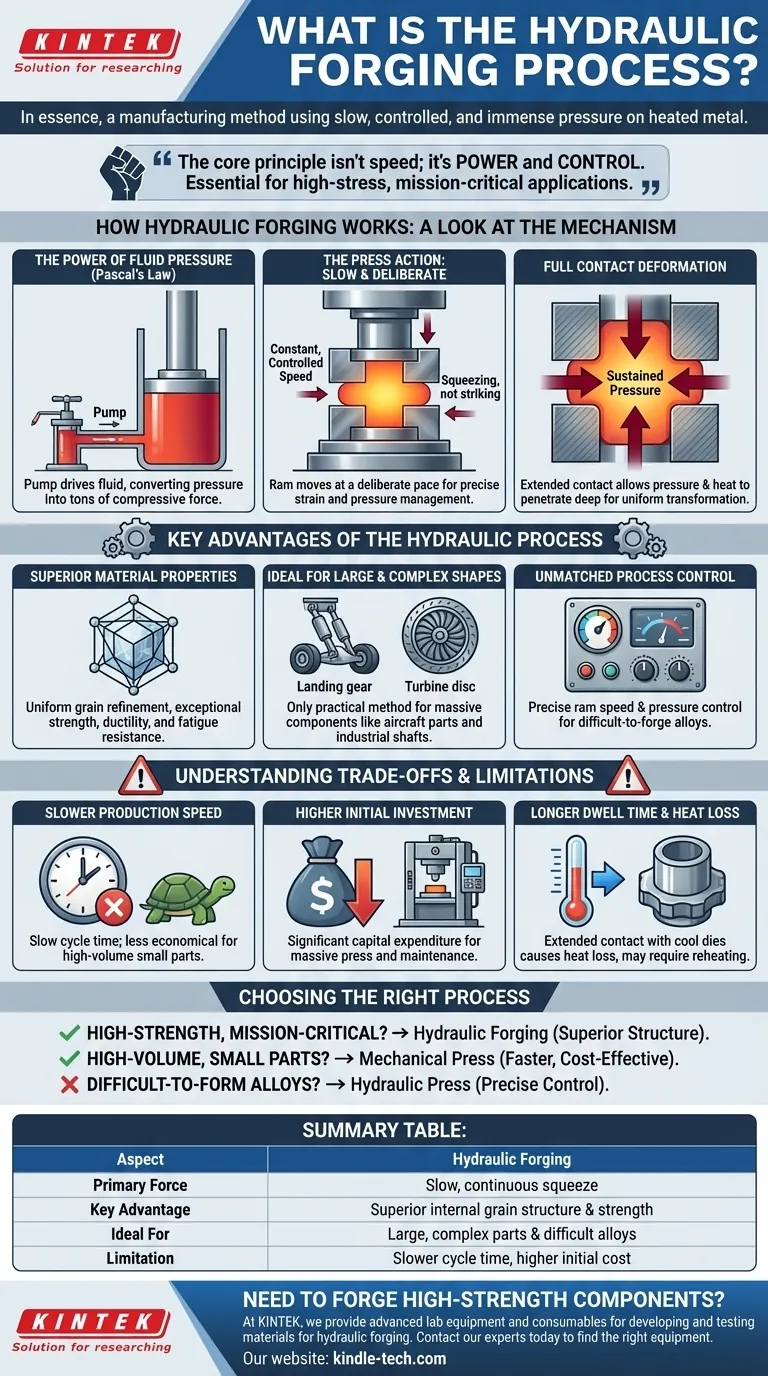
In essence, the hydraulic forging process is a manufacturing method that uses a hydraulic press to apply slow, controlled, and immense pressure to a heated metal workpiece. Unlike processes that rely on a rapid strike, hydraulic forging squeezes the metal, holding it under pressure to form it between two dies. This sustained force allows the material to flow and conform to the die's shape completely.
