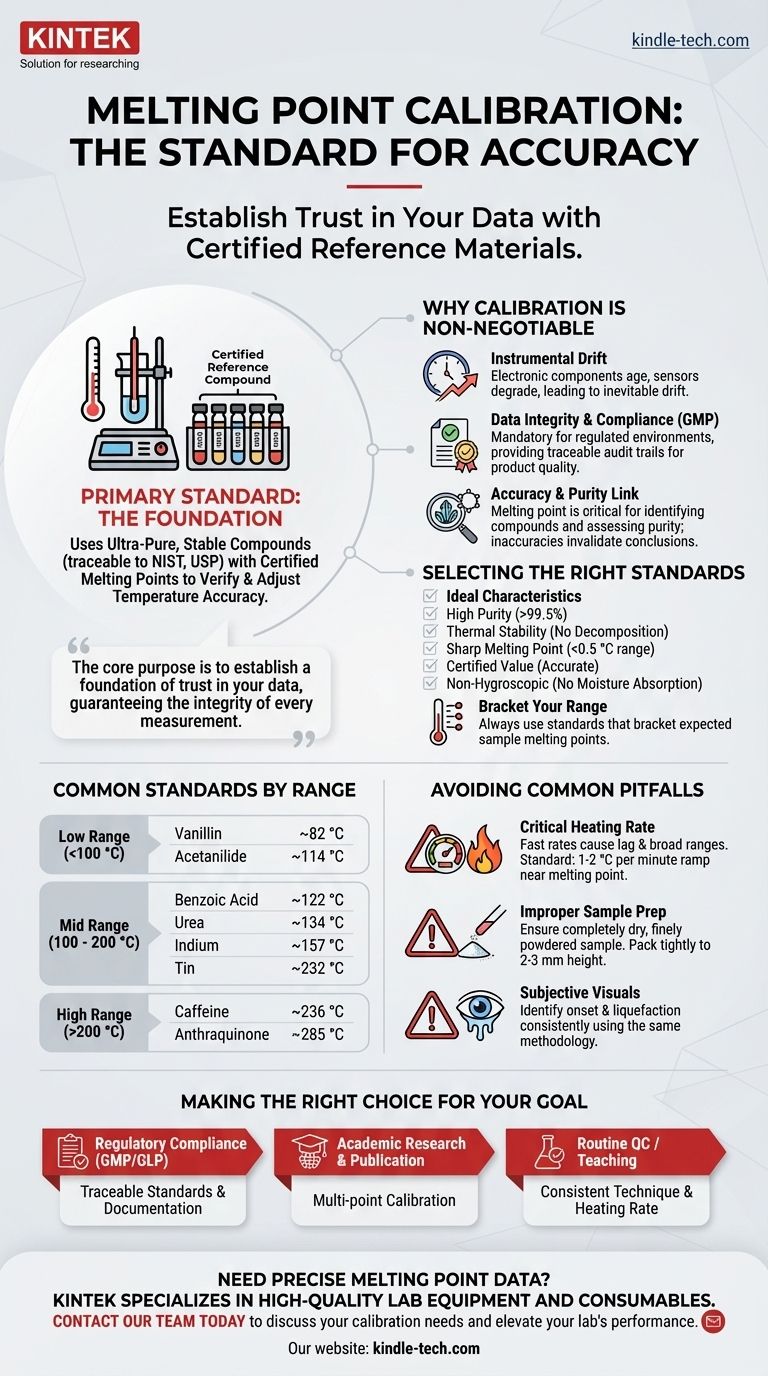
The primary standard for melting point calibration involves using a set of ultra-pure, stable chemical compounds with precisely known and certified melting points. These reference materials, often traceable to metrological institutes like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) or defined in pharmacopeias (e.g., USP), are used to verify and adjust the temperature accuracy of a melting point apparatus across its operational range.
The core purpose of calibration is not just to check an instrument, but to establish a foundation of trust in your data. It ensures that a temperature reading from your device corresponds accurately to the true physical temperature of the sample, guaranteeing the integrity of every subsequent measurement.
