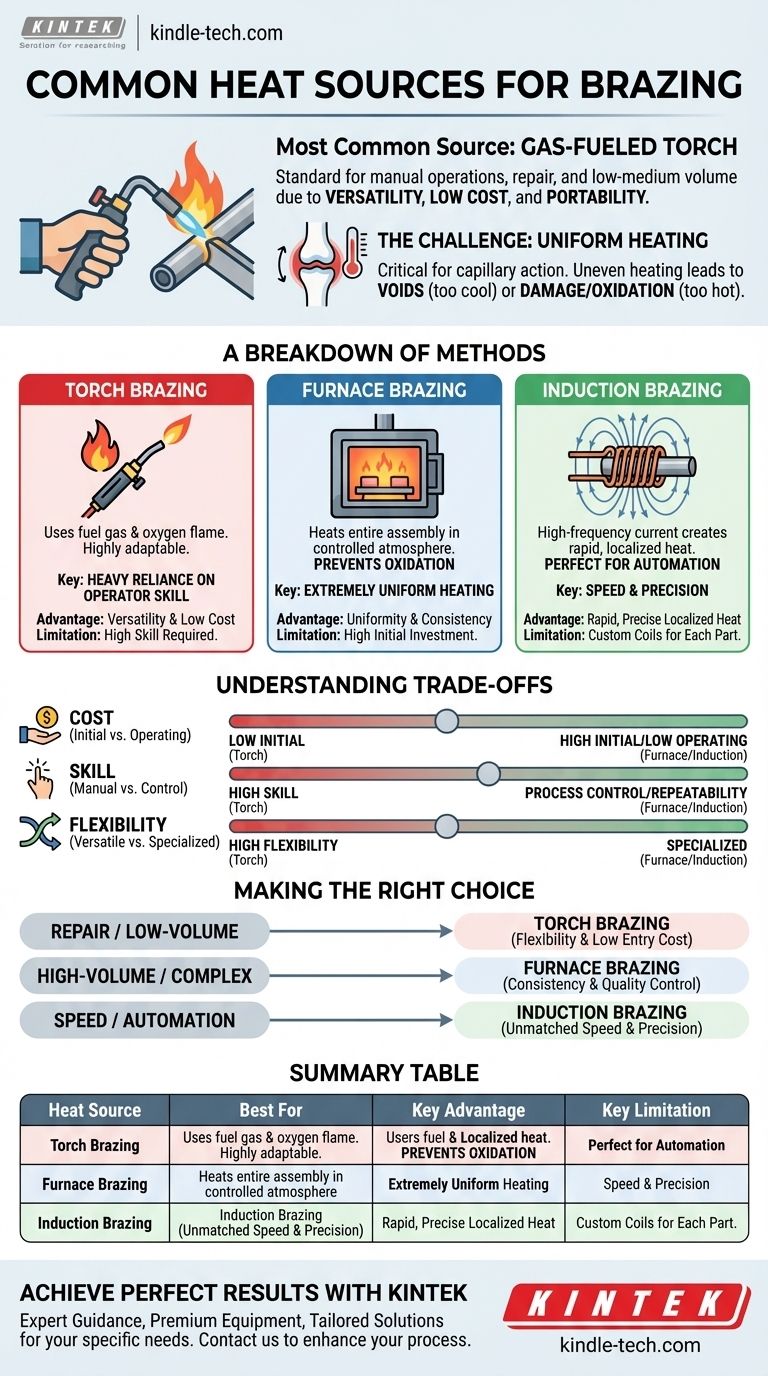
By far the most common source of heat for brazing is a gas-fueled torch. Its versatility, relatively low equipment cost, and portability make it the standard for manual operations, repair work, and low-to-medium volume production across countless industries.
The central challenge in brazing is not merely reaching a target temperature, but applying heat uniformly and controllably. While a torch is the most widespread tool, the ideal heating method is ultimately dictated by your production volume, joint complexity, and required precision.

