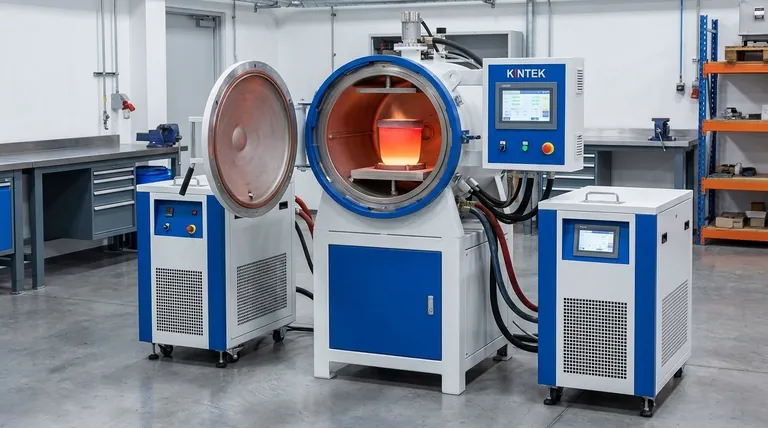
At its core, melting in an electric furnace is the process of using electrical energy to generate intense heat and liquefy metals. Unlike traditional fuel-fired furnaces, this method generates heat directly within the metal charge itself, primarily through two distinct technologies: electric arc furnaces (EAF) and, more commonly for specialized applications, electric induction furnaces. The process is valued for its precision, efficiency, and ability to achieve high levels of purity.
The fundamental advantage of electric furnace melting is its shift from external combustion to internal heat generation. By using principles like electromagnetic induction, it offers unparalleled control over temperature, composition, and purity, making it a clean, rapid, and highly efficient method for modern metallurgy.

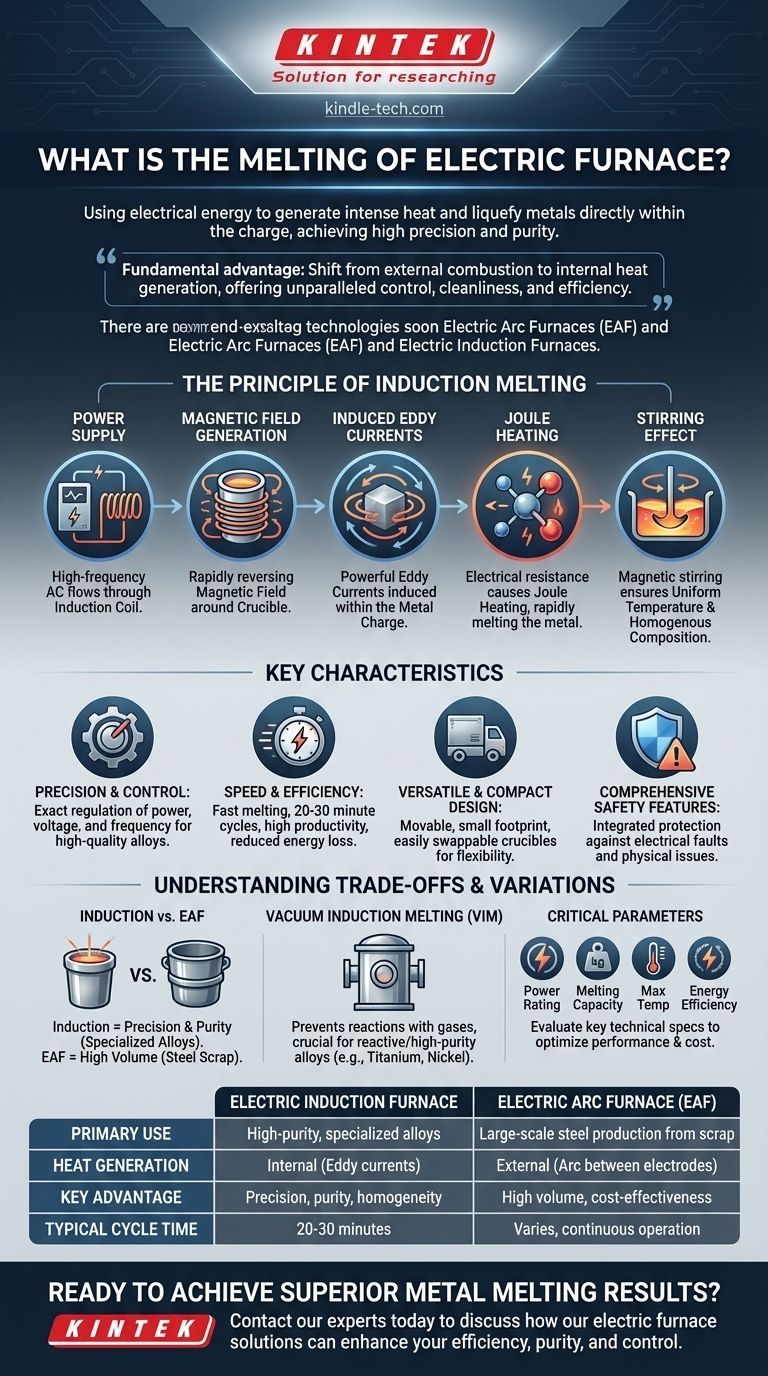
The Principle of Induction Melting: From Current to Heat
The most sophisticated electric furnaces operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This process converts electrical energy into thermal energy without any direct contact between the heating element and the material.
