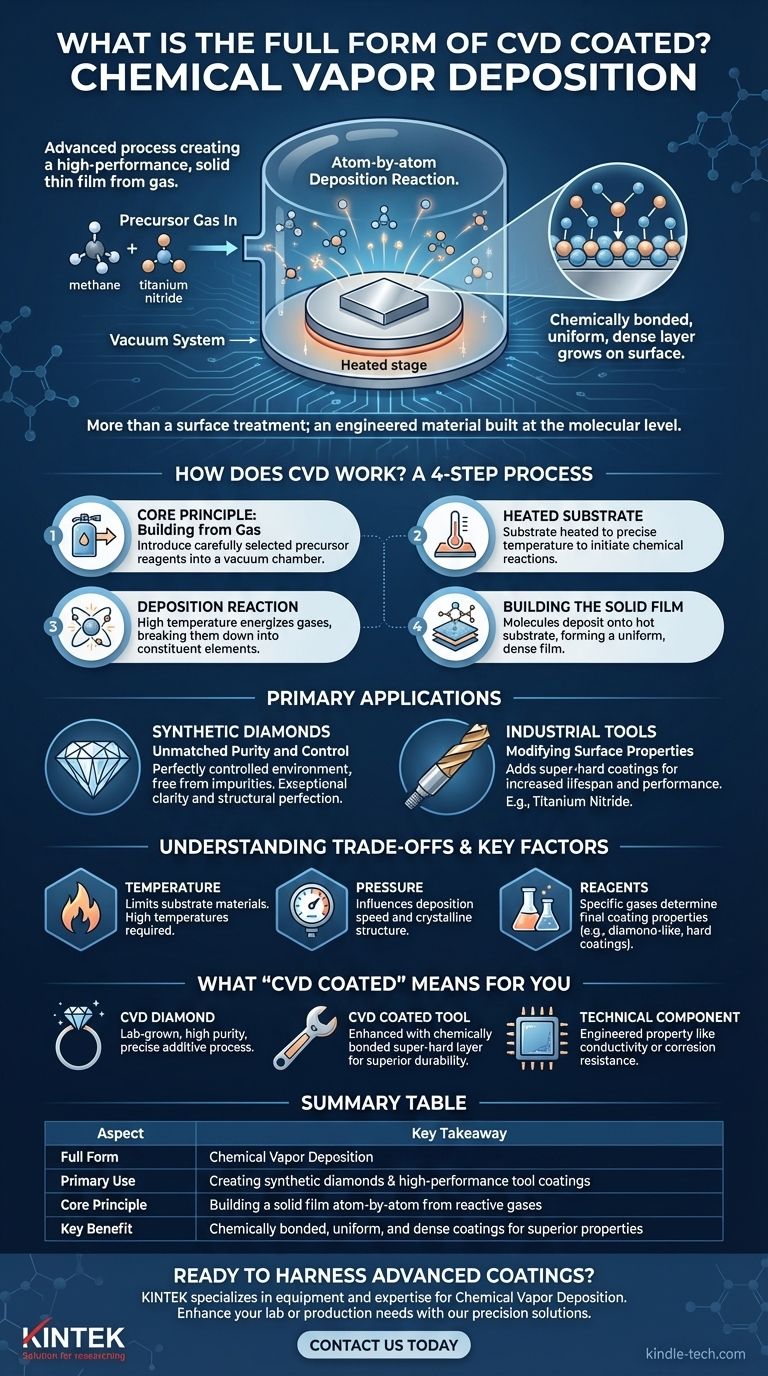
CVD coated stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. This is an advanced process where a high-performance, solid thin film is created on the surface of an object (the substrate) by introducing specific gases into a heated chamber. These gases react and deposit material atom-by-atom, essentially "growing" a new layer onto the original item.
The term "CVD coated" signifies more than just a surface treatment; it describes an engineered material built at the molecular level. It's a method for fundamentally enhancing a material's properties—like hardness or purity—by bonding a new, superior layer directly to its surface.

How Does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Work?
The CVD process is a highly controlled method of material synthesis. It can be broken down into a few core steps, whether it's being used to create a synthetic diamond or a durable tool coating.
