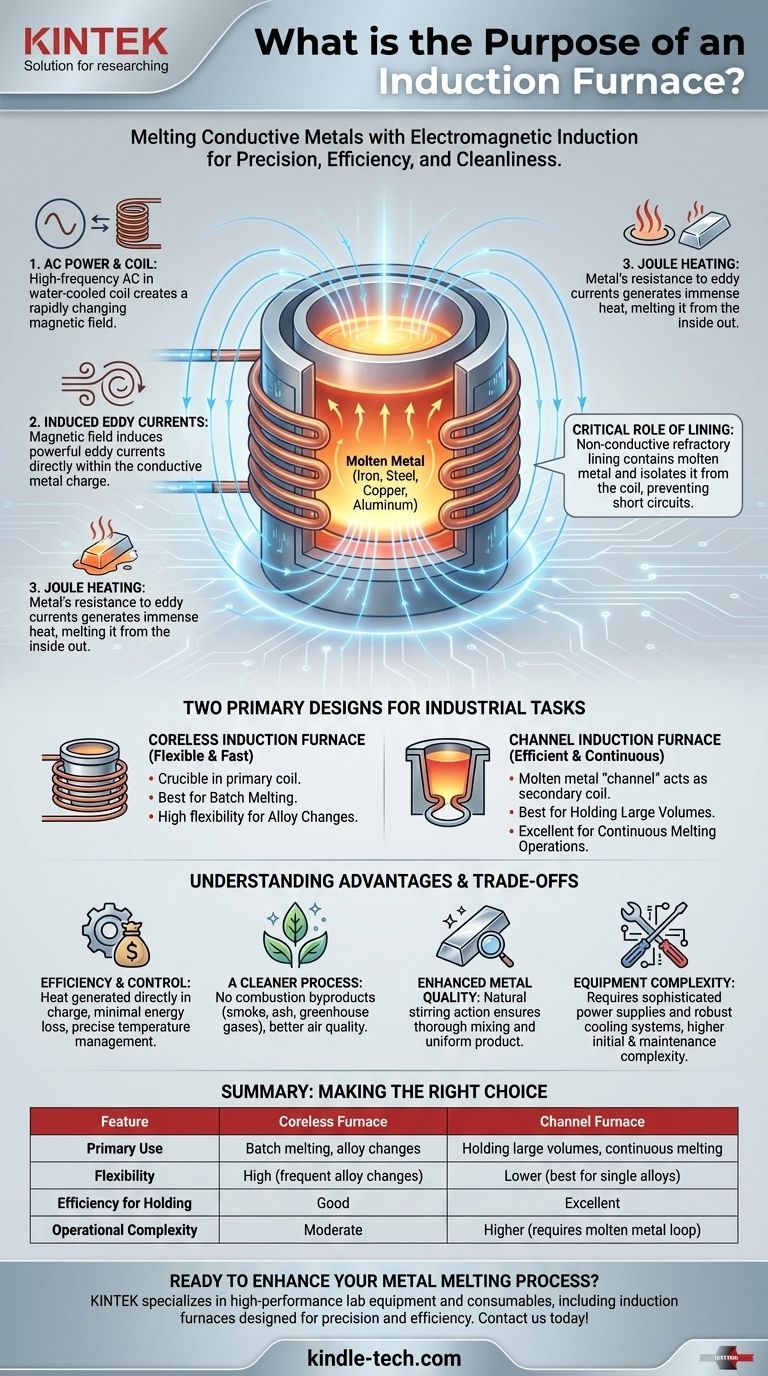
At its core, the purpose of an induction furnace is to melt electrically conductive metals like iron, steel, copper, and aluminum. It achieves this using the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate intense heat directly within the metal itself, offering a process that is significantly cleaner, more efficient, and more controllable than traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
The fundamental advantage of an induction furnace is not just that it melts metal, but how it does so. By transforming the metal itself into the source of heat, it bypasses the inefficiencies and pollution of external combustion, giving operators unparalleled precision and a cleaner work environment.

How Induction Furnaces Generate Intense Heat
To understand an induction furnace's purpose, you must first understand its unique heating mechanism. It does not rely on burning fuel. Instead, it operates like a powerful, specialized transformer.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through a water-cooled copper coil. This creates a strong and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space at the center of the coil.
The Metal as the Heating Element
When a conductive metal is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow directly inside the metal.
Resistance Creates Heat
The metal's own electrical resistance opposes the flow of these eddy currents. This opposition generates immense heat—a phenomenon known as Joule heating—causing the metal to heat up rapidly and melt from the inside out.
The Critical Role of the Lining
A non-conductive, heat-resistant crucible or lining is placed inside the copper coil. This refractory lining is crucial, as it contains the molten metal and isolates it from the water-cooled coil, preventing a catastrophic short circuit.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces: Two Key Designs
While the principle is the same, induction furnaces are built in two primary configurations, each suited for different industrial tasks.
Coreless Induction Furnaces
This is the simplest design, where the crucible containing the metal is placed directly inside the primary coil. They are excellent for melting material in batches and are flexible enough to handle frequent changes between different types of alloys.
Channel Induction Furnaces
This design functions more explicitly like a transformer. The furnace has a "channel" or loop of molten metal that acts as a secondary coil, which is coupled with the primary induction coil and an iron core. This configuration is exceptionally efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature for long periods or for continuous melting operations.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
The choice to use an induction furnace is driven by a clear set of benefits, but it also comes with specific limitations.
Key Advantage: Efficiency and Control
Because heat is generated directly within the charge material, very little energy is lost to the environment. This makes induction furnaces highly energy-efficient. Furthermore, the power can be controlled instantly, allowing for precise temperature management.
Key Advantage: A Cleaner Process
Induction heating is a completely clean process. With no combustion, there are no byproducts like smoke, ash, or greenhouse gases. This improves air quality within the foundry and helps meet strict environmental regulations.
Key Advantage: Enhanced Metal Quality
The intense magnetic fields create a natural stirring action within the molten bath. This ensures all elements, including alloys, are mixed thoroughly, resulting in a more uniform and high-quality final product.
The Primary Trade-off: Equipment Complexity
Induction furnaces require sophisticated power supplies to manage the high-frequency currents, as well as robust water-cooling systems to protect the copper coil. This makes the initial investment and maintenance more complex than for a simple cupola or reverb furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best furnace technology depends entirely on your operational goals and priorities.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse alloys in batches: A coreless induction furnace provides the flexibility and speed required for frequent material changes.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of molten metal or continuous melting: A channel induction furnace offers superior efficiency for maintaining temperature over long periods.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and energy savings: Both types of induction furnaces are vastly superior to traditional combustion-based furnaces.
Ultimately, the purpose of an induction furnace is to provide precise, clean, and efficient control over the entire metal melting process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting, alloy changes | Holding large volumes, continuous melting |
| Flexibility | High (frequent alloy changes) | Lower (best for single alloys) |
| Efficiency for Holding | Good | Excellent |
| Operational Complexity | Moderate | Higher (requires molten metal loop) |
Ready to enhance your metal melting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces designed for precision, efficiency, and a cleaner work environment. Whether you need batch melting flexibility or continuous operation, our solutions are tailored to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys



















