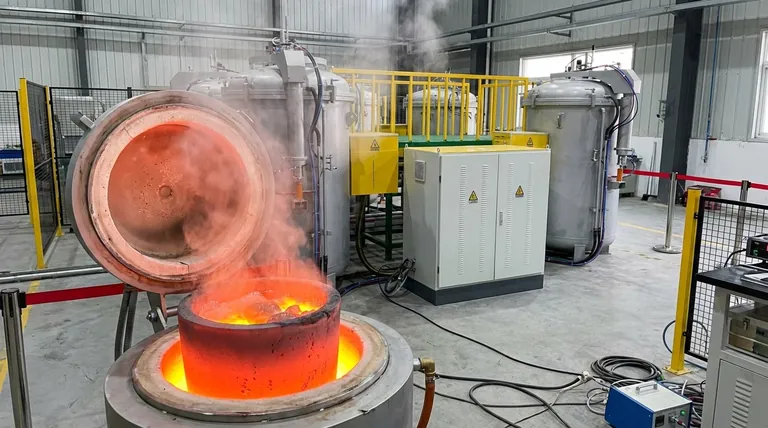
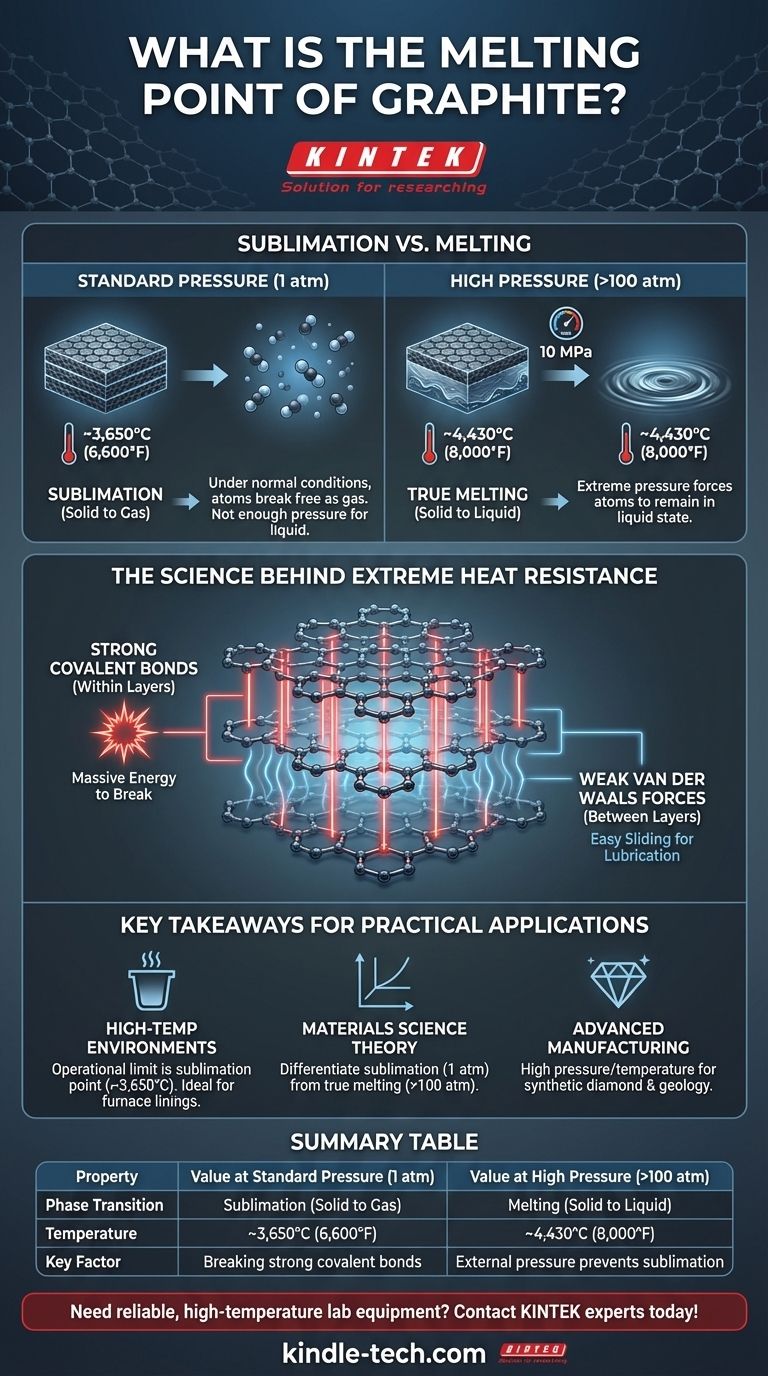
Under normal conditions, graphite does not melt. Instead of turning into a liquid, it sublimes—transforming directly from a solid into a gas—at approximately 3,650°C (6,600°F). True melting only occurs under extreme pressure, which forces the carbon atoms to remain in a liquid state at a much higher temperature.