The core principle of hydraulic forging isn't speed; it's power and control. It excels at creating very large, complex components with deep, uniform internal structures, making it indispensable for high-stress, mission-critical applications.

How Hydraulic Forging Works: A Look at the Mechanism
To understand why hydraulic forging is chosen for specific jobs, we must first look at its unique mechanical principle. It operates on a foundation of controlled force application, which fundamentally differs from the rapid impact of a hammer or mechanical press.
The Power of Fluid Pressure
The press generates its immense force using Pascal's Law. A pump pushes hydraulic fluid into a large cylinder, which drives a massive piston (the ram) downwards. This system acts as a force multiplier, converting fluid pressure into tons of compressive force.
The Press Action: Slow and Deliberate
The defining characteristic of a hydraulic press is its constant, controlled speed throughout the entire stroke. The ram moves at a deliberate pace, squeezing the metal rather than striking it. This action is fully programmable, allowing operators to precisely manage strain rate and pressure.
Full Contact Deformation
Because the pressure is maintained for the duration of the stroke, the die remains in full contact with the workpiece. This extended contact time allows the pressure and heat to penetrate deep into the material's core, ensuring a complete and uniform transformation.
Key Advantages of the Hydraulic Process
The slow and powerful nature of hydraulic forging delivers distinct metallurgical and manufacturing benefits that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
Superior Material Properties
The slow squeeze creates a uniform grain refinement throughout the entire volume of the workpiece, from the surface to the core. This results in exceptional strength, improved ductility, and superior fatigue resistance, as it minimizes internal stresses and voids.
Ideal for Large and Complex Shapes
The immense and sustained force makes it the only practical method for forging massive components. This includes parts like aircraft landing gear, large turbine discs, and industrial shafts that can weigh many tons.
Unmatched Process Control
Operators have precise control over the ram's speed and pressure. This control is critical when working with difficult-to-forge materials like high-alloy steels, titanium, and nickel-based superalloys that can crack under the sudden impact of other forging methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect for every application. The strengths of hydraulic forging are accompanied by clear trade-offs that make it unsuitable for certain types of production.
Slower Production Speed
The primary drawback is its slow cycle time. The deliberate nature of the pressing action means it cannot compete with the high-speed output of mechanical or screw presses, making it less economical for high-volume production of smaller parts.
Higher Initial Investment
Hydraulic forging presses are massive, complex machines. They represent a significant capital expenditure in both initial cost and ongoing maintenance compared to simpler mechanical presses.
Longer Dwell Time and Heat Loss
The extended contact time between the hot workpiece and the relatively cool dies causes significant heat loss. This can necessitate reheating the part between forging stages, adding time and cost to the overall process.
Choosing the Right Forging Process for Your Application
Selecting the correct forging method depends entirely on the material, the part's size and complexity, and the required production volume.
- If your primary focus is high-strength, mission-critical components: Hydraulic forging is the superior choice for its ability to create uniform internal grain structures and exceptional mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of smaller parts: A faster mechanical press is almost always the more cost-effective and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is working with difficult-to-form alloys: The precise speed and pressure control offered by a hydraulic press is often a technical necessity to prevent defects.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs is the key to selecting a manufacturing process that ensures both ultimate performance and economic viability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hydraulic Forging |
|---|---|
| Primary Force | Slow, continuous squeeze |
| Key Advantage | Superior internal grain structure & strength |
| Ideal For | Large, complex parts & difficult alloys |
| Limitation | Slower cycle time, higher initial cost |
Need to forge high-strength, mission-critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing materials for demanding applications like hydraulic forging. Whether you're researching new alloys or ensuring quality control, our solutions help you achieve the superior material properties this process is known for.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required during the preparation of Ti3AlC2 precursor pellets?
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- What is an example of a hydraulic press? Discover the Power of Laboratory Sample Preparation
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis
- What is the purpose of a laboratory hydraulic press for LATP electrolyte pellets? Achieve Optimal Density & Conductivity



















