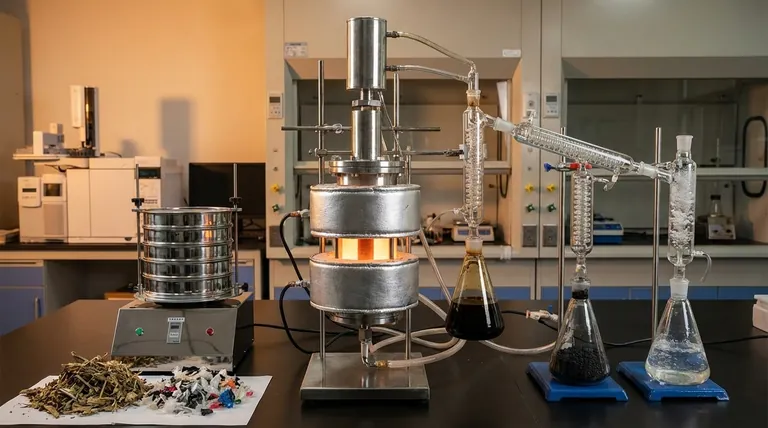
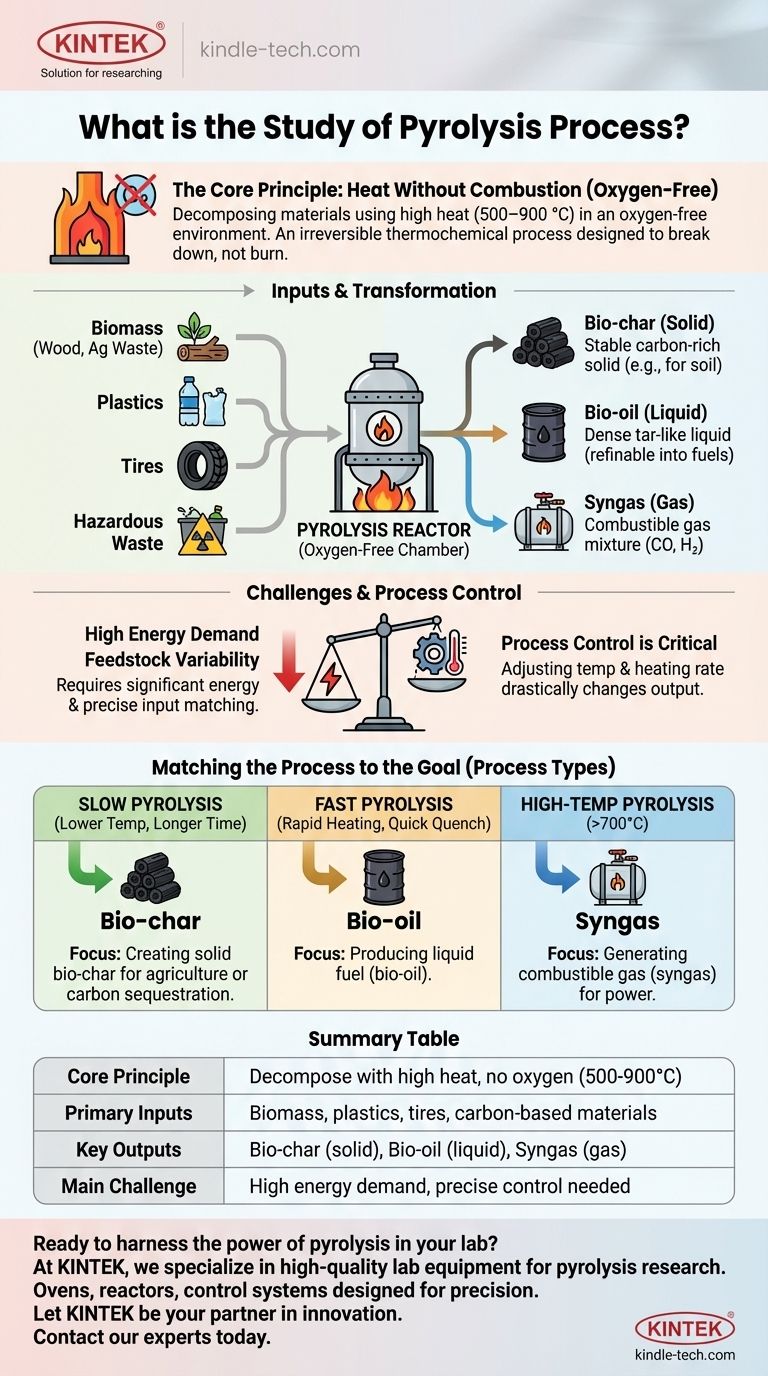
In essence, the study of pyrolysis is the analysis of how to decompose materials using high heat in an environment completely devoid of oxygen. It is an irreversible thermochemical process designed not to burn a substance, but to break it down into a new set of valuable outputs: a solid char, a liquid oil, and a combustible gas.
