In short, secondary melting is a refining process applied to metals that have already been melted and solidified once. Its purpose is not simply to re-melt the material, but to purify and homogenize its structure, removing detrimental impurities and defects to create a higher-quality, higher-performance final product.
Think of secondary melting as a critical purification step for high-stakes materials. While primary melting creates the initial metal alloy, secondary melting refines it, removing unwanted elements and inconsistencies to unlock the material's maximum performance for the most demanding applications.

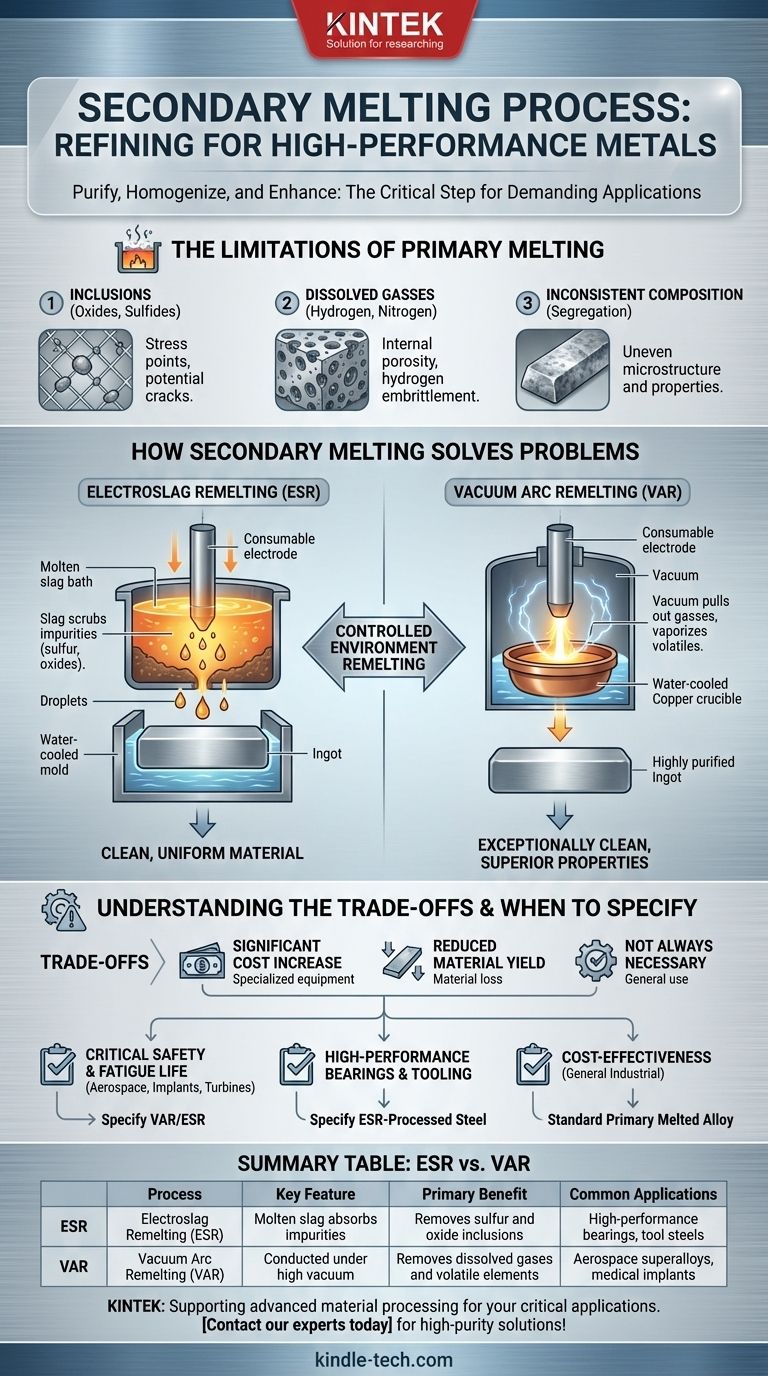
The Limitations of Primary Melting
To understand the need for secondary melting, we must first recognize the inherent limitations of primary melting processes, where raw materials like scrap or ore are first turned into liquid metal.
The Problem of Inclusions
During primary melting, non-metallic impurities like oxides and sulfides can become trapped within the metal. These microscopic inclusions act as stress concentration points, creating weak spots that can initiate cracks and lead to premature failure under load.