The Core Principle: Building from Gas
The process begins by introducing carefully selected gases, known as precursor reagents, into a vacuum chamber. These gases contain the specific elements that will form the final coating.
The Heated Substrate
Inside the chamber is the object to be coated, referred to as the substrate. This substrate is heated to a precise temperature, which is critical for initiating the necessary chemical reactions.
The Deposition Reaction
The high temperature at the substrate's surface energizes the precursor gases, causing them to react or decompose. This chemical reaction breaks the gases down into their constituent elements.
Building the Solid Film
As the gases decompose, the desired solid material is deposited onto the hot substrate. This happens molecule by molecule, building a highly uniform, dense, and strong thin film that is chemically bonded to the surface. For synthetic diamonds, a carbon-containing gas deposits pure carbon atoms onto a tiny diamond "seed."
The Primary Application: Creating Synthetic Diamonds
While CVD has many industrial uses, its most well-known application is the creation of lab-grown diamonds. The process allows for exceptional control over the final product.
Unmatched Purity and Control
The vacuum chamber provides a perfectly controlled environment, free from the impurities found in natural geological processes. By managing the gases, temperature, and pressure, producers can "grow" diamonds with exceptional clarity and structural perfection.
Modifying Surface Properties
In other industries, CVD isn't used to create an entire object but to add a crucial surface property. For example, a super-hard coating can be applied to a cutting tool, dramatically increasing its lifespan and performance without changing the tool's core material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
The quality and success of a CVD coating are not automatic. The process is a careful balance of scientific parameters that dictate the outcome.
The Importance of Temperature
The substrate must be able to withstand the high temperatures required for the reaction, which can range from moderate to very high. This limits the types of materials that can be effectively coated using CVD.
The Role of Pressure
Along with temperature, the pressure inside the chamber is meticulously controlled. This influences the speed of the deposition and the final crystalline structure of the coating.
The Choice of Reagents
The specific gases used determine everything. Using a carbon-rich gas like methane creates a diamond or diamond-like carbon film. Using other gases, such as titanium nitride, produces coatings known for extreme hardness and wear resistance on industrial tools.
What "CVD Coated" Means for Your Goal
Ultimately, the significance of a CVD coating depends on the context. Your takeaway should be tailored to the specific application you are encountering.
- If your primary focus is a CVD diamond: This refers to a lab-grown diamond created through a precise, additive process, known for yielding high purity and quality.
- If your primary focus is a CVD coated tool: This means a base material has been enhanced with a chemically bonded layer of a super-hard material for superior durability and performance.
- If your primary focus is a technical component (e.g., in electronics): The CVD coating provides a specific, engineered property, such as electrical conductivity or corrosion resistance, that the underlying material lacks.
Understanding CVD means recognizing it as a mark of advanced material engineering, where a surface is fundamentally transformed for a specific, high-performance purpose.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Full Form | Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| Primary Use | Creating synthetic diamonds & high-performance tool coatings |
| Core Principle | Building a solid film atom-by-atom from reactive gases |
| Key Benefit | Chemically bonded, uniform, and dense coatings for superior properties |
Ready to harness the power of advanced coatings for your laboratory or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the equipment and expertise for cutting-edge processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you are developing new materials, enhancing tool durability, or require high-purity components, our lab equipment and consumables are engineered for precision and performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring the benefits of CVD technology to your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the physical Vapour deposition theory? A Guide to PVD Coating Principles
- What is the mechanism of DC sputtering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits and applications of Atomic Layer Chemical Vapour Deposition (ALCVD)? Unlock Atomic Precision
- What are the advantages of using a hot-wall CVD reactor? Optimize Tantalum Carbide Coatings for Semiconductor Purity
- What is thin films explain sputtering techniques of thin film deposition? A Guide to DC, RF & Reactive Sputtering
- What are sputtering systems? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the working principle of chemical vapor deposition? Grow Superior Thin Films from Gas
- What is the deposition of chemicals? A Guide to Growing High-Performance Thin Films



















