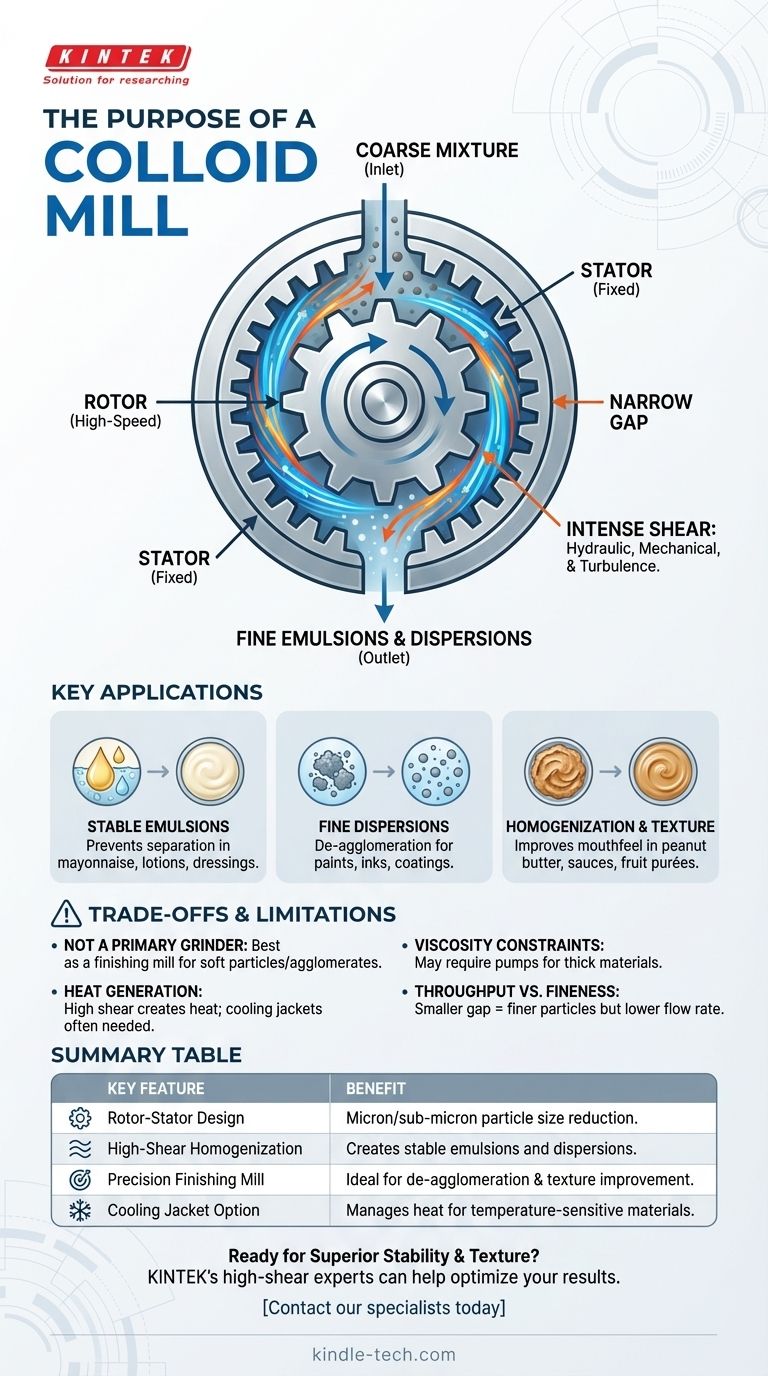
At its core, a colloid mill is a high-shear rotor-stator machine used for particle size reduction and homogenization. Its primary purpose is to create stable emulsions (liquid-in-liquid mixtures) or dispersions (solid-in-liquid mixtures) by subjecting materials to intense mechanical and hydraulic forces. This process breaks down droplets or solid agglomerates into a very fine, uniform size, typically in the micron or sub-micron range.
A colloid mill is not a simple mixer. It is a precision tool for engineering the microstructure of a fluid, transforming coarse, unstable mixtures into smooth, homogeneous, and stable final products.

How a Colloid Mill Achieves Intense Shear
The effectiveness of a colloid mill comes from its unique mechanical design, which generates forces far greater than those found in conventional agitators or mixers.
The Rotor-Stator Principle
The heart of the mill consists of two components: a high-speed rotating element called the rotor and a fixed element called the stator. The rotor spins at several thousand RPM within the stationary stator.
Hydraulic Shear and Mechanical Action
Material is fed into the center of the rotor-stator assembly and accelerated outwards by centrifugal force. It is then forced through a very narrow, precisely machined gap between the rotor and stator surfaces.
As the material passes through this gap, it is subjected to a combination of extreme forces:
- High Hydraulic Shear: The steep velocity gradient in the tiny gap tears apart droplets and particles.
