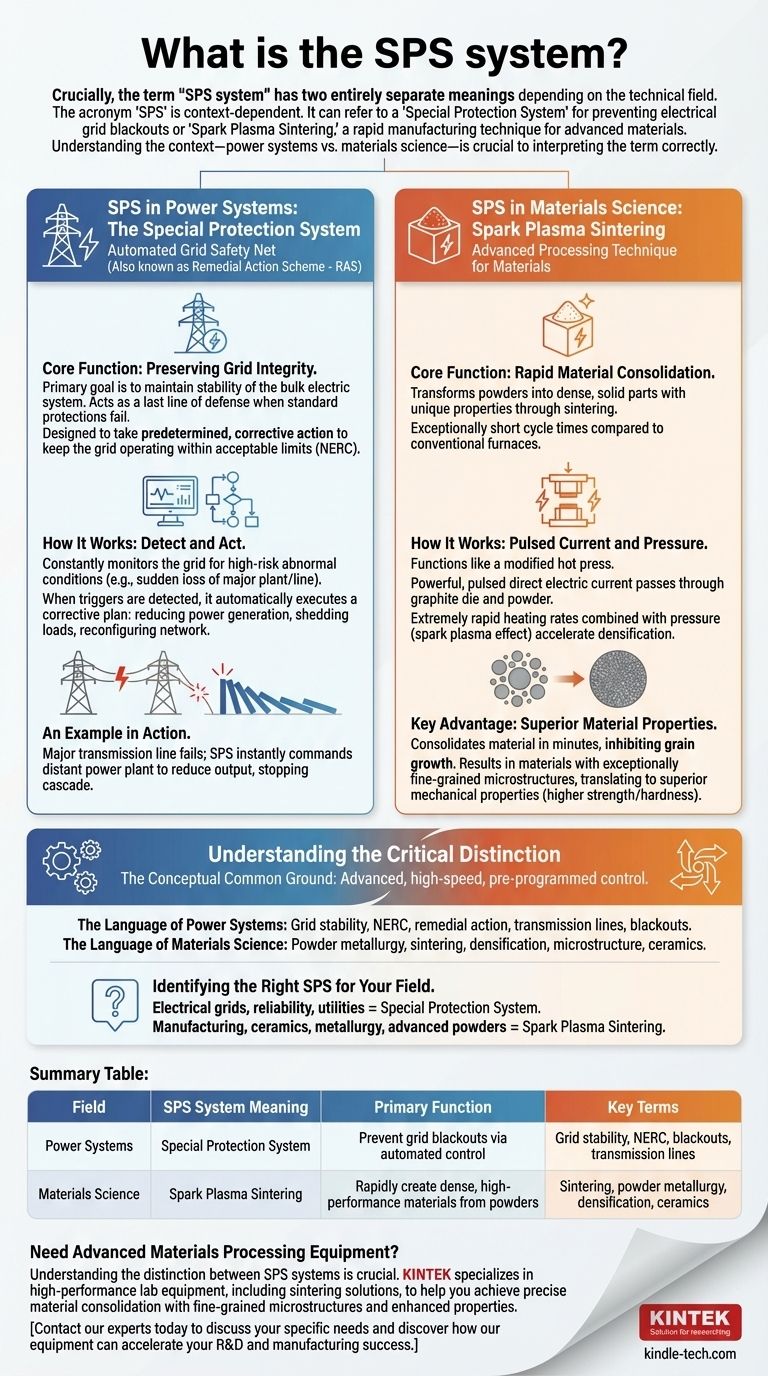
Crucially, the term 'SPS system' has two entirely separate meanings depending on the technical field. In power systems engineering, it refers to a Special Protection System designed to prevent grid blackouts. In materials science, it refers to Spark Plasma Sintering, a rapid manufacturing process for creating high-performance materials.
The acronym 'SPS' is context-dependent. It can refer to a 'Special Protection System' for preventing electrical grid blackouts or 'Spark Plasma Sintering,' a rapid manufacturing technique for advanced materials. Understanding the context—power systems vs. materials science—is crucial to interpreting the term correctly.

SPS in Power Systems: The Special Protection System
A Special Protection System (SPS), also known as a Remedial Action Scheme (RAS), is an automated safety net for a regional power grid. Its job is to prevent a localized problem from escalating into a widespread blackout.
