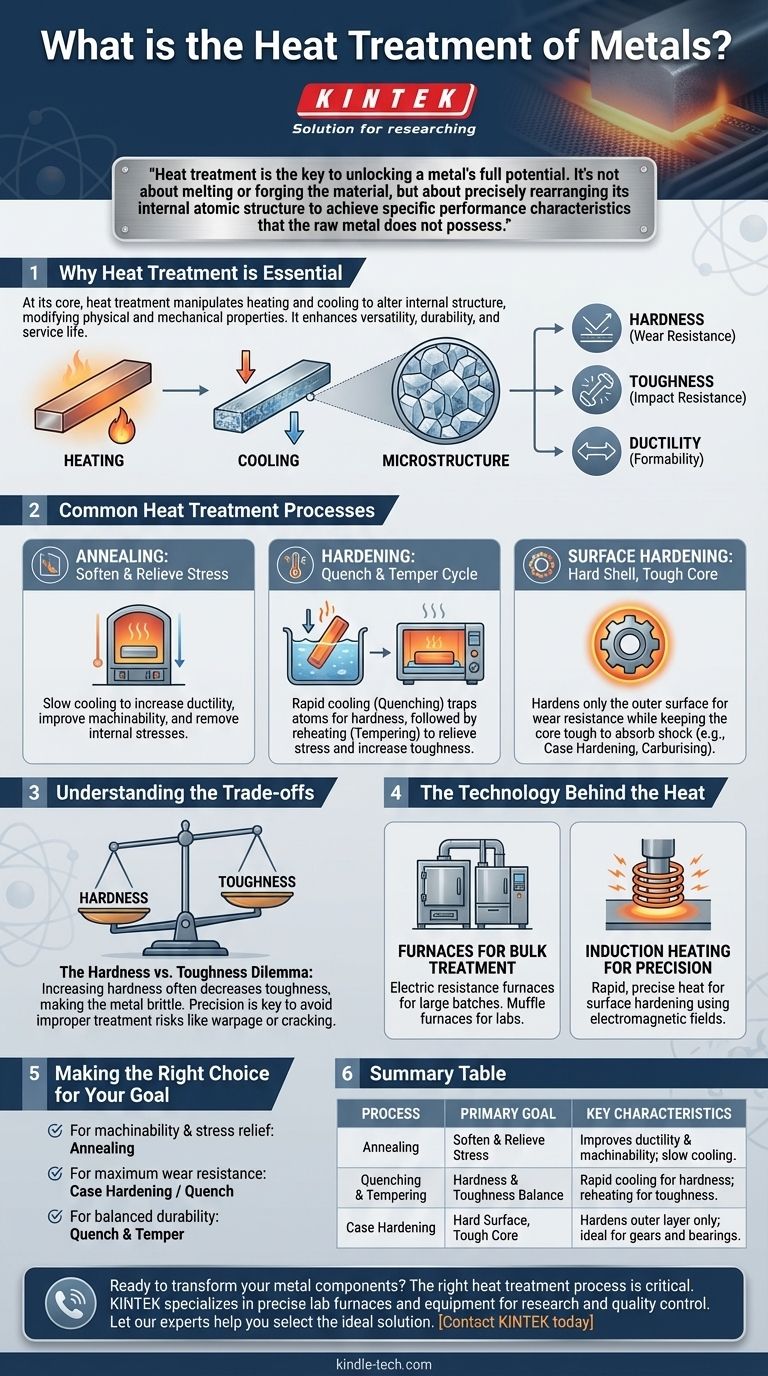
At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled industrial process where metals are heated and cooled to precise temperatures and rates. This manipulation doesn't change the metal's shape but fundamentally alters its internal crystalline structure, thereby modifying its physical and mechanical properties like hardness, toughness, and ductility.
Heat treatment is the key to unlocking a metal's full potential. It's not about melting or forging the material, but about precisely rearranging its internal atomic structure to achieve specific performance characteristics that the raw metal does not possess.

