The most common inert gas in the Earth's atmosphere is Argon (Ar). It makes up approximately 0.93% of the air we breathe, making it the third most abundant gas overall, after nitrogen and oxygen.
While Argon is the definitive answer, the deeper understanding lies in distinguishing between the chemical definition of a "noble gas" and the practical application of an "inert gas" in science and industry.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
The term "inert" refers to a substance that is chemically inactive. In the context of gases, this property is most famously associated with a specific group of elements on the periodic table.
The Noble Gas Family
The inert gases are also known as noble gases. This group includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
Their defining characteristic is a full outer shell of electrons. This stable configuration makes them extremely reluctant to share, gain, or lose electrons.
Extreme Chemical Stability
Because they do not readily form chemical bonds with other elements, noble gases are highly non-reactive. They exist as individual atoms, not as molecules like oxygen (O₂) or nitrogen (N₂).
Why This Property Matters
This non-reactivity is incredibly useful. Inert gases are used to create a stable environment for processes like welding, to prevent filaments from burning out in incandescent light bulbs, and to preserve sensitive materials.
A Closer Look at Earth's Atmosphere
To understand Argon's place, it's crucial to see the complete picture of our atmosphere's composition.
The Two Dominant Gases
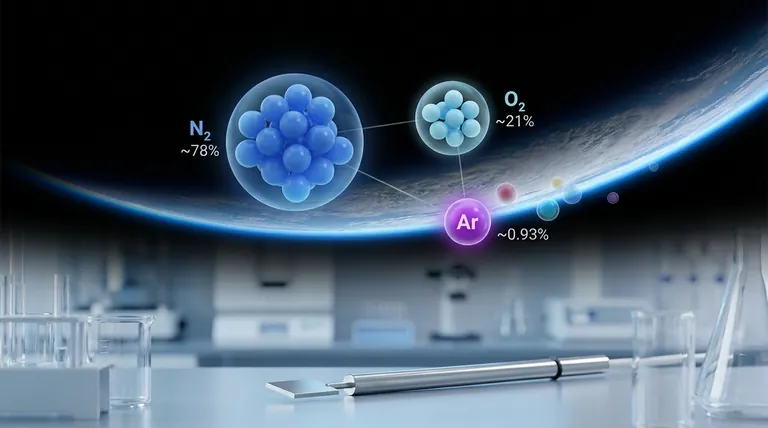
The air is overwhelmingly composed of two gases: Nitrogen (N₂) at approximately 78% and Oxygen (O₂) at approximately 21%. These two elements make up 99% of the air.
Argon's Position
The remaining 1% is where we find Argon. At about 0.93%, it is by far the most significant noble gas present.
Traces of Other Noble Gases
The other noble gases exist in far smaller amounts. For context, Neon is present at about 0.0018%, while Helium, Krypton, and Xenon are found in even smaller trace amounts.
Understanding the Nuances
The terms "inert" and "noble gas" are often used interchangeably, but there are important distinctions to understand.
Is "Inert" Truly Inert?
While noble gases are highly stable, they are not completely inert under all conditions. Scientists have forced noble gases like Xenon and Krypton to form chemical compounds in a laboratory setting under extreme pressure and temperature.
Nitrogen: The "Almost" Inert Gas
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is not a noble gas. However, the strong triple bond holding its two atoms together makes it very stable and non-reactive under many conditions.
Because it is far more abundant and cheaper than Argon, Nitrogen is frequently used as an "inert" gas for industrial applications like food packaging and electronics manufacturing, where extreme non-reactivity isn't required.
Putting It All in Perspective
Choosing or identifying an inert gas depends entirely on the context of your question—are you focused on chemical purity or practical application?
- If your primary focus is chemistry: Argon is the most abundant noble gas, defined by its atomic structure and full electron shell.
- If your primary focus is atmospheric composition: Argon is the third most common gas in the air, but it's a distant third behind Nitrogen and Oxygen.
- If your primary focus is industrial use: The choice between Argon and Nitrogen often comes down to the required level of non-reactivity versus cost, with Nitrogen being a common substitute.
Understanding the distinction between a gas's elemental nature and its practical behavior is key to mastering the topic.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Type | Abundance in Atmosphere | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Noble Gas (Inert) | ~0.93% | Most common inert gas; full electron shell |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Diatomic Gas | ~78% | Often used as a practical, cost-effective inert gas |
| Helium (He) | Noble Gas (Inert) | Trace | Very low abundance but highly inert |
| Neon (Ne) | Noble Gas (Inert) | ~0.0018% | Low abundance; used in lighting |
Need a Reliable Inert Gas Supply for Your Lab?
Understanding the properties of gases like Argon is crucial for precise laboratory work. Whether you require ultra-pure inert gases for sensitive experiments or reliable gas delivery systems, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your research. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to ensure your processes are efficient and contamination-free.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your specific laboratory gas needs!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the available specifications for platinum sheet electrodes? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Electrochemical Needs
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be pretreated before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the expected lifespan of a platinum sheet electrode? Maximize Your Electrode's Service Life
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum sheet electrodes? Unlock Superior Electrochemical Performance







