In short, the vacuum induction method is a highly controlled metallurgical process that melts metals and alloys using electromagnetic induction inside a vacuum chamber. This combination of induction heating and a vacuum environment is crucial for producing extremely pure, high-performance materials by preventing the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen.
The core problem this method solves is contamination. Many advanced alloys are highly reactive when molten and would be ruined by exposure to air. By removing the air, vacuum induction melting makes it possible to create the ultra-clean, precisely-engineered materials required for the most demanding technological applications.

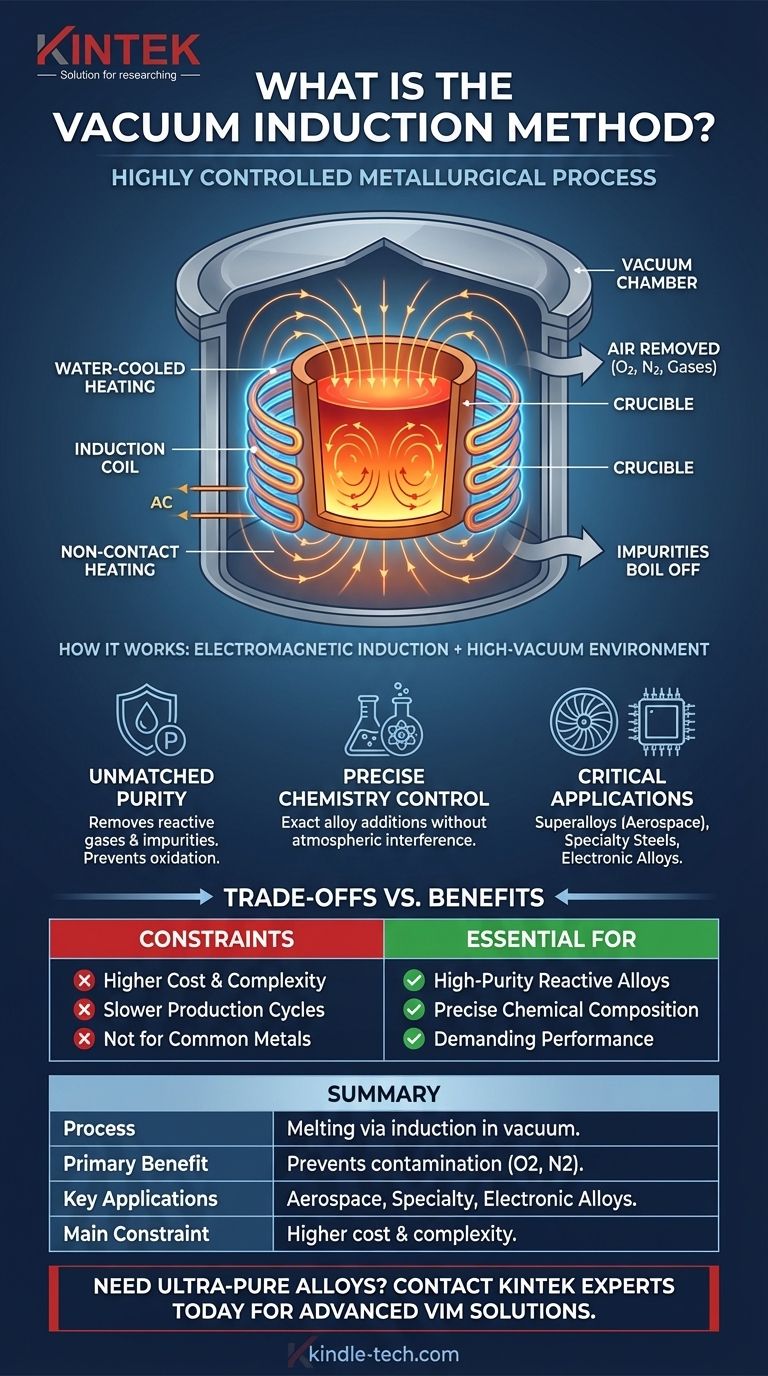
How Vacuum Induction Melting Works: The Core Principles
The process is an elegant solution to a fundamental chemistry problem. It combines two key technologies—electromagnetic induction and high-vacuum systems—to achieve a result that is impossible in a standard furnace.
