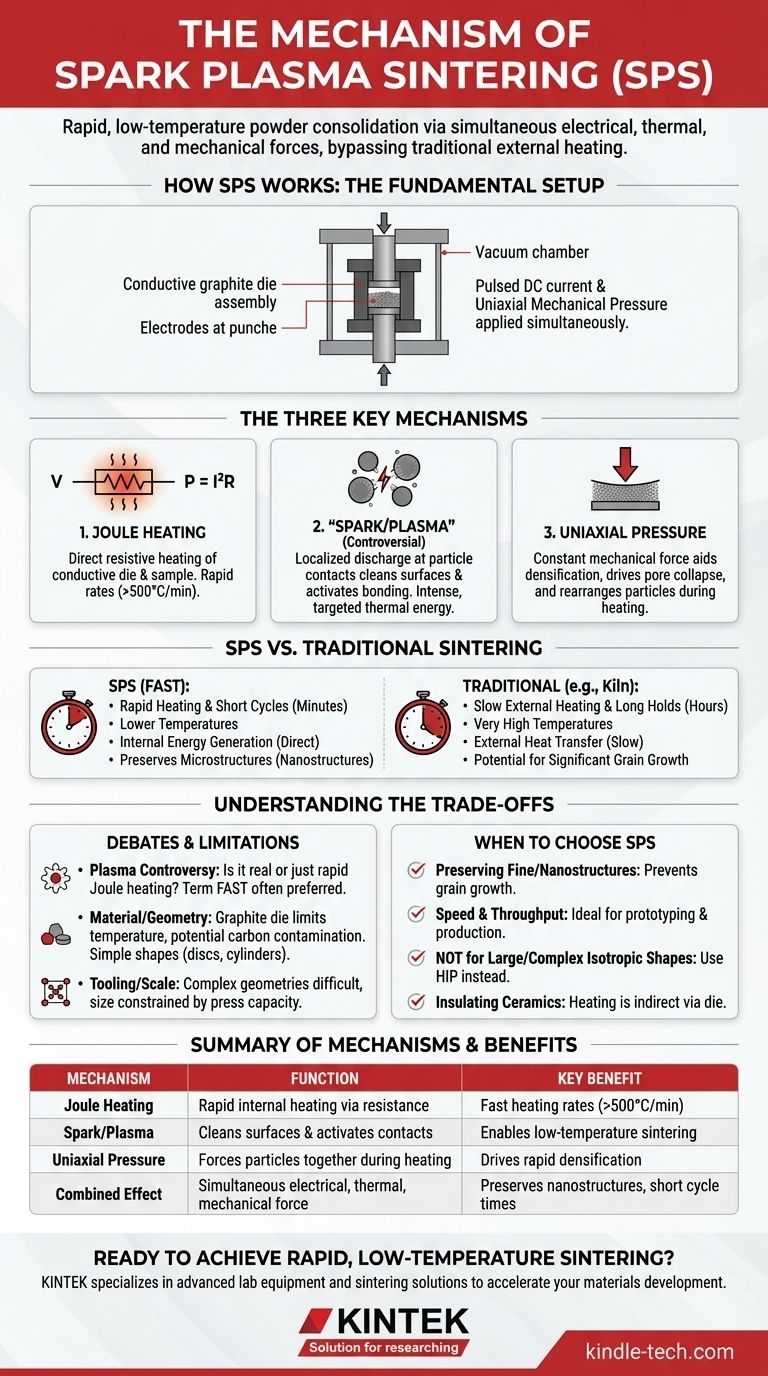
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a process that consolidates powders into a dense solid by simultaneously applying high-amperage, pulsed direct current (DC) and uniaxial mechanical pressure. Unlike conventional methods that heat the sample from the outside-in, SPS uses the material's own electrical resistance (and that of its container) to generate intense heat internally and at particle contact points. This unique combination of electrical, thermal, and mechanical forces enables densification at much lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time.
The central advantage of SPS is not merely speed, but its mechanism. By using electricity as a direct tool for heating and surface activation, it bypasses the slow, inefficient thermal transfer of traditional furnaces, enabling the creation of advanced materials with preserved microstructures.