Why Heat Treatment is Essential
The primary goal of heat treatment is to make a metal part better suited for its intended application. This process is a critical step in manufacturing, enhancing the versatility, durability, and service life of metallic components.
Controlling the Microstructure
Heating a metal provides the energy for its atoms to move and rearrange into different crystal structures. The rate of cooling then "locks in" a desired structure, known as the microstructure. This internal architecture is what dictates the final properties of the component.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
By changing the microstructure, we can fine-tune critical properties. For example, we can increase hardness for better wear resistance, improve toughness to resist fracture from impact, or enhance ductility to allow the metal to be formed or drawn without breaking.
Common Heat Treatment Processes
Different combinations of heating cycles, temperatures, and cooling rates define specific treatment processes, each designed to produce a distinct set of properties.
Annealing: To Soften and Relieve Stress
Annealing involves heating a metal and then cooling it very slowly. This process is used to soften the material, making it more ductile and easier to machine or form. It also serves to remove internal stresses created during previous manufacturing steps.
Hardening: The Quench and Temper Cycle
Quenching is the process of rapidly cooling a metal, typically in water, oil, or air, after heating it to a high temperature. This traps the atoms in a very hard but brittle structure.
Because quenching creates brittleness, it is almost always followed by tempering. This involves reheating the part to a lower temperature to relieve some internal stress, which reduces brittleness and increases toughness at the cost of a small amount of hardness.
Surface Hardening: A Tough Core with a Hard Shell
Also known as case hardening, this group of processes hardens only the outer surface of a part while leaving the inner core (the "case") softer and tougher.
This creates an ideal combination for components like gears, which need a highly wear-resistant surface to mesh with other parts but a tough core to absorb shock and prevent catastrophic failure. Carburising is a common method where carbon is infused into the surface of steel to enable this localized hardening.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a discipline of carefully balanced compromises. You rarely get to maximize all desirable properties at once.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and toughness. As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost invariably decrease its toughness, making it more brittle and prone to shattering under sudden impact. A perfectly hardened file can cut steel, but it will shatter if you drop it on a concrete floor. This is why tempering is so critical after quenching.
The Risk of Improper Treatment
Heat treatment requires extreme precision. Using the wrong temperature, timing, or cooling medium can not only fail to produce the desired properties but can permanently damage or destroy the component. This can lead to warpage, cracking, or a final part that is too soft or too brittle for its job.
The Technology Behind the Heat
The method used to apply heat is chosen based on the process, the material, and the scale of production.
Furnaces for Bulk Treatment
For processing entire components or large batches, electric resistance furnaces are common. These operate like large, highly controlled ovens. Smaller muffle furnaces are often used in labs for testing material properties or for treating very small parts.
Induction Heating for Precision
Induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to rapidly generate heat directly within the metal's surface. This method is extremely fast and precise, making it ideal for surface hardening processes where only the outer layer of a part needs to be treated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the final performance requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is machinability and stress relief: Annealing is the correct process to soften the material and make it easier to work with.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and surface hardness: Case hardening or a full quench with minimal tempering will provide the hardest possible surface.
- If your primary focus is balanced durability against impact and wear: A quench-and-temper cycle is the standard approach to achieve a good combination of hardness and toughness.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms a simple piece of metal into a high-performance engineering component.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften & Relieve Stress | Improves ductility and machinability; slow cooling. |
| Quenching & Tempering | Hardness & Toughness Balance | Rapid cooling (quench) for hardness; reheating (temper) for toughness. |
| Case Hardening | Hard Surface, Tough Core | Hardens only the outer layer; ideal for gears and bearings. |
Ready to transform your metal components? The right heat treatment process is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and durability. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab furnaces and equipment needed for research, development, and quality control of heat treatment processes. Let our experts help you select the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare samples for IR? A Guide to Solid, Liquid, and Gas Sample Prep
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties
- What is the heat capacity of a muffle furnace? Understanding Thermal Mass for Optimal Performance
- How does quenching work chemistry? Mastering the Atomic Race for Harder Steel



