- Intense Mechanical Action: Toothed or slotted rotor-stator designs create a milling and cutting effect on the material.
- High-Frequency Turbulence: Rapid pressure and energy fluctuations further contribute to the breakdown of particles.
The Result: Fine Emulsions and Dispersions
This intense energy input overcomes the surface tension holding liquid droplets together and the binding forces holding solid particles in agglomerates. The result is a dramatic reduction in particle or droplet size, leading to a smooth, uniform, and often more stable product.
Key Applications: When to Use a Colloid Mill
A colloid mill is the tool of choice when the goal is to create a truly homogeneous product with a specific texture and long-term stability.
Creating Stable Emulsions
For immiscible liquids like oil and water, simple mixing results in a temporary mixture that quickly separates. A colloid mill reduces the droplet size of the dispersed phase so drastically that the emulsion becomes stable, preventing separation over time. This is critical for products like mayonnaise, salad dressings, creams, and lotions.
Producing Fine Dispersions
When incorporating solid powders into a liquid base, particles often clump together in agglomerates. A colloid mill excels at de-agglomeration, breaking these clumps apart and dispersing the individual particles evenly throughout the liquid. This is essential for manufacturing paints, inks, pharmaceutical suspensions, and pigmented coatings.
Homogenization and Texture Improvement
In the food industry, colloid mills are used to improve the texture, mouthfeel, and consistency of products. Applications include producing smooth peanut butter, processing fruit purées, and creating uniform sauces and gravies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a colloid mill is a specialized tool with specific operating boundaries. Understanding these is key to its successful implementation.
Not a Primary Grinder
A colloid mill is best described as a finishing mill. It is designed to reduce the size of soft particles or to break apart agglomerates. It is not suitable for the primary grinding of hard, abrasive solids from a large initial size.
Significant Heat Generation
The high-shear action generates considerable heat. For heat-sensitive materials, such as many pharmaceuticals and food products, this can be a significant issue. Most industrial colloid mills can be equipped with a cooling jacket to manage the process temperature.
Viscosity Constraints
The mill's performance is dependent on its ability to move material through the rotor-stator gap. While they can handle a range of viscosities, extremely thick, paste-like materials may require a positive displacement pump to ensure consistent flow into the milling chamber.
Throughput vs. Fineness
There is a direct trade-off between the degree of processing and the flow rate. A smaller rotor-stator gap produces a finer particle size but restricts the flow, reducing throughput. Conversely, a larger gap increases throughput but results in a coarser final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right processing equipment depends entirely on your end goal. A colloid mill is a superior choice for specific applications but is overkill for others.
- If your primary focus is creating stable, fine emulsions (lotions, sauces, dressings): A colloid mill is an excellent and often necessary tool to achieve the required droplet size for long-term stability.
- If your primary focus is producing smooth, clump-free dispersions (paints, inks): The de-agglomeration power of a colloid mill is ideal for ensuring a uniform and high-quality final product.
- If your primary focus is basic blending or dissolving soluble solids: A simpler and more cost-effective high-speed disperser or standard agitator is likely sufficient for your needs.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute smallest particle size possible (nanometer range): You may need to consider a high-pressure homogenizer, though it comes at a significantly higher capital and operational cost.
Ultimately, the purpose of a colloid mill is to impart a high level of controlled energy to a fluid system to achieve a specific microstructure and desired product quality.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotor-Stator Design | Generates intense shear for micron/sub-micron particle size reduction. |
| High-Shear Homogenization | Creates stable emulsions (e.g., sauces, lotions) and dispersions (e.g., paints, inks). |
| Precision Finishing Mill | Ideal for de-agglomeration and texture improvement in food and pharmaceuticals. |
| Cooling Jacket Option | Manages heat generation for temperature-sensitive materials. |
Ready to achieve superior product stability and texture?
A colloid mill is the precision tool you need to transform coarse mixtures into smooth, homogeneous, and stable final products. Whether you are developing pharmaceuticals, food products, coatings, or chemicals, KINTEK's expertise in high-shear processing equipment can help you optimize your results.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our lab equipment specialists today to find the perfect colloid mill solution for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What size mesh is a ball mill? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Your Materials
- Why is a circulating water cooling system necessary for a ball mill when processing CuCr50? Enhance Powder Purity
- What kind of balls are used in ball mills? Optimize Your Grinding with the Right Media
- Why use zirconia grinding media of varying diameters for LATP? Optimize Efficiency and Purity in Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the chemical composition of grinding media balls? Achieve Optimal Wear Resistance and Toughness
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- What is the role of a 3D powder mixer in the preparation of metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Perfect Homogeneity
- How much power does a hammer mill use? From 5HP to 600HP, Key Factors Explained



















