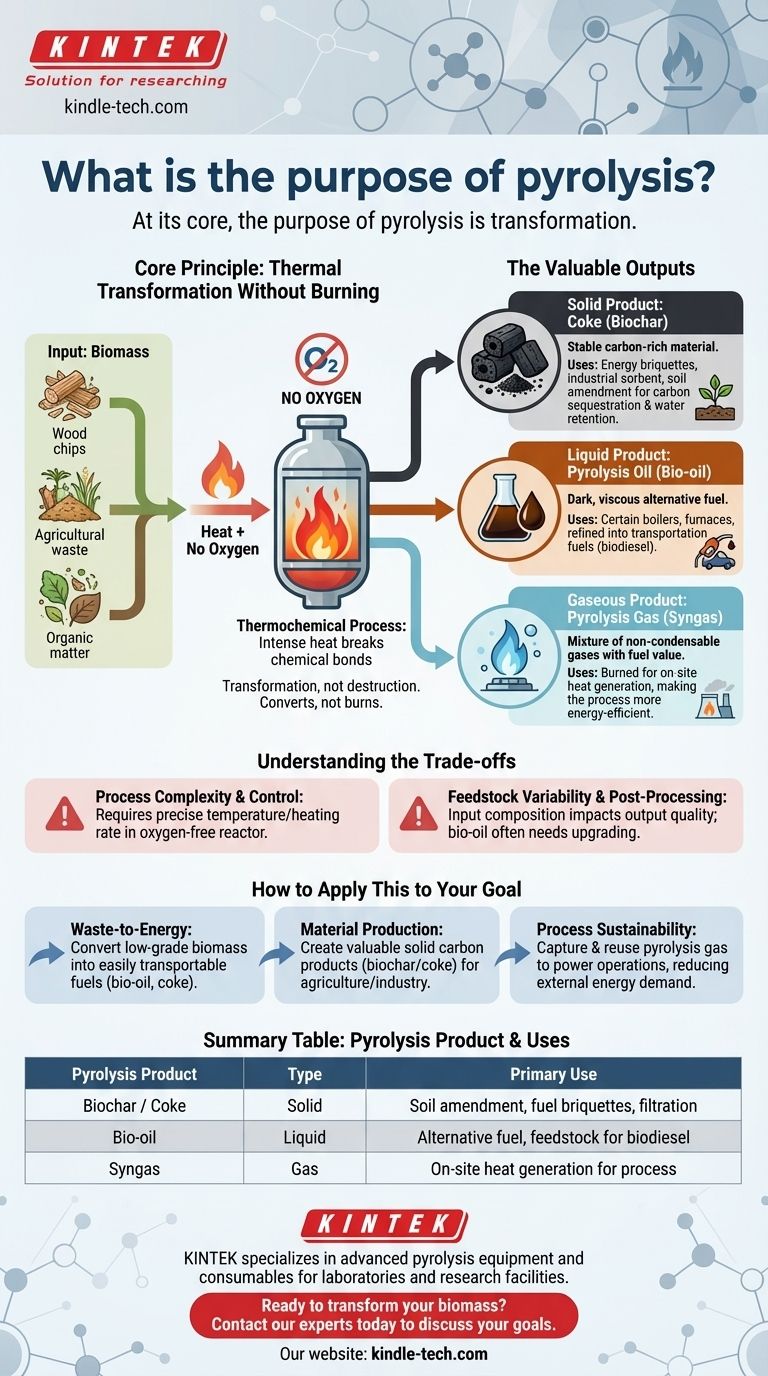
At its core, the purpose of pyrolysis is transformation. It is a thermochemical process that uses high heat in a completely oxygen-free environment to decompose organic material, like biomass, into more stable and useful products. Instead of burning the material, which would release its energy and carbon into the atmosphere, pyrolysis breaks it down to preserve its carbon in concentrated solid, liquid, and gaseous forms.
The fundamental goal of pyrolysis is not destruction but conversion. It strategically deconstructs low-value organic matter to create a portfolio of higher-value, energy-dense products by removing water and oxygen while concentrating the carbon.