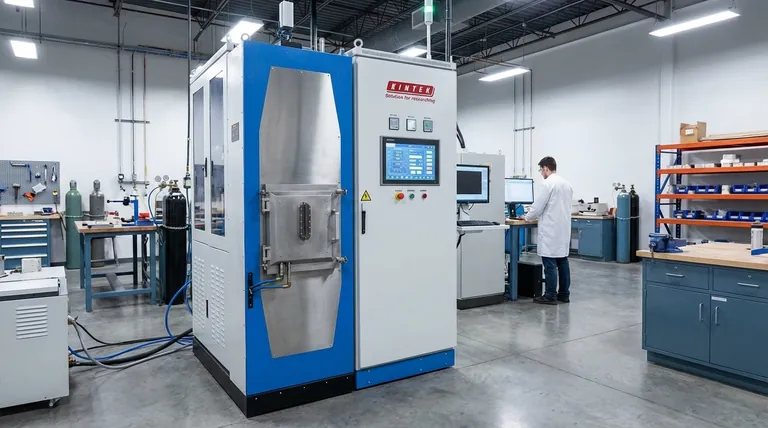

How SPS Overcomes Traditional Sintering Limits
Conventional sintering, like firing pottery in a kiln, is slow. It relies on external heating elements to gradually heat a material, requiring long hold times at very high temperatures. SPS fundamentally changes the source and application of energy.
The Fundamental Setup
The process begins by loading a powder into a conductive die, which is almost always made of graphite. This die assembly is placed between two electrodes inside a vacuum chamber. A mechanical press applies a constant, uniaxial pressure on the powder through the electrodes, which also act as punches.
The Power of Joule Heating
The primary mechanism behind the rapid heating of SPS is Joule heating. When the pulsed DC current is applied, it flows through the conductive graphite die and, if the powder is conductive, through the sample itself. The electrical resistance of these components causes them to heat up incredibly quickly, with rates often exceeding 500°C per minute. This is the direct conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy (P = I²R).
The "Spark Plasma" Phenomenon
The name "Spark Plasma Sintering" comes from a secondary, more localized effect. At the microscopic contact points between individual powder particles, the electrical field can become extremely concentrated. This can ionize any residual gas in the pores, creating a momentary spark discharge or plasma.
This localized plasma serves two key functions: it can blast away surface contaminants (like oxide layers) that inhibit bonding, and it delivers an intense burst of thermal energy exactly where it's needed—at the particle-particle interface.
The Role of Uniaxial Pressure
Throughout this rapid heating process, the constant mechanical pressure forces the particles together. As the material softens and particle surfaces become active, this pressure aids in the collapse of pores and the rearrangement of particles, driving the material toward full densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Debates
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution, and its exact mechanisms are still a subject of expert discussion.
The "Plasma" Controversy
Many researchers in the materials science community argue that the term "Spark Plasma Sintering" is a misnomer. They contend that the dominant mechanism is simply rapid resistive heating (Joule heating) combined with pressure, and that the existence or effect of a sustained plasma is negligible. For this reason, the more scientifically precise term Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST) is often preferred.
Material and Geometry Limitations
The standard use of a graphite die imposes limitations. It restricts the maximum processing temperature and can introduce carbon contamination in sensitive materials. Furthermore, the uniaxial pressure can result in an anisotropic microstructure, where material properties are different in one direction than another.
Tooling and Scale Constraints
SPS is generally used for producing relatively simple shapes like discs or cylinders. Creating complex geometries is difficult and costly. The size of the final part is also limited by the practical constraints of the press and die assembly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on your priorities for the final material, balancing speed, cost, and desired properties.
- If your primary focus is preserving fine or nanostructures: SPS is the superior choice, as its extremely short cycle times prevent the grain growth that plagues slower, high-temperature methods.
- If your primary focus is speed and throughput for prototyping or production: SPS offers an unparalleled advantage, reducing sintering cycles from many hours to mere minutes.
- If your primary focus is creating large, isotropic components with complex shapes: You will likely need to consider other methods, such as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), which applies pressure uniformly from all directions.
- If your primary focus is sintering highly insulating ceramics: Understand that in SPS, the heating will be indirect via the conductive die, making the process function more like a very fast hot press rather than utilizing internal current flow.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering leverages the power of direct electrical current to achieve material consolidation results that are simply not possible with purely thermal methods.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Joule Heating | Rapid internal heating via electrical resistance | Fast heating rates (>500°C/min) |
| Spark/Plasma | Cleans surfaces & activates particle contacts | Enables low-temperature sintering |
| Uniaxial Pressure | Forces particles together during heating | Drives rapid densification |
| Combined Effect | Simultaneous electrical, thermal, mechanical force | Preserves nanostructures, short cycle times |
Ready to achieve rapid, low-temperature sintering and preserve your material's microstructure?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions. Our expertise can help you select the right technology to accelerate your materials development and prototyping.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology


















