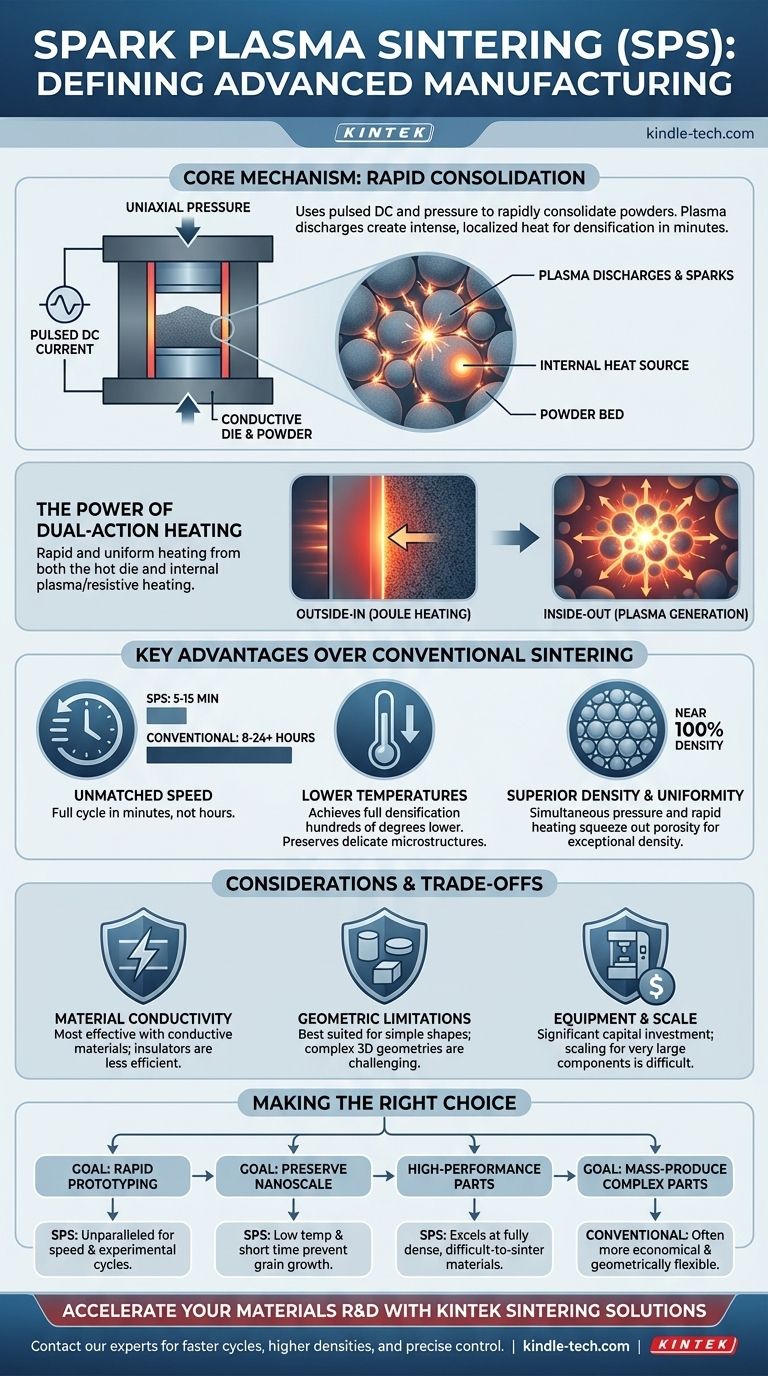
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced manufacturing technique that uses pulsed direct current and uniaxial pressure to rapidly consolidate powders into a dense, solid mass. Unlike traditional sintering that relies on slow, external heating in a furnace over many hours, SPS passes electricity directly through the powder and its tooling, creating intense, localized heat that dramatically accelerates the process.
The critical distinction of plasma sintering is its heating mechanism. It generates plasma discharges in the microscopic gaps between powder particles, creating a highly efficient, internal heat source that allows for full densification in minutes rather than hours, often at significantly lower overall temperatures.