The Role of Electromagnetic Induction
The heating mechanism is entirely non-contact. An alternating electrical current is passed through a water-cooled copper coil that surrounds a crucible containing the metal.
This current generates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. The magnetic field, in turn, induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge itself.
The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to generate immense heat, quickly raising the temperature of the charge above its melting point.
The Critical Function of the Vacuum
Simultaneously, the entire process takes place inside a sealed, airtight steel chamber from which the air has been pumped out.
This vacuum environment is the key to the method's success. It removes reactive gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen, which would otherwise aggressively bond with the hot, molten metal.
This prevention of oxidation and nitridation is essential for maintaining the purity and intended properties of reactive metals like titanium and the complex elements within superalloys.
Key Furnace Components
A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace consists of three primary components working in concert:
- The Vacuum Chamber: An airtight, robust steel jacket, often water-cooled, capable of withstanding the high vacuum and internal heat.
- The Induction Coil: A water-cooled copper coil that generates the magnetic field for heating.
- The Crucible: A refractory-lined vessel that sits inside the induction coil and holds the metal charge. The refractory lining is chosen to be non-reactive with the specific alloy being melted.
Why This Method is Essential for Advanced Materials
The benefits of the vacuum induction method directly translate to the performance of the final product. It is not just about melting metal; it's about refining it to a state of near-perfect purity and composition.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
The vacuum actively helps to purify the melt. It removes harmful dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from the liquid metal.
Furthermore, the low-pressure environment encourages the "boiling off" of other unwanted elements and impurities that have high vapor pressures, leaving behind a cleaner and more refined final alloy.
Precise Control Over Alloy Chemistry
In the controlled vacuum environment, metallurgists have an unobstructed view of the molten bath. They can make highly precise additions of alloying elements to the melt.
Because there are no atmospheric gases to interfere, these additions incorporate fully and predictably into the molten metal. This allows for the creation of alloys with chemical compositions that are accurate to within hundredths of a percent.
Applications in Critical Industries
This level of quality is non-negotiable for industries where material failure is not an option.
VIM is the standard for producing high-temperature superalloys for jet engine turbine blades, specialty steels for aerospace structures and atomic energy equipment, and high-purity magnetic and electronic alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the vacuum induction method is a specialized process with specific constraints that make it unsuitable for all applications.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Building and operating a VIM furnace is significantly more complex and expensive than a standard air-melting furnace. Creating and maintaining a high vacuum while managing extreme temperatures requires sophisticated engineering and substantial energy input.
Slower Production Cycles
The process is inherently slower. Time is required to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level before melting can begin, and the controlled nature of the process often extends the "tap-to-tap" time compared to high-volume steelmaking.
Not Ideal for All Metals
This method is overkill for producing common materials like structural steel or simple aluminum alloys, where the minimal impurities from air-melting are acceptable and cost is a primary driver. VIM is reserved for materials where ultimate purity dictates performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum induction melting is driven entirely by the required quality and performance of the final material.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, reactive alloys (like titanium or superalloys): This method is non-negotiable for preventing contamination and achieving the required material properties.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical composition for specialty steels or magnetic materials: The controlled vacuum environment is essential for exact alloying, free from unwanted side reactions.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing standard-grade metals where cost is paramount: Simpler, more cost-effective air-melting techniques are the appropriate choice.
Ultimately, vacuum induction melting is the foundational technology that enables the existence of the most advanced materials shaping our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Melts metals using electromagnetic induction inside a vacuum chamber. |
| Primary Benefit | Prevents contamination by removing reactive gases (oxygen, nitrogen). |
| Key Applications | Superalloys for aerospace, specialty steels, high-purity electronic alloys. |
| Main Constraint | Higher cost and complexity compared to standard air-melting furnaces. |
Need to produce ultra-pure, high-performance alloys? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum induction melting systems, to help you achieve precise chemical composition and unmatched material purity for your most demanding applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















