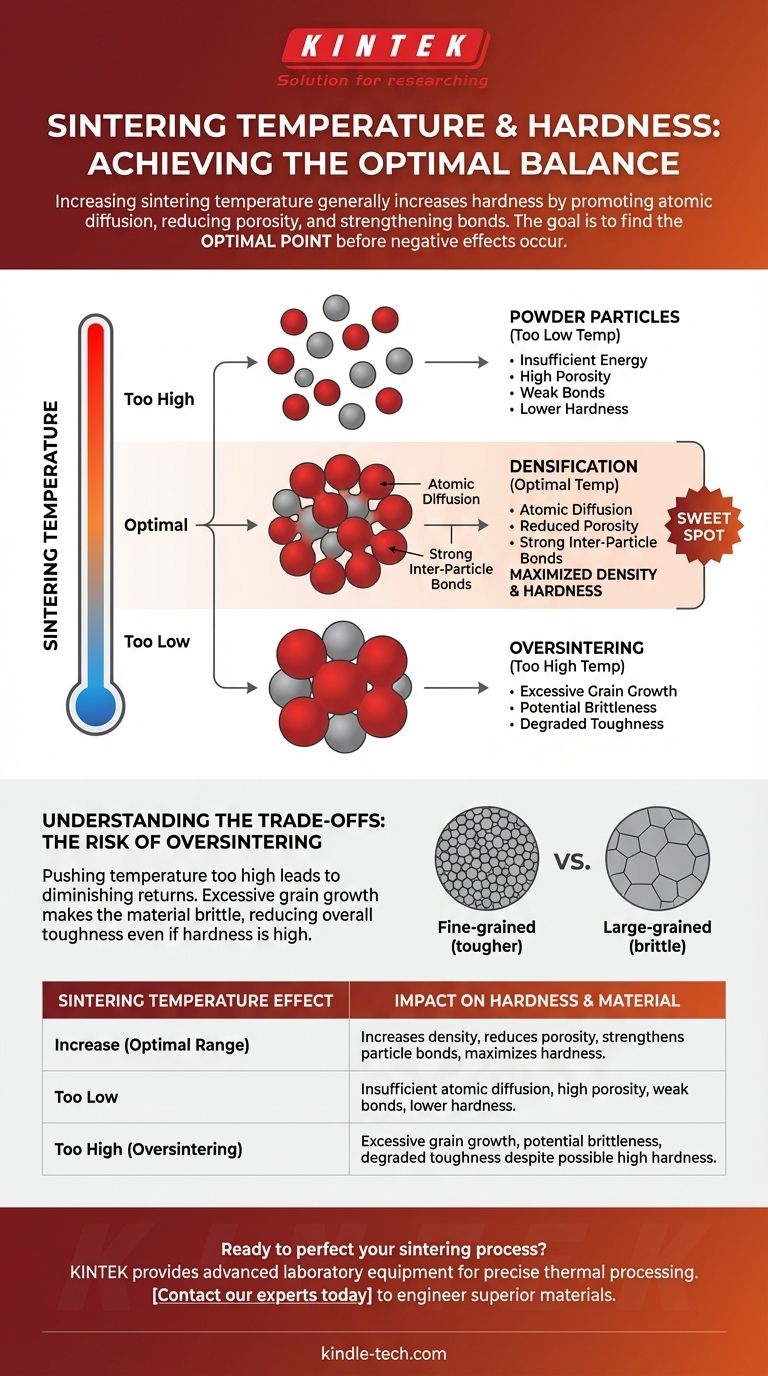
In short, increasing the sintering temperature generally increases the hardness of a material. This occurs because higher temperatures provide the necessary energy for powder particles to bond more effectively, reducing empty spaces (porosity) and creating a denser, more solid final part. However, this relationship is not infinite; an excessively high temperature can lead to other issues that compromise the material's integrity.
The key to mastering the process is understanding that sintering temperature is the primary control for hardness. The goal is not simply to use the highest possible temperature, but to find the optimal point that maximizes density and particle bonding before negative effects like excessive grain growth begin to degrade the material's properties.

The Fundamental Relationship: Temperature, Density, and Hardness
Sintering is fundamentally a process of thermal transformation. Temperature is the catalyst that drives the physical changes converting loose powder into a coherent, solid mass. The effect on hardness is a direct result of these microstructural changes.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Heat provides the energy required for atomic diffusion. This is the mechanism where atoms from individual powder particles migrate and move across the boundaries of adjacent particles. Without sufficient thermal energy, this process is too slow to be effective.
Reducing Porosity
As atoms diffuse, the particles begin to fuse. The small contact points, or "necks," between particles grow larger. This process actively pulls the particles closer together, shrinking the pores and voids that were trapped between them.
A reduction in porosity is a primary driver of increased hardness. With fewer empty spaces, the material has a greater cross-sectional area to resist indentation and deformation.
Strengthening Inter-Particle Bonds
The growth of the necks between particles creates a strong, continuous network throughout the material. This transforms a collection of individual grains into a unified, solid body with significantly improved mechanical strength and, therefore, hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Risk of Oversintering
While higher temperatures are generally beneficial, there is a point of diminishing returns. Pushing the temperature too high, a condition known as oversintering, introduces new problems that can compromise the final part.
The Onset of Grain Growth
After the majority of densification has occurred, continued exposure to high temperatures will cause grain growth. In this phenomenon, smaller grains are consumed by larger, more energetically stable ones. The average grain size of the material begins to increase significantly.
Why Excessive Grain Growth is a Problem
While a dense material is hard, a material with excessively large grains can become brittle. A fine-grained structure is typically tougher and more resistant to fracture. The boundaries between many small grains act as obstacles that impede the propagation of cracks.
When grains become too large, the material loses this structural advantage, potentially reducing its overall toughness even if the hardness measurement remains high. This can lead to unexpected failures in application.
The Concept of an Optimal Temperature
This creates a processing window. The optimal sintering temperature is the one that achieves maximum density and strong inter-particle bonding just before the onset of rapid and detrimental grain growth. Finding this sweet spot is critical for achieving the desired material properties repeatably.
Finding the Optimal Sintering Temperature
To engineer a material effectively, you must balance these competing factors. Your approach will depend entirely on the specific performance requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is maximizing raw hardness: You will need to carefully test and identify the temperature that achieves near-full density right before rapid grain growth begins.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness with toughness: You may need to operate slightly below the peak hardness temperature to maintain a finer, more robust grain structure.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and cost-efficiency: The goal is to determine the lowest temperature and shortest time that reliably meets your minimum required hardness specification.
Ultimately, mastering sintering temperature allows you to move from simply making a part to precisely engineering a material.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Temperature Effect | Impact on Hardness & Material |
|---|---|
| Increase (Optimal Range) | Increases density, reduces porosity, strengthens particle bonds, maximizes hardness. |
| Too Low | Insufficient atomic diffusion, high porosity, weak bonds, lower hardness. |
| Too High (Oversintering) | Excessive grain growth, potential brittleness, degraded toughness despite possible high hardness. |
Ready to perfect your sintering process and achieve the ideal balance of hardness and toughness in your materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing existing protocols, our solutions deliver the control and consistency you need to hit your target properties every time.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your lab's specific sintering challenges and help you engineer superior materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the working temperature of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Control for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of muffle furnace? Achieving Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the safety of a muffle furnace? Ensuring Secure Operation with Modern Design and Protocols
- What heat can a muffle furnace produce? Achieve Precise High Temperatures Up to 1800°C



















