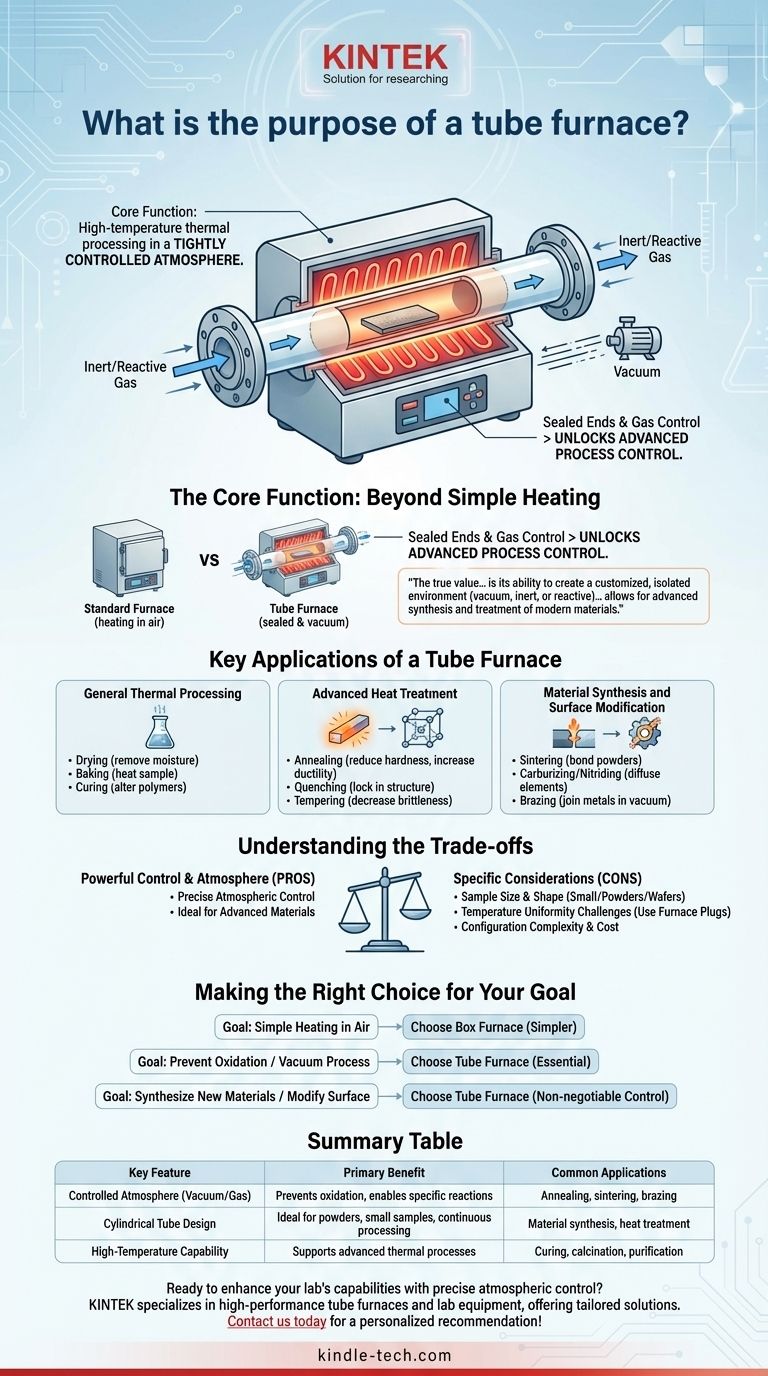
At its core, a tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for high-temperature thermal processing of materials within a tightly controlled atmosphere. Its primary purpose is to heat samples in a cylindrical chamber, which can be sealed to create a vacuum or filled with a specific gas, enabling processes that are impossible in ambient air.
The true value of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to create a customized, isolated environment. This control over the atmosphere—whether vacuum, inert, or reactive—is what allows for the advanced synthesis and treatment of modern materials.