The immense thermal stability of graphite is not an accident of its composition but a direct consequence of its atomic structure. The exceptionally strong covalent bonds holding carbon atoms together in sheets require a massive amount of energy to break, resulting in one of the highest sublimation points of any element.

The Science Behind Graphite's Extreme Heat Resistance
To understand why graphite is so resistant to heat, we must look at how its carbon atoms are arranged and bonded together.
The Power of Covalent Bonds
Graphite is an allotrope of carbon, meaning it's one of several physical forms the element can take. Its structure consists of flat, two-dimensional planes of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice.
Within each of these planes (a single layer is known as graphene), every carbon atom is linked to three others by extremely strong covalent bonds. These bonds are what give graphite its incredible thermal stability. Breaking them requires a tremendous amount of energy, which translates directly to a very high temperature.
Layers vs. Bonds: A Key Distinction
A common point of confusion is graphite's use as a lubricant. If it's so strong, why is it also slippery?
The answer lies in the difference between the forces within the layers and the forces between them. While the covalent bonds within each graphene sheet are powerful, the bonds holding the separate sheets together are very weak van der Waals forces.
These weak interlayer forces allow the planes to slide past one another easily, creating graphite's lubricating effect. However, melting or sublimating the material requires breaking the strong covalent bonds inside the layers, not the weak ones between them.
Melting vs. Sublimation: A Critical Distinction
The terms "melting point" and "sublimation point" are often used interchangeably for graphite, but they describe different physical phenomena that occur under very different conditions.
Sublimation at Standard Pressure
At standard atmospheric pressure (1 atm), there is not enough force to hold the carbon atoms together in a liquid phase as they gain energy from heat.
Instead of the bonds loosening enough to form a liquid, the atoms gain so much energy that they break free from the solid structure entirely and escape as a gas. This direct solid-to-gas transition is sublimation.
True Melting at High Pressure
To force graphite to melt, you must apply immense pressure. The triple point of carbon—the specific condition where solid, liquid, and gas can coexist—occurs at a pressure of about 10 megapascals (MPa), or roughly 100 times normal atmospheric pressure.
Under these conditions, the external pressure prevents the carbon atoms from flying apart into a gas. Instead, they transition into a liquid state at a temperature of approximately 4,430°C (8,000°F). This is the true melting point of graphite.
Key Takeaways for Practical Applications
Your understanding of graphite's behavior at high temperatures directly informs its use in science and industry.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature environments (e.g., crucibles, furnace linings): Rely on graphite's sublimation point as the operational limit, as melting is not a concern under normal pressures.
- If your primary focus is materials science theory: Differentiate clearly between the sublimation point (at 1 atm) and the true melting point (at >100 atm) to accurately describe the phase diagram of carbon.
- If your primary focus is advanced manufacturing or geology: The high pressure and temperature required for liquid carbon are relevant for understanding processes like synthetic diamond formation and conditions deep within the Earth's mantle.
Ultimately, graphite's resilience is a direct reflection of the powerful covalent bonds that form the fundamental building block of its structure.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value at Standard Pressure (1 atm) | Value at High Pressure (>100 atm) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transition | Sublimation (Solid to Gas) | Melting (Solid to Liquid) |
| Temperature | ~3,650°C (6,600°F) | ~4,430°C (8,000°F) |
| Key Factor | Breaking strong covalent bonds in graphene sheets | External pressure prevents sublimation |
Need reliable, high-temperature lab equipment? Graphite's exceptional thermal stability makes it ideal for furnace linings, crucibles, and high-heat applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in premium lab equipment and consumables, providing the durable tools your laboratory needs to operate safely and efficiently at extreme temperatures. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere



















