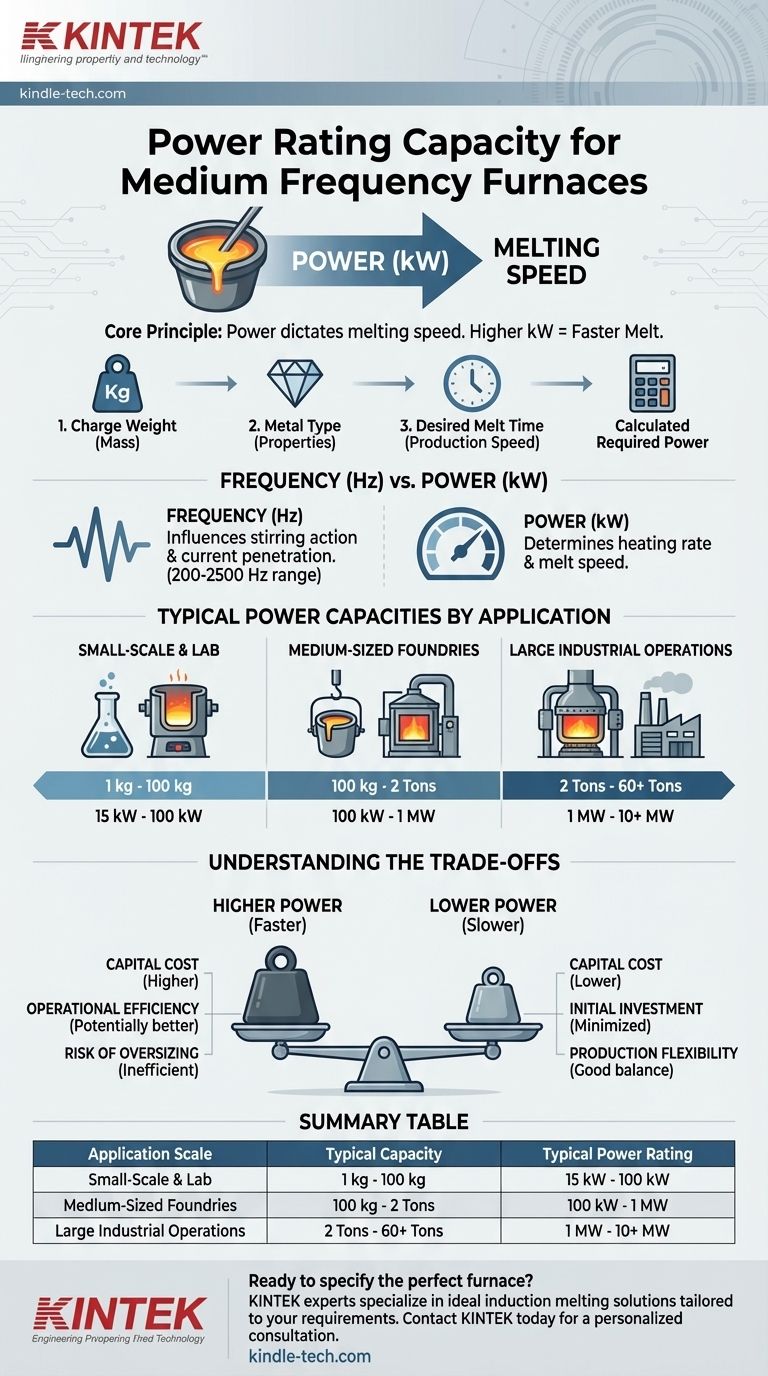
For a medium frequency induction furnace, there is no single power rating. The capacity ranges dramatically from small laboratory units rated at approximately 15 kilowatts (kW) to massive industrial systems exceeding 10 megawatts (MW). The correct power rating is not a fixed attribute but is determined entirely by the furnace's intended application, specifically the mass of metal you need to melt and how quickly you need to melt it.
The core principle is this: power (kW) dictates the melting speed. A higher power rating means more energy is delivered to the metal per unit of time, resulting in a faster melt. Selecting the right capacity is a critical engineering decision that balances production throughput against capital and operational costs.

How Power Rating Dictates Furnace Performance
The power capacity of the furnace's supply is the single most important factor determining its productivity. Understanding this relationship is key to specifying a system that meets your operational goals.
