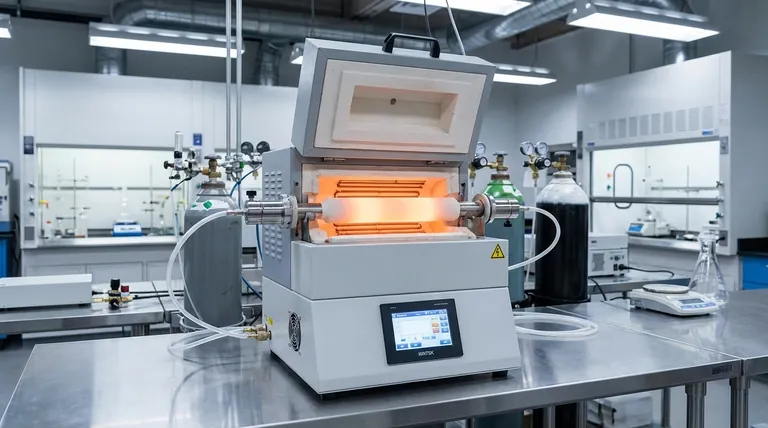
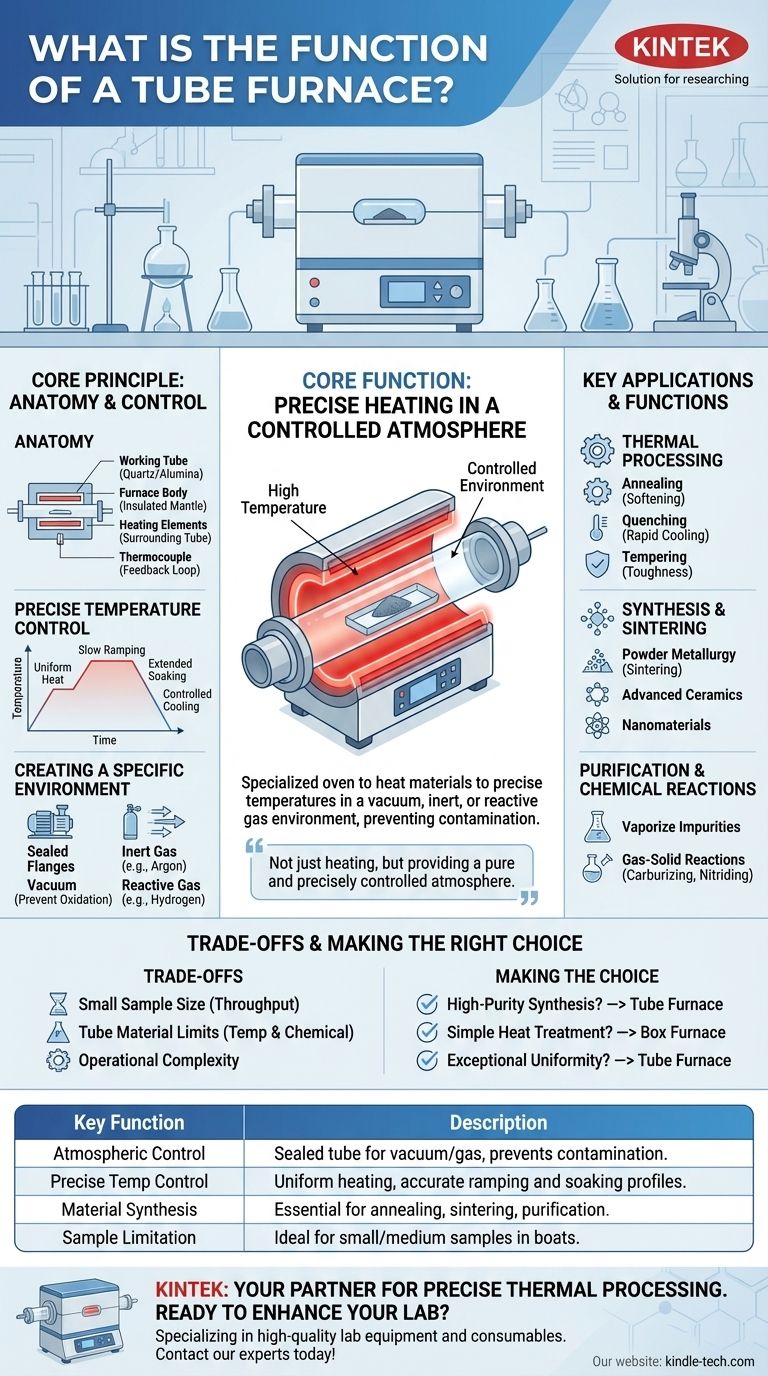
At its core, a tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven whose primary function is to heat materials to precise temperatures within a highly controlled environment. Unlike a conventional oven, it uses a cylindrical chamber (the "tube") that can be sealed and isolated from the ambient air. This allows operators to conduct processes in a vacuum, with specific inert or reactive gases, or simply with exceptional temperature uniformity.