Core Function: Preserving Grid Integrity
The primary goal of an SPS is to maintain the stability of the bulk electric system. It acts as a last line of defense when standard protection systems, which simply isolate a faulted component, are not enough.
According to the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), an SPS is designed to take predetermined, corrective action to keep the grid operating within acceptable limits.
How It Works: Detect and Act
An SPS constantly monitors the grid for specific, high-risk abnormal conditions, such as the sudden loss of a major power plant or transmission line.
When it detects one of these predefined triggers, it automatically executes a corrective plan. This could involve reducing power generation at certain plants, shedding specific industrial loads, or reconfiguring the network to redirect power flow.
An Example in Action
Imagine a major transmission line unexpectedly fails. This could overload adjacent lines, causing them to fail in a domino effect. An SPS would detect the initial line loss and might instantly command a distant power plant to reduce its output, relieving stress on the remaining lines and stopping the cascade.
SPS in Materials Science: Spark Plasma Sintering
In materials science and manufacturing, SPS stands for Spark Plasma Sintering. It is an advanced processing technique used to transform powders into dense, solid parts with unique properties.
Core Function: Rapid Material Consolidation
The main purpose of Spark Plasma Sintering is to rapidly heat and pressurize a powder material, fusing the particles together in a process called sintering. It is known for its exceptionally short cycle times compared to conventional furnaces.
How It Works: Pulsed Current and Pressure
An SPS machine functions like a modified hot press. A powerful, pulsed direct electric current is passed directly through a graphite die and, in many cases, through the powder sample itself.
This direct heating, combined with externally applied pressure, allows for extremely rapid heating rates. The process utilizes a phenomenon sometimes called the "spark plasma effect" between particles to accelerate densification.
Key Advantage: Superior Material Properties
The speed of SPS is its defining advantage. By consolidating the material in minutes rather than hours, the process inhibits grain growth.
This results in materials with exceptionally fine-grained microstructures, which often translates to superior mechanical properties like higher strength and hardness. It enables the creation of novel materials that are not possible to make with slower, traditional methods.
Understanding the Critical Distinction
The two 'SPS' systems operate in completely different domains. The context in which you encounter the acronym is the only way to determine its meaning.
The Language of Power Systems
If your discussion involves terms like grid stability, NERC, remedial action, transmission lines, or blackouts, you are dealing with a Special Protection System. It is a concept of large-scale control and automation.
The Language of Materials Science
If your discussion involves terms like powder metallurgy, sintering, densification, microstructure, or ceramics, you are dealing with Spark Plasma Sintering. It is a physical manufacturing process.
The Conceptual Common Ground
Though functionally unrelated, both systems represent a form of advanced, high-speed, pre-programmed control. One acts to stabilize an electrical network, while the other acts to create a stable material structure.
Identifying the Right SPS for Your Field
To apply this knowledge, simply identify the domain of your problem.
- If your primary focus is electrical grids, reliability, or utilities: You are dealing with a Special Protection System (SPS), a control scheme to prevent widespread outages.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing, ceramics, metallurgy, or advanced powders: You are dealing with Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), a rapid consolidation technique for creating dense, high-performance materials.
By understanding this critical distinction, you can confidently engage in technical discussions within your specific domain.
Summary Table:
| Field | SPS System Meaning | Primary Function | Key Terms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Systems | Special Protection System | Prevent grid blackouts via automated control | Grid stability, NERC, blackouts, transmission lines |
| Materials Science | Spark Plasma Sintering | Rapidly create dense, high-performance materials from powders | Sintering, powder metallurgy, densification, ceramics |
Need Advanced Materials Processing Equipment?
Understanding the distinction between SPS systems is crucial, especially if your work involves Spark Plasma Sintering for creating superior materials. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including sintering solutions, to help you achieve precise material consolidation with fine-grained microstructures and enhanced properties.
Let us provide the right tools for your materials science challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our equipment can accelerate your R&D and manufacturing success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between spark plasma sintering and conventional sintering? A Guide to Faster, Better Materials
- What is the plasma sintering method? Unlock Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the applications of spark plasma sintering? Fabricate High-Performance Materials with Precision
- What is the mechanism of SPS? Unlock Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is spark plasma sintering of polymers? Rapidly Create Dense, High-Performance Materials



