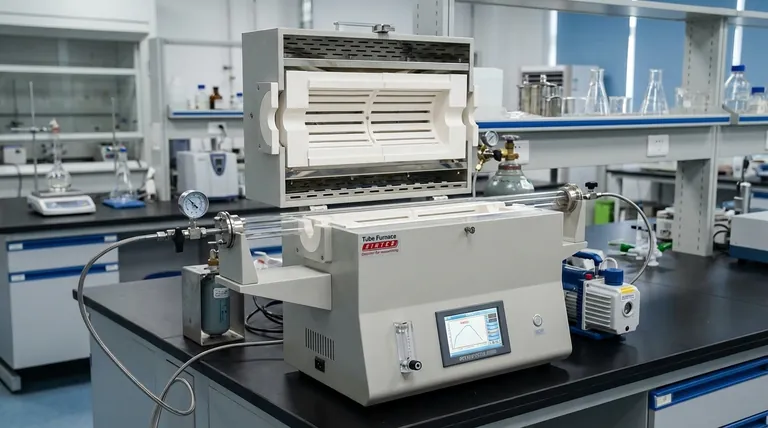

The Core Function: Beyond Simple Heating
A standard oven or box furnace heats a sample in air. A tube furnace fundamentally changes this by containing the sample within a tube, unlocking a new level of process control.
The Anatomy of Control
The design is simple but powerful. Heating elements surround a cylindrical tube, which is typically made of alumina, quartz, or another ceramic. This tube passes through the heated chamber.
This setup allows an operator to seal the ends of the tube. From there, one can pull a vacuum or flow a precise gas or mixture of gases over the sample as it's being heated.
Why Atmosphere Matters
Controlling the atmosphere is critical for preventing unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, or for intentionally introducing specific reactions. This capability is the gateway to advanced materials processing.
Key Applications of a Tube Furnace
The ability to control both temperature and atmosphere makes the tube furnace an indispensable tool for a wide range of scientific and industrial processes.
General Thermal Processing
In its simplest use, a tube furnace can perform standard heating tasks such as drying to remove moisture, baking to heat a sample, or curing to physically or chemically alter a material like a polymer.
Advanced Heat Treatment
Many applications focus on modifying the properties of a material.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material (like a metal or semiconductor) to reduce its hardness and increase its ductility.
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling a material from high temperature to lock in specific structural properties.
- Tempering: Heating a previously quenched material to a lower temperature to decrease brittleness.
Material Synthesis and Surface Modification
This is where the tube furnace truly excels. By introducing reactive gases, scientists can create new materials or alter surfaces.
- Sintering: Heating compressed powders below their melting point until their particles bond together, forming a solid piece. This is common in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
- Carburizing/Nitriding: Introducing carbon or nitrogen-rich gases at high temperatures to diffuse those elements into the surface of a metal, dramatically increasing its surface hardness.
- Brazing: Joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal that melts and flows between them. Performing this in a vacuum or inert gas prevents oxidation and creates a stronger, cleaner joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is not the right tool for every job. Its specialized nature comes with specific considerations.
Sample Size and Shape
The primary limitation is the diameter of the tube. Tube furnaces are ideal for processing small samples, powders, wafers, or batches of small components. They are not suitable for large, bulky items, for which a box or chamber furnace would be more appropriate.
Temperature Uniformity
Achieving a perfectly uniform temperature across the entire length of the tube can be a challenge. The ends of the furnace are naturally cooler. To counteract this, technicians often use ceramic furnace plugs to insulate the ends of the process tube, creating a more stable and balanced hot zone in the center.
Configuration Complexity
Compared to a simple box furnace, a tube furnace system is more complex. It requires gas lines, vacuum pumps, flow controllers, and sealed flanges. This adds cost and requires more operator expertise to run safely and effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is simple heating of samples in air: A less expensive and simpler box furnace is likely the more practical choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or processing in a vacuum: A tube furnace is essential for creating the necessary inert or vacuum environment.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing new materials or modifying a material's surface chemistry: The precise atmospheric control offered by a tube furnace is non-negotiable.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the instrument of choice when the environment surrounding your sample is just as important as the temperature you heat it to.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere (Vacuum/Gas) | Prevents oxidation, enables specific chemical reactions | Annealing, sintering, brazing |
| Cylindrical Tube Design | Ideal for powders, small samples, and continuous processing | Material synthesis, heat treatment |
| High-Temperature Capability | Supports advanced thermal processes | Curing, calcination, purification |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise atmospheric control? KINTEK specializes in high-performance tube furnaces and lab equipment, offering tailored solutions for your thermal processing, sintering, and material synthesis needs. Our experts will help you select the ideal system to achieve superior results in vacuum or specific gas environments. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