The Core Components
An electric induction melting furnace is built around three key parts: a powerful power supply, a conductive coil (or inductor), and a crucible made from refractory materials designed to contain the molten metal.
Generating the Magnetic Field
When a high-frequency alternating current from the power supply flows through the induction coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly reversing magnetic field around the crucible.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This magnetic field penetrates the metal charge placed inside the crucible. According to the laws of electromagnetism, the fluctuating field induces powerful, swirling electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Joule Heating: The Source of the Melt
As these eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance causes intense friction on a molecular level, generating heat in a process called Joule heating. It is this internally generated heat that causes the metal to melt rapidly and efficiently.
The Stirring Effect for Uniformity
A key benefit of induction is the natural magnetic stirring caused by the interaction of the magnetic field and the eddy currents. This stirring action constantly mixes the molten bath, ensuring a uniform temperature and homogenous chemical composition throughout the melt.
Key Characteristics of Modern Electric Furnaces
Modern electric furnaces are defined by a set of characteristics that make them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Precision and Control
Advanced solid-state power supplies and control systems allow for precise regulation of power, voltage, and frequency. This gives operators exact control over the heating rate and final temperature, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the charge material, the process is extremely fast. A typical melting cycle can be completed in as little as 20-30 minutes, leading to high productivity and reduced energy loss compared to other methods.
Versatile and Compact Design
Many modern induction furnaces are designed to be lightweight and movable, with a small physical footprint. The ability to easily swap out crucible bodies allows a single unit to handle different types of metals and batch sizes, increasing operational flexibility.
Comprehensive Safety Features
These systems are engineered with integrated protection against common electrical faults, including overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuits. They also monitor for physical issues like overheating or insufficient water cooling, ensuring safe operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, electric melting is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The technology chosen depends entirely on the application's scale and material requirements.
Induction vs. Electric Arc Furnaces
Induction furnaces excel at producing high-quality, specialized alloys where purity and chemical precision are paramount. In contrast, Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) are the workhorses of the steel industry, primarily used for melting massive quantities of steel scrap by passing a high-voltage arc between graphite electrodes and the metal. EAFs are built for volume, while induction furnaces are built for precision.
The Role of Vacuum Induction Melting
For the most demanding applications, Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is used. By conducting the melt inside a vacuum chamber, it prevents the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This is essential for producing reactive and high-purity alloys, such as those made from titanium or nickel.
Critical Selection Parameters
When choosing a furnace, key technical specifications must be evaluated. These include the power rating (kW), melting capacity (kg), maximum temperature range, and overall energy efficiency. Aligning these parameters with your production needs is crucial for optimizing performance and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct electric furnace technology is a direct function of your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, reactive alloys: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is the definitive choice to prevent contamination and ensure precise chemical control.
- If your primary focus is rapid, versatile melting of various non-ferrous and ferrous metals: A standard induction furnace offers an excellent balance of speed, efficiency, and cleanliness for most foundry operations.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap: An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the industry standard, engineered specifically for high-volume, continuous melting.
By understanding these fundamental principles, you can select the precise electrical melting technology required to achieve your material quality and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Induction Furnace | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-purity, specialized alloys | Large-scale steel production from scrap |
| Heat Generation | Internal (Eddy currents in the metal) | External (Arc between electrode and metal) |
| Key Advantage | Precision, purity, homogeneity | High volume, cost-effectiveness for scrap |
| Typical Cycle Time | 20-30 minutes | Varies, suited for continuous operation |
Ready to achieve superior metal melting results?
Whether your laboratory or production facility requires the precision of an induction furnace for high-purity alloys or a robust solution for larger-scale operations, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs. We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific metallurgical challenges.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our electric furnace solutions can enhance your efficiency, purity, and control.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