The Core Principle: Thermal Transformation Without Burning
How It Works: Heat Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from combustion (burning). Combustion requires oxygen to react with a fuel source, releasing heat and light.
By completely removing oxygen from the equation, pyrolysis prevents burning. Instead, the intense heat breaks the complex chemical bonds within the biomass, causing it to decompose into simpler, more stable substances.
The Input: From Biomass to Value
The process is typically applied to biomass—organic materials like wood, agricultural waste, or manure. These raw materials are often bulky, wet, and have relatively low energy density.
Pyrolysis effectively refines this raw feedstock, solving the problem of its unwieldy nature and unlocking its chemical potential.
The Goal: Carbon Concentration
The primary objective is to remove the water and oxygen atoms bound to the carbon in the original biomass.
This act of removing less valuable components concentrates the carbon into the final products, making them significantly more stable and energy-dense than the original material.
The Valuable Outputs of Pyrolysis
The transformation yields three distinct product streams, each with its own applications. The specific yield of each product can be controlled by adjusting the pyrolysis temperature, pressure, and speed.
Solid Product: Coke (Biochar)
This solid, carbon-rich product is known as coke or, when derived from biomass, biochar.
It is a stable material used for creating energy briquettes, as an industrial sorbent for filtration, or as a valuable soil amendment in agriculture to improve water retention and carbon sequestration.
Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil)
The condensable vapors from the process are collected to form a dark, viscous liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
This liquid can serve as an alternative fuel for certain boilers and furnaces or be further refined to produce transportation fuels like biodiesel.
Gaseous Product: Pyrolysis Gas (Syngas)
The process also produces non-condensable gases, a mixture often called pyrolysis gas or syngas.
This gas has fuel value and is frequently redirected back into the pyrolysis plant. It is burned to generate the heat required for the process, making the system more energy-efficient and potentially self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is a sophisticated process with inherent complexities that must be managed for successful operation.
Process Complexity and Control
Achieving the desired product yields requires precise control over temperature and the heating rate within an oxygen-free reactor. This necessitates specialized equipment and significant operational expertise compared to simple combustion.
Feedstock Variability
The chemical makeup of the input biomass directly impacts the quality and proportion of the final products. Inconsistent or contaminated feedstock can lead to unpredictable outputs and operational challenges.
Post-Processing Requirements
The products of pyrolysis, particularly bio-oil, are not always "drop-in" replacements for their conventional counterparts. Bio-oil is often acidic and unstable, typically requiring further upgrading and refinement before it can be widely used as a transportation fuel.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the distinct outputs of pyrolysis allows you to align the technology with a specific strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Pyrolysis is an effective method for converting low-grade biomass into more easily transportable and energy-dense fuels like bio-oil and coke.
- If your primary focus is material production: The process is a direct route to creating valuable solid carbon products (biochar/coke) for use in agriculture, filtration, or advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is process sustainability: The ability to capture and reuse the pyrolysis gas to power the operation significantly reduces external energy demand and improves the overall carbon footprint.
Ultimately, pyrolysis serves as a powerful tool for transforming low-value carbon sources into a portfolio of valuable, refined products.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Type | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar / Coke | Solid | Soil amendment, fuel briquettes, filtration |
| Bio-oil | Liquid | Alternative fuel, feedstock for biodiesel |
| Syngas | Gas | On-site heat generation for the pyrolysis process |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment and consumables for laboratories and research facilities. Our solutions help you efficiently convert biomass into stable, high-value products like biochar and bio-oil, enabling your waste-to-energy or material production projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis technology can support your specific laboratory and research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is spray pyrolysis method? A Guide to Precision Thin Film & Powder Synthesis
- What are waste to energy pyrolysis plants? Convert Non-Recyclable Waste into Valuable Energy
- What happens to the feedstock during pyrolysis? A Guide to Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What is the major product of pyrolysis? Tailoring the Output for Your Specific Needs
- What is the use of biochar from pyrolysis? Unlock its potential as fuel, material, and soil amendment
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is the temperature of slow pyrolysis? Optimize for High-Quality Biochar Production
- What is the process of pyrolysis example? Transform Waste into Value with Thermal Decomposition



