How Plasma Sintering Redefines the Process
Traditional sintering is a slow, methodical process of baking powders until they fuse. Plasma sintering, also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), fundamentally changes the energy delivery system for a faster and more controlled outcome.
The Core Mechanism: Current, Pressure, and Plasma
The process begins by loading a material powder into a conductive die, typically made of graphite. This assembly is placed between two electrodes inside a vacuum chamber.
A high-power pulsed direct current (DC) is then applied through the electrodes. Simultaneously, a mechanical system applies high uniaxial pressure to the powder.
The electric current passing through the powder generates sparks across the voids between individual particles. This energy creates tiny, localized pockets of high-temperature plasma, the fourth state of matter.
The Power of Dual-Action Heating
This plasma discharge, combined with the electrical resistance of the powder and die (Joule heating), creates an incredibly rapid and uniform heating effect.
The material is heated from the outside-in by the hot die, and from the inside-out by the internal plasma generation and resistive heating. This dual action is the key to its speed and efficiency.
A Controlled Environment
The entire process is conducted within a vacuum or a controlled, inert atmosphere. This prevents oxidation and ensures the chemical purity of the final material, which is critical when working with reactive or advanced materials.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Sintering
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several significant advantages over the methods that have been used for decades in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
Unmatched Speed
The most dramatic advantage is speed. The rapid heating rates—often hundreds of degrees Celsius per minute—allow a full sintering cycle to be completed in as little as 5 to 15 minutes. This is a stark contrast to conventional furnace sintering, which can take 8 to 24 hours.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
By delivering energy so efficiently at the particle surfaces, SPS can achieve full densification at temperatures hundreds of degrees lower than conventional methods. This is crucial for preserving delicate microstructures, such as nanoscale grains, which would otherwise be destroyed by prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Superior Density and Uniformity
The combination of simultaneous pressure and rapid, uniform heating effectively squeezes out porosity between particles. This results in final products that are exceptionally dense, often approaching 100% of the material's theoretical density, with a highly homogenous microstructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Its unique operating principles introduce specific limitations that must be considered for any potential application.
Material Conductivity
The "spark" mechanism is most effective in materials that possess at least some electrical conductivity. While insulating ceramics can be sintered, the heating is primarily driven by the conductive die. This is less efficient and reduces some of the core speed and temperature advantages of the process.
Geometric Limitations
The use of a rigid die and pressure applied along a single axis (uniaxial) means that SPS is best suited for producing simple shapes. Cylinders, discs, and rectangular blocks are common, but highly complex, three-dimensional geometries are challenging to produce directly.
Equipment and Scale
SPS systems are highly specialized and represent a significant capital investment compared to traditional furnaces. Furthermore, while excellent for lab-scale research and small-part production, scaling the technology for very large components presents significant technical and economic challenges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on the priorities of your project, balancing material properties, speed, cost, and geometry.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or materials discovery: SPS is an unparalleled tool, enabling dozens of experimental cycles in the time a conventional furnace completes one.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanoscale or fine-grained structures: The low temperatures and short processing times of SPS are essential to prevent grain growth and maintain desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is producing simple, high-performance parts from advanced materials: SPS excels at creating fully dense components from difficult-to-sinter ceramics, alloys, and composites.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex, low-cost metal parts: Traditional powder metallurgy methods like press-and-sinter or metal injection molding are often more economical and geometrically flexible.
Ultimately, plasma sintering provides a powerful capability for materials processing where speed, final density, and microstructural control are the most critical drivers of success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Time | Minutes (5-15 min) | Hours (8-24+ hours) |
| Sintering Temperature | Lower (by 100s of °C) | Higher |
| Final Density | Very High (near 100%) | Lower |
| Microstructural Control | Excellent (preserves nanoscale grains) | Limited (grain growth likely) |
Ready to accelerate your materials R&D with superior sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions for demanding research and production. Our expertise helps you achieve faster cycles, higher densities, and precise microstructural control for ceramics, alloys, and composites.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our sintering technology can enhance your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



