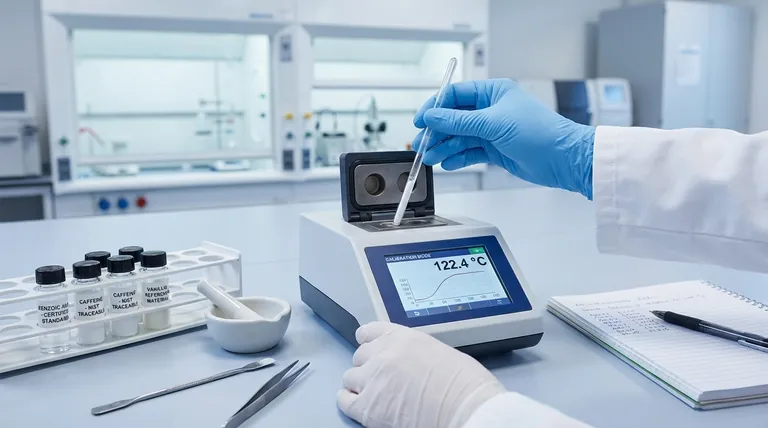

Why Instrument Calibration is Non-Negotiable
An uncalibrated instrument produces data that is, at best, unreliable and, at worst, invalid. Calibration addresses the fundamental need for accuracy and reproducibility in scientific measurement.
The Problem of Instrumental Drift
No instrument maintains perfect accuracy indefinitely. Electronic components age, sensors degrade, and heating blocks can change their thermal properties over time. Regular calibration corrects for this inevitable instrumental drift.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Compliance
In regulated environments, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing (GMP), calibration is a mandatory requirement. It provides a documented, traceable audit trail proving that measurements are accurate and that product quality is being assessed against a valid standard.
The Link Between Accuracy and Purity
Melting point is a critical physical property used to identify compounds and assess their purity. Impurities typically depress and broaden the melting range. Without an accurate temperature reading, you cannot confidently draw conclusions about a substance's identity or purity.
Selecting the Right Calibration Standards
The quality of your calibration depends entirely on the quality of your standards. Not every pure chemical is suitable for this purpose.
Characteristics of an Ideal Standard
A substance used for melting point calibration must have several key properties:
- High Purity: Typically greater than 99.5%.
- Thermal Stability: It should not decompose on melting.
- Sharp Melting Point: It must melt over a very narrow range (e.g., <0.5 °C).
- Certified Value: Its melting point must be accurately determined and certified by a recognized authority.
- Non-Hygroscopic: It should not readily absorb moisture from the air.
Common Standards by Temperature Range
Calibration should always be performed using standards that bracket the expected melting point of your unknown samples. It is insufficient to only check one point on the temperature scale.
- Low Range (<100 °C): Vanillin (~82 °C), Acetanilide (~114 °C)
- Mid Range (100 - 200 °C): Benzoic Acid (~122 °C), Urea (~134 °C), Indium (metal, ~157 °C), Tin (metal, ~232 °C)
- High Range (>200 °C): Caffeine (~236 °C), Anthraquinone (~285 °C)
Common Pitfalls and Sources of Error
A successful calibration requires more than just high-quality standards; it demands meticulous technique. The most common errors are procedural, not instrumental.
The Critical Impact of Heating Rate
This is the single most significant source of error in melting point determination. A fast heating rate causes the thermometer's reading to lag behind the actual temperature of the sample, resulting in an artificially high and broad melting range.
A ramp rate of 1-2 °C per minute is standard practice when approaching the expected melting point.
Improper Sample Preparation and Packing
The sample must be completely dry and finely powdered to ensure uniform heat transfer. It should be packed tightly into the capillary tube to a height of 2-3 mm. A loosely packed sample will heat unevenly and lead to an inaccurate reading.
Subjectivity in Visual Detection
Identifying the exact onset of melting (the first tiny droplet) and the point of complete liquefaction can be subjective. It is crucial for the operator to use a consistent methodology for every measurement, for both standards and samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Implementing a calibration protocol is about defining the level of accuracy your work requires and consistently adhering to the procedures that achieve it.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance (e.g., GMP/GLP): You must use certified, traceable standards (e.g., USP) and maintain rigorous documentation of all calibration procedures and results.
- If your primary focus is academic research or publication: A multi-point calibration using high-purity standards is essential to ensure your data is accurate, reproducible, and will withstand peer review.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or teaching: The emphasis should be on consistent technique, especially controlling the heating rate, to build good habits and generate reliable day-to-day data.
Ultimately, proper calibration transforms a melting point apparatus from a simple heater into a precise analytical instrument.
Summary Table:
| Standard Compound | Typical Melting Point (°C) | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Vanillin | ~82 °C | Low Range (<100 °C) |
| Benzoic Acid | ~122 °C | Mid Range (100-200 °C) |
| Caffeine | ~236 °C | High Range (>200 °C) |
| Indium | ~157 °C | Mid Range (Metal Standard) |
Need precise and reliable melting point data? Proper calibration is the foundation of trust in your laboratory measurements. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the pure reference materials essential for accurate melting point calibration. Our experts can help you select the right standards for your specific application—from GMP compliance to academic research.
Ensure the integrity of your results. Contact our team today to discuss your calibration needs and elevate your lab's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Anion Exchange Membrane for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals












