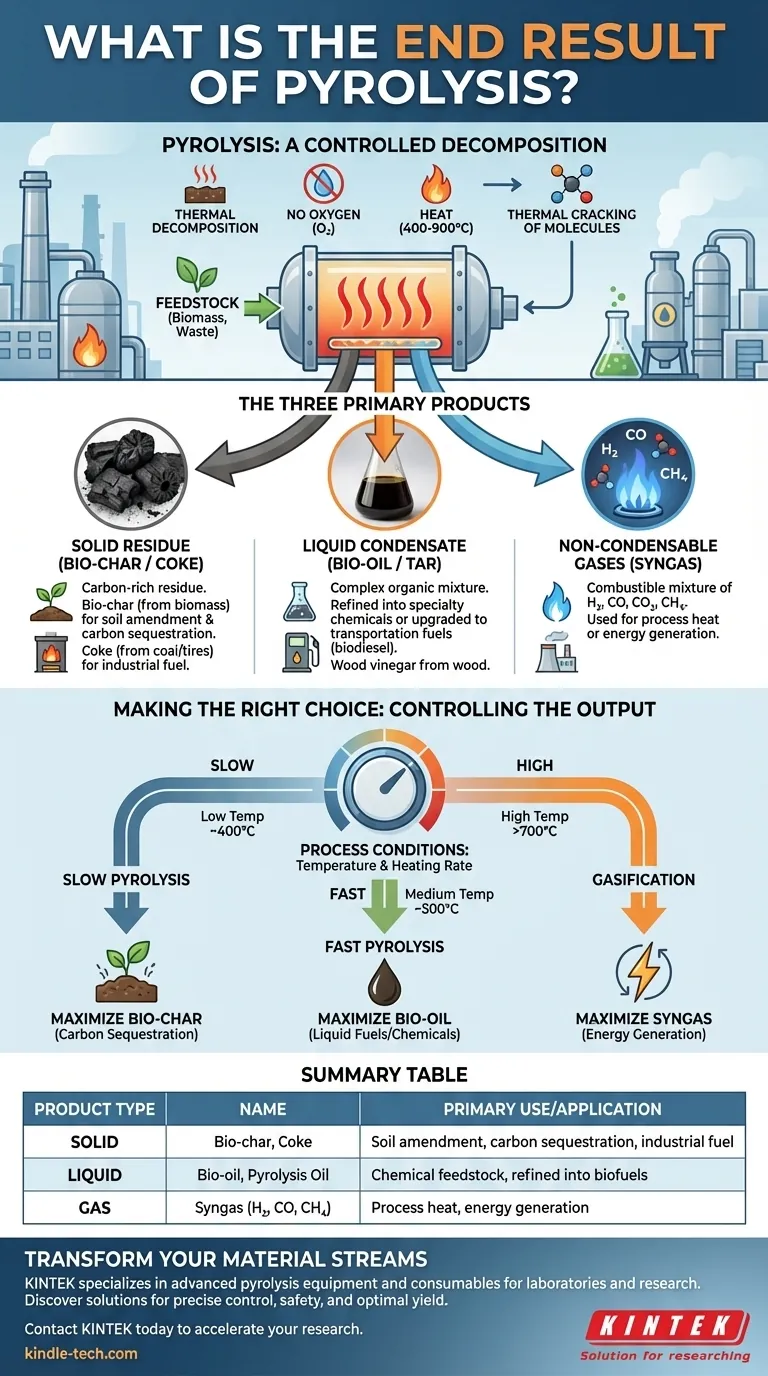
In short, pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that breaks down a material in the absence of oxygen, resulting in three distinct product types: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The solid is a carbon-rich residue called bio-char or coke, the liquid is a complex substance called bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), and the gas is a mixture of combustible gases called syngas.
Pyrolysis is not simply a disposal method; it is a controlled conversion process. The key insight is that by manipulating the process conditions—primarily temperature and heating rate—you can intentionally control which of the three end products (solid, liquid, or gas) is maximized, transforming waste streams into valuable resources.