Why the Heat Source is Critical
The success of a brazed joint depends entirely on the filler metal flowing evenly throughout the joint via capillary action. This can only happen if the entire joint area on the base metals is heated uniformly to the correct brazing temperature.
The Role of Uniform Heating
If one part of the joint is too cool, the filler metal will not flow into that area, creating voids and a weak bond. If another area is overheated, it can damage the base metals or burn away the flux, leading to oxidation and a failed joint.
Matching the Method to the Application
The choice of heat source directly impacts the quality of the joint, the speed of the operation, the level of operator skill required, and the overall cost. Selecting the wrong method leads to inefficiency and inconsistent results.
A Breakdown of Brazing Heat Sources
While torch brazing is most common, several other methods are used for specific industrial applications, each with distinct advantages.
Torch Brazing: The Versatile Standard
This method uses a flame from the combustion of a fuel gas (like acetylene, propane, or natural gas) with oxygen or air. It is highly adaptable and can be used on parts of almost any size or configuration.
The primary drawback of manual torch brazing is its heavy reliance on operator skill. The quality of the joint is directly determined by the operator's ability to apply heat evenly and recognize the visual cues of proper temperature.
Furnace Brazing: For High-Volume Precision
In furnace brazing, the entire assembly (with filler metal pre-placed) is heated in a furnace with a controlled atmosphere. This atmosphere is typically inert or reducing, which prevents oxidation and often eliminates the need for flux.
This method ensures extremely uniform heating, making it ideal for complex assemblies and high-volume production runs. Every part in a batch receives the exact same thermal cycle, resulting in exceptional consistency.
Induction Brazing: Speed and Automation
Induction heating uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates an electromagnetic field that induces current within the metal part, generating precise, localized heat very rapidly.
Because it is so fast and controllable, induction brazing is perfectly suited for automation and integration into production lines. The main considerations are the initial equipment cost and the need to design custom coils for each specific joint geometry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat source involves balancing four key factors: cost, volume, precision, and the required skill level.
Initial Investment vs. Operating Cost
Torch systems have a very low initial cost, making them accessible to virtually any shop. Furnace and induction systems require a significant capital investment but can offer a lower cost-per-part in high-volume scenarios.
Operator Skill vs. Process Control
Manual torch brazing demands a highly skilled operator to achieve consistent results. In contrast, furnace and induction brazing remove most of the human variable, embedding the "skill" into the machine's programming for unparalleled repeatability.
Flexibility vs. Specialization
A torch can be used on an infinite variety of parts with minimal setup. Induction coils are custom-designed for a specific part, and furnaces are best suited for batch processing parts of a similar size, making them less flexible for one-off jobs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of heating method should be a direct reflection of your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is repair, prototyping, or low-volume work: Torch brazing offers the best combination of flexibility and low entry cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with complex joints: Furnace brazing provides the highest level of consistency and quality control.
- If your primary focus is speed and automation in a mass-production line: Induction brazing delivers unmatched speed and precise, repeatable heating.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heat source is the first step toward creating a strong, reliable, and cost-effective brazed joint.
Summary Table:
| Heat Source | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Repair, Low-Volume, Prototyping | Versatility & Low Cost | High Operator Skill Required |
| Furnace Brazing | High-Volume, Complex Assemblies | Uniform Heating & Consistency | High Initial Investment |
| Induction Brazing | Automated, High-Speed Production | Rapid, Precise Localized Heat | Custom Coils for Each Part |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Results with KINTEK
Struggling to choose the right brazing method for your laboratory or production needs? The quality of your brazed joints depends heavily on precise, uniform heating. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific brazing requirements.
Why choose KINTEK for your brazing solutions?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists help you select the perfect heating method—whether you need the flexibility of torch systems, the consistency of furnace brazing, or the speed of induction heating.
- Premium Equipment: We supply reliable, high-performance brazing systems designed for durability and precision.
- Tailored Solutions: From small-scale R&D to high-volume production, we provide equipment that matches your volume, complexity, and precision needs.
Ready to enhance your brazing process? Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's solutions can deliver stronger, more reliable joints for your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.



