The Direct Link: Power and Melt Rate
Think of the power rating (kW) as the rate of energy flow into your furnace. Just as a high-wattage kettle boils water faster, a high-kilowatt furnace melts metal faster.
This relationship is directly proportional. Doubling the power applied to a given mass of metal will roughly halve the time it takes to reach melting temperature.
Calculating Required Power
The power needed is not an arbitrary number. It is calculated based on three primary factors:
- Charge Weight: The mass of the metal to be melted.
- Metal Type: Different metals have different specific heat capacities and latent heat of fusion, meaning they require different amounts of energy to melt.
- Desired Melt Time: The production speed you need to achieve.
A furnace supplier will use these variables, along with an efficiency factor, to calculate the minimum power required to meet your production targets.
The Role of Frequency vs. Power
It is critical to distinguish between frequency (Hz) and power (kW). The provided frequency range of 200-2500 Hz for medium frequency furnaces relates to the characteristics of the heating itself.
- Frequency (Hz) influences the stirring action in the molten metal and the depth of current penetration. Higher frequencies are better for smaller furnaces, while lower frequencies induce more vigorous stirring, which is useful in larger melts.
- Power (kW) determines the rate of heating. It dictates how much energy is put into the charge per minute, and therefore, how fast it melts.
Typical Power Capacities by Application
Power ratings correspond directly to the scale of the operation.
Small-Scale & Laboratory Furnaces
These are used for R&D, precious metal casting, or small art foundries.
- Capacity: 1 kg to 100 kg
- Typical Power: 15 kW to 100 kW
Medium-Sized Foundries
This is the most common range, used for producing parts, ingots, and various castings.
- Capacity: 100 kg to 2 Tons
- Typical Power: 100 kW to 1,000 kW (1 MW)
Large Industrial Operations
These systems are used in large foundries and steel plants for high-volume production.
- Capacity: 2 Tons to over 60 Tons
- Typical Power: 1 MW to 10+ MW
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a power rating involves balancing competing priorities. A higher power rating is not always the better choice.
Higher Power vs. Capital Cost
The most direct trade-off is cost. A higher-kilowatt power supply is significantly more expensive. This increased capital expenditure may also require costly upgrades to your facility's electrical service and infrastructure.
Operational Costs and Efficiency
While a high-power furnace consumes more electricity while running, it can be more energy-efficient on a per-ton basis. By melting the charge faster, it reduces the total time the furnace shell loses heat to the environment, potentially lowering the total kilowatt-hours needed per melt.
The Risk of Oversizing
Specifying a furnace with excessive power for your typical charge size is inefficient. It's like using a sledgehammer to crack a nut. The system will run for very short periods at full power, leading to poor energy efficiency and potentially excessive stirring of the metal bath, which can increase gas pickup and oxidation.
How to Specify the Right Power Capacity
To make the right choice, you must first define your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid production and high throughput: Opt for a higher power rating to maximize your melt rate, but be prepared for the corresponding increase in capital and infrastructure costs.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for varied batch sizes: A moderately powered system offers the best balance, providing good performance without the high costs or inefficiencies of an oversized unit when handling smaller melts.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment: Specify the lowest power rating that can meet your minimum acceptable melt time, understanding this will inherently limit your maximum production capacity.
Ultimately, selecting the correct power rating is about aligning your operational goals with your financial and infrastructural realities.
Summary Table:
| Application Scale | Typical Capacity | Typical Power Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale & Laboratory | 1 kg - 100 kg | 15 kW - 100 kW |
| Medium-Sized Foundries | 100 kg - 2 Tons | 100 kW - 1 MW |
| Large Industrial Operations | 2 Tons - 60+ Tons | 1 MW - 10+ MW |
Ready to specify the perfect medium frequency furnace for your lab or foundry?
Selecting the right power rating is critical for balancing production throughput, energy efficiency, and cost. The experts at KINTEK specialize in matching laboratory and industrial clients with the ideal induction melting solutions. We provide equipment and consumables tailored to your specific metal type, charge weight, and melt time requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation to ensure your furnace investment delivers optimal performance and value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