The Issue of Dissolved Gasses
Gasses like hydrogen and nitrogen readily dissolve in molten metal and can get trapped during solidification. This leads to internal porosity (tiny holes) and can cause hydrogen embrittlement, a phenomenon that severely reduces the material's ductility and toughness.
Inconsistent Alloy Composition
As a large batch of metal cools and solidifies in an ingot mold, the alloying elements may not distribute perfectly evenly. This phenomenon, known as segregation, results in a non-uniform microstructure and inconsistent mechanical properties throughout the final product.
How Secondary Melting Solves These Problems
Secondary melting processes directly target the impurities and inconsistencies left behind by primary melting. They work by re-melting the solid metal, called an electrode, in a highly controlled environment.
The Core Principle: Remelting in a Controlled Environment
The key is to remelt the electrode slowly and methodically, allowing physics and chemistry to separate the pure metal from its impurities. The two most common and effective processes are Electroslag Remelting (ESR) and Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR).
Electroslag Remelting (ESR)
In the ESR process, the electrode is slowly melted by passing a large electric current through a bath of highly reactive molten slag. As droplets of metal fall from the electrode, they must pass through this slag layer.
The slag acts like a chemical sponge, scrubbing the metal droplets and absorbing sulfur and oxide inclusions. A new, highly purified ingot solidifies slowly beneath the slag, resulting in a clean, uniform material.
Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
The VAR process is used to achieve the highest levels of purity, especially for aerospace superalloys. An electric arc is struck between the electrode and the base of a water-cooled copper crucible, all inside a deep vacuum.
As the electrode melts, the vacuum pulls out dissolved gasses like hydrogen and nitrogen. The intense heat also vaporizes other undesirable elements with low boiling points, which are then removed. This process yields an exceptionally clean material with superior fatigue life and strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While secondary melting produces superior materials, it is not a universal solution. The decision to use it involves significant trade-offs.
Significant Cost Increase
Secondary melting is an additional, energy-intensive manufacturing step that requires specialized and expensive equipment. This substantially increases the final cost of the material compared to a standard primary-melted alloy.
Reduced Material Yield
Some material is inevitably lost during the refining process. In ESR, a "slag skin" forms on the ingot that must be removed. In VAR, some metallic elements can be vaporized and lost to the vacuum system.
Not Always Necessary
For the vast majority of engineering applications, from structural beams in buildings to automotive body panels, the properties achieved through primary melting are perfectly sufficient. Specifying a secondary-melted alloy where it is not required is wasteful over-engineering.
When to Specify a Secondary Melted Alloy
Your material choice should always align with the demands and risks of the application. Use these guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is critical safety and fatigue life: You must consider secondary melting processes like VAR or ESR, especially for aerospace components, medical implants, or power generation turbines where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is high-performance bearings or tooling: Specify ESR-processed steel to achieve the cleanliness required for exceptional rolling contact fatigue life and toughness.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general industrial use: A standard primary melted alloy is almost always the correct and most economical choice.
Ultimately, understanding secondary melting allows you to specify a material that is not just suitable, but perfectly optimized for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Feature | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electroslag Remelting (ESR) | Uses molten slag to absorb impurities | Removes sulfur and oxide inclusions | High-performance bearings, tool steels |
| Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) | Conducted under high vacuum | Removes dissolved gases and volatile elements | Aerospace superalloys, medical implants |
Need high-purity metals for your critical applications? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables to support advanced material processing like secondary melting. Whether you're developing aerospace components or medical implants, our solutions ensure the material quality and performance your projects demand. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can stainless steel be soldered or brazed? Master the Process for Strong, Durable Joints
- What is the concept of a vacuum furnace? Harnessing Physics for Safer, More Efficient Heating
- How does the heating rate in a nitriding furnace affect nitrogen diffusion? Optimize Layer Thickness and Quality
- Why is specialized heating equipment necessary for TiC-steel debinding? Ensure Purity Before Sintering
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- How does HIP furnace post-treatment improve fluoride ceramic optical quality? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density
- What are the common defects of brazing? A Guide to Identifying and Preventing Joint Failures
- What furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Equipment



