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a transformation process. It re-engineers the chemical structure of low-value materials like biomass or plastic waste, converting them into high-value products like fuel and stable carbon, but requires precise control and significant energy to do so effectively.

How Pyrolysis Fundamentally Works
The name itself, derived from the Greek words ‘pyro’ (fire) and ‘lysis’ (separation), perfectly describes the core function: separating a substance's components using heat.
The Core Principle: Heat Without Combustion
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When you heat organic material with oxygen, you get combustion—burning—which releases energy, smoke, and ash.
By removing oxygen, pyrolysis prevents burning. Instead, the intense heat (typically 500–900 °C) breaks the complex chemical bonds within the material, rearranging them into simpler, smaller molecules.
The Key Inputs: What Can Be Processed?
Pyrolysis is highly versatile and can be applied to a wide range of organic and carbon-based materials.
Common feedstocks include biomass (like wood or agricultural waste), plastics, used tires, and even certain types of hazardous waste. The goal is to take a low-value or problematic material and convert it.
The Primary Outputs: A Trio of Products
The process consistently yields three distinct product streams, though the exact ratio depends on the input material and process conditions.
- Bio-char (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil (Liquid): A dense, tar-like liquid that can be refined into fuels.
- Syngas (Gas): A mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a simple solution. Its effectiveness is governed by a balance of factors that present both opportunities and challenges.
High Energy Demand
The process is energy-intensive. Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required to break down materials consumes a significant amount of energy, which can impact the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of an operation.
Process Control is Critical
Pyrolysis is not a one-size-fits-all technique. Minor adjustments to temperature, heating rate, and time can drastically change the output.
For example, slow heating at lower temperatures tends to maximize the yield of bio-char, while very rapid heating ("flash pyrolysis") maximizes the production of bio-oil. This sensitivity requires sophisticated control systems.
Feedstock Variability
The composition of the final products is directly tied to the chemical makeup of the input material. The results from pyrolyzing wood will be vastly different from pyrolyzing plastic, requiring different equipment and process parameters for optimal results.
Matching the Process to the Goal
The ideal pyrolysis setup depends entirely on the desired outcome. Understanding your primary objective is the first step in applying this technology effectively.
- If your primary focus is creating solid bio-char for agriculture or carbon sequestration: You should utilize a "slow pyrolysis" process with lower temperatures and longer processing times.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuel (bio-oil): You need a "fast pyrolysis" setup characterized by very rapid heating rates and quick quenching of the resulting vapors.
- If your primary focus is generating combustible gas (syngas) for power: You should operate at higher temperatures (above 700°C) to favor the cracking of larger molecules into gaseous components.
By precisely controlling heat in an oxygen-free chamber, pyrolysis offers a powerful method to unlock chemical and energetic value from materials often considered waste.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Decomposition of material using high heat (500-900°C) in the absence of oxygen. |
| Primary Inputs | Biomass, plastics, tires, and other carbon-based materials. |
| Key Outputs | Bio-char (solid), Bio-oil (liquid), and Syngas (combustible gas). |
| Process Types | Slow Pyrolysis (maximizes char), Fast Pyrolysis (maximizes oil), High-Temperature (maximizes gas). |
| Main Challenge | High energy demand and the need for precise control of temperature and heating rates. |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment for pyrolysis research and analysis. Whether you are developing new processes for waste conversion, optimizing bio-fuel production, or analyzing material decomposition, our reliable ovens, reactors, and control systems are designed for precision and performance.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your research goals efficiently and safely.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision



