The essential function of a tube furnace is not just heating, but providing a pure and precisely controlled atmosphere. This makes it indispensable for advanced material processing, synthesis, and research where contamination or unwanted chemical reactions must be prevented.

The Core Principle: Heating in a Controlled Atmosphere
The unique capabilities of a tube furnace stem from its fundamental design, which isolates the sample from the outside world and the heating elements themselves.
The Anatomy of a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace consists of a few key components working in concert. A central working tube, typically made of quartz, alumina, or a specialized metal alloy, contains the sample.
This tube is housed within an insulated furnace body or "mantle." Inside this body, heating elements surround the tube, and a thermocouple provides temperature feedback to a controller for precise regulation.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
The cylindrical design is not arbitrary. By arranging the heating coils around the tube, the furnace can deliver highly uniform heat to the sample from all sides.
The thermocouple's feedback loop allows the controller to maintain a specific temperature profile, enabling processes that require slow ramping, extended soaking at a set point, and controlled cooling.
Creating a Specific Environment
This is the most critical function that distinguishes a tube furnace. The ends of the tube can be sealed with flanges, allowing a vacuum pump to remove the air.
This vacuum environment is crucial for preventing oxidation at high temperatures. Alternatively, specific gases—such as argon to create an inert atmosphere or hydrogen for a reducing atmosphere—can be flowed through the tube to facilitate specific chemical reactions.
Key Applications and Functions
The combination of precise temperature and atmospheric control makes the tube furnace a vital tool for a wide range of scientific and industrial processes.
Thermal Processing of Materials
One of the most common functions is the heat treatment of metals and other materials. This includes processes such as:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material to soften it and relieve internal stresses.
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling a material to lock in a specific crystalline structure.
- Tempering: Heating a previously quenched material to increase its toughness.
Synthesis and Sintering
Tube furnaces are essential in materials science for creating new materials from scratch. The controlled atmosphere prevents contamination that could ruin the final product.
This includes powder metallurgy, where metal powders are heated until they bond together (sinter) to form a solid part, as well as the synthesis of advanced ceramics, crystals, and nanomaterials.
Purification and Chemical Reactions
The furnace can be used to purify materials by heating them to burn off or vaporize impurities in a vacuum.
It also functions as a chemical reactor. By flowing reactive gases over a sample at high temperatures, chemists can perform gas-solid reactions, such as carburizing (adding carbon to steel) or nitriding (adding nitrogen).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized instrument with specific constraints that are important to understand.
Sample Size and Throughput
Most laboratory tube furnaces are designed for relatively small sample sizes that can fit inside the tube, often placed in ceramic or metal "boats."
While multiple furnaces can be linked for larger-scale or continuous production, a single unit is generally not suited for high-volume industrial manufacturing.
Tube Material Constraints
The maximum operating temperature is fundamentally limited by the material of the working tube. Quartz tubes are common and relatively inexpensive but typically cannot exceed ~1200°C.
For higher temperatures, more expensive alumina ceramic tubes are required, which can often reach 1600°C or higher. The tube material must also be compatible with the chemical environment and thermal stress of the process.
Operational Complexity
While the basic heating function is straightforward, setting up a specific atmosphere requires technical knowledge. Properly sealing vacuum flanges, managing gas flow rates, and operating a vacuum system add layers of complexity compared to a simple air-filled box furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To determine if a tube furnace is the appropriate tool, you must evaluate your process requirements against its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis or reactions: A tube furnace is essential because its sealed design provides the necessary atmospheric control (vacuum or specific gases) to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of samples in air: A standard box or muffle furnace might be a simpler and more cost-effective solution, as it forgoes the complexity of atmospheric controls.
- If your primary focus is achieving exceptional temperature uniformity for a small sample: A tube furnace is an excellent choice due to its cylindrical heating element configuration.
Ultimately, the function of a tube furnace is to provide an unmatched level of control over the thermal and atmospheric environment, enabling advanced material processing and research.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Sealed tube allows for vacuum, inert, or reactive gas environments to prevent contamination. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Uniform heating from all sides with accurate temperature profiles for ramping and soaking. |
| Material Synthesis & Processing | Essential for annealing, sintering, purification, and gas-solid reactions. |
| Sample Limitation | Ideal for small to medium-sized samples placed in boats within the tube. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thermal processing?
A tube furnace from KINTEK is more than just an oven; it's your partner in achieving unparalleled control over your material synthesis and heat treatment processes. Whether you are working in research and development, materials science, or advanced manufacturing, our tube furnaces provide the critical controlled atmosphere and temperature uniformity your work demands.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories worldwide. Let us help you select the perfect tube furnace for your specific application, ensuring purity, accuracy, and repeatability in your results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification



