What is Pyrolysis? A Controlled Decomposition
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from incineration or burning. Instead of destroying material with oxygen, it uses heat in an inert atmosphere to deconstruct it into its valuable chemical components.
The Core Mechanism: Thermal Cracking
At high temperatures, typically between 400-900°C (750-1650°F), long, complex organic molecules within the feedstock become unstable. The intense heat "cracks" these molecules apart into smaller, simpler, and often more valuable compounds.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The absence of oxygen is the defining feature of pyrolysis. If oxygen were present, the material would combust, producing primarily ash, carbon dioxide, and water. By excluding oxygen, we prevent combustion and instead force a thermochemical decomposition that preserves the chemical energy and carbon in the resulting products.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
Every pyrolysis reaction yields a mix of solids, liquids, and gases. The proportion and specific composition of each depend heavily on the input material (feedstock) and the process conditions.
The Solid Residue: Bio-char or Coke
This black, carbon-rich solid is what remains after the volatile components have vaporized.
When the feedstock is biomass (like wood or agricultural waste), this solid is called bio-char. It is highly porous and valued in agriculture as a soil amendment to improve water retention and sequester carbon. When derived from coal or tires, it is often called coke and can be used as a fuel source or in industrial processes.
The Liquid Condensate: Bio-oil or Tar
As the feedstock heats up, it releases hot vapors. When these vapors are cooled, they condense into a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil, pyrolysis oil, or sometimes tar.
This liquid is a complex mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds. It can be refined into specialty chemicals or upgraded into transportation fuels like biodiesel, though this often requires significant further processing. When wood is the feedstock, a portion of this liquid is also known as wood vinegar.
The Non-Condensable Gases: Syngas
Not all the vapors produced will condense into a liquid. The remaining gases are collectively called synthesis gas, or syngas.
This mixture typically includes hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄). Syngas is combustible, and its most common use is to be looped back to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor itself, making the process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is a technically demanding process with specific challenges that must be managed for a successful operation.
Significant Energy Input
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius requires a substantial initial energy investment. While the syngas produced can offset a large portion of this demand, the system is not self-powering from a cold start.
Technical Complexity
Operating a high-temperature, oxygen-free reactor is not a simple task. It requires specialized equipment, precise monitoring, and robust control systems to ensure both safety and optimal product yield.
Product Refinement is Often Required
The direct outputs of pyrolysis are not always ready for immediate use. Bio-oil, for example, is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable. It cannot be used as a "drop-in" fuel for standard engines without undergoing further hydrotreating or upgrading, which adds cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of pyrolysis lies in your ability to steer the output based on your desired outcome. By adjusting the process variables, you can select for one product fraction over the others.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Use slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures (around 400°C) with a long residence time to maximize the yield of solid bio-char.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks: Use fast pyrolysis with very rapid heating rates and short vapor residence times (around 500°C) to maximize the production of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating energy or synthesis gas: Use very high-temperature pyrolysis, often called gasification (above 700°C), to maximize the conversion of the material into syngas.
Ultimately, pyrolysis offers a sophisticated tool for converting low-value materials into a diverse portfolio of high-value products.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Name | Primary Use/Application |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Bio-char (from biomass) / Coke | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, industrial fuel |
| Liquid | Bio-oil / Pyrolysis Oil | Chemical feedstock, refined into biofuels |
| Gas | Syngas (H₂, CO, CH₄) | Process heat, energy generation |
Ready to transform your material streams into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment and consumables for laboratories and research facilities. Whether your goal is to maximize bio-char for carbon sequestration, produce bio-oil for fuel research, or generate syngas for energy, our solutions are designed for precise control, safety, and optimal yield.
Let our experts help you select the right system for your specific feedstock and target products. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our lab equipment can accelerate your pyrolysis research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies



















