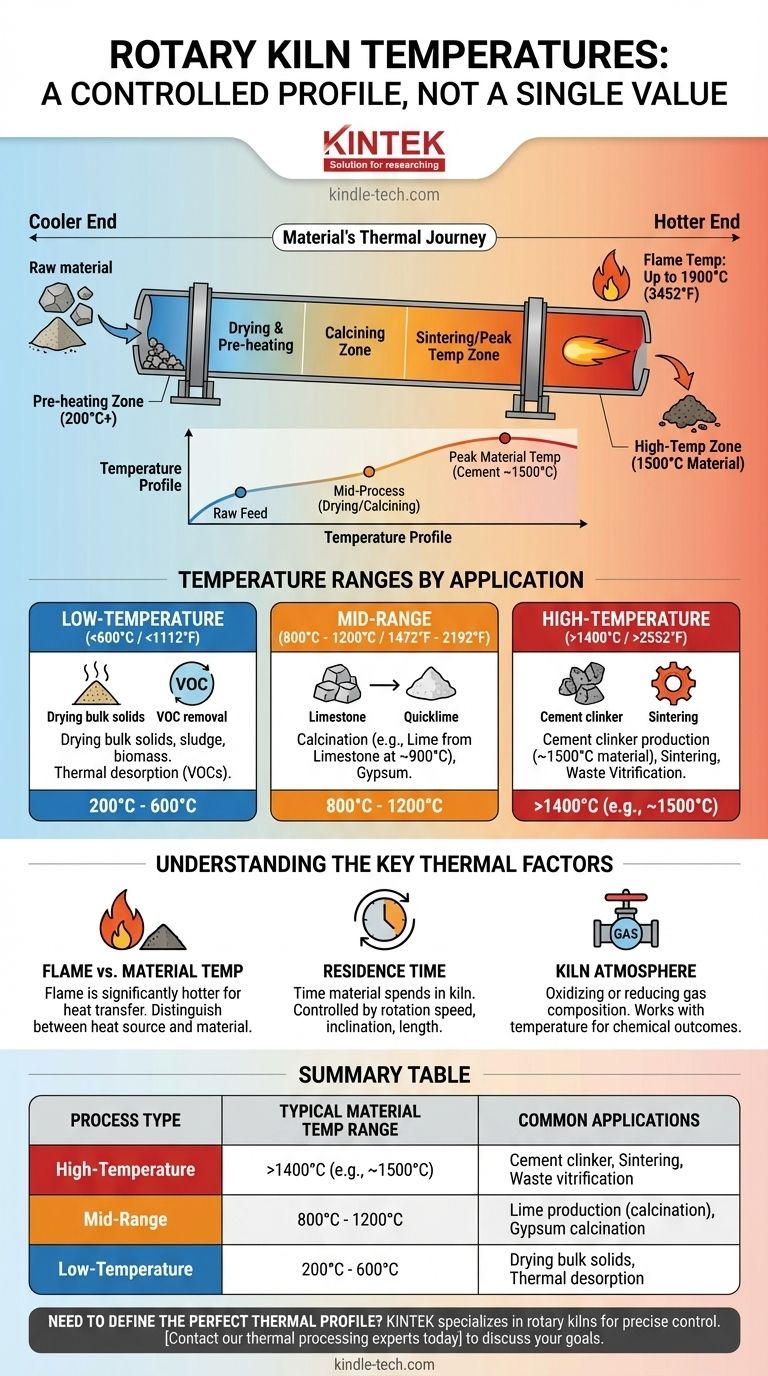
The temperature of a rotary kiln is not a single value but a highly controlled profile that spans a vast range. While specific high-temperature processes like cement manufacturing heat material to 1500°C (2732°F) using flames that can reach 1900°C (3452°F), the overall operational capability of rotary kilns extends from as low as 200°C to over 2500°C to meet diverse industrial requirements.
A rotary kiln does not have one temperature. Instead, it is engineered to maintain a precise temperature profile along its length, with distinct zones customized to drive a specific chemical reaction or physical change in the material being processed.

Why a Kiln Has a Profile, Not a Single Temperature
Asking for "the" temperature of a kiln is like asking for "the" speed of a car during a cross-country trip. The value changes based on the terrain and the objective. A kiln's temperature is similarly dynamic and purposeful.
The Critical Role of Temperature Zones
A rotary kiln is functionally divided into different temperature zones. A common configuration includes a pre-heating zone and a high-temperature heating or calcining zone.
Each of these zones can be set and controlled independently. This allows for the gradual and precise heating of material as it travels down the length of the inclined, rotating drum.
The Material's Thermal Journey
Raw material is fed into the upper, cooler end of the kiln. As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and progresses toward the lower, hotter end where the burner is located.
This journey ensures the material is dried, pre-heated, and then subjected to the peak process temperature in a controlled sequence, maximizing efficiency and ensuring product quality.
Temperature Ranges by Application
The required temperature profile is dictated entirely by the process goal. A kiln used for drying wood chips operates in a completely different thermal realm than one used for producing cement.
High-Temperature Processes (>1400°C)
This is the range for creating cement clinker, sintering ores, or vitrifying hazardous waste. In these applications, the goal is to induce fundamental chemical changes in the material.
For cement, the raw mix is heated to approximately 1500°C (2732°F). To achieve this, the flame at the burner can reach temperatures as high as 1900°C (3452°F).
Mid-Range Processes (800°C - 1200°C)
This range is typical for calcination, a process that removes chemically bound components through heat. A primary example is producing lime from limestone (calcium carbonate).
Heating limestone to around 900°C (1652°F) drives off carbon dioxide, converting it into calcium oxide (quicklime).
Low-Temperature Processes (<600°C)
Kilns are also used for processes that require much gentler heating. These applications often start as low as 200°C (392°F).
Common uses include drying bulk solids, sludge, or biomass, as well as thermal desorption to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from contaminated soils.
Understanding the Key Thermal Factors
Temperature is the primary parameter, but it doesn't work in isolation. Several other factors are critical for a successful thermal process.
Flame vs. Material Temperature
It is crucial to distinguish between the temperature of the heat source (the flame) and the temperature of the material itself. The flame is always significantly hotter to facilitate efficient heat transfer to the material bed.
Residence Time
The amount of time the material spends inside the kiln is just as important as the peak temperature it reaches. Residence time is controlled by the kiln's rotation speed, its angle of inclination, and its length.
Kiln Atmosphere
The gas composition inside the kiln (the atmosphere) can be controlled to be oxidizing (excess oxygen) or reducing (oxygen-starved). This factor works in tandem with temperature to achieve specific chemical outcomes, particularly in minerals and metals processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct temperature profile is determined by your end product. Understanding your material's required transformation is the first step in defining your process.
- If your primary focus is cement production or sintering: You will operate at the highest end of the spectrum, with material temperatures nearing 1500°C.
- If your primary focus is calcination (e.g., lime or gypsum): Your target temperature profile will typically fall within the 800°C to 1200°C range.
- If your primary focus is drying or thermal desorption: You will utilize a low-temperature process, often operating between 200°C and 600°C.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln is a versatile tool defined not by a single temperature, but by its ability to deliver the precise thermal journey your material requires.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Typical Material Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature | >1400°C (e.g., ~1500°C) | Cement clinker production, sintering, waste vitrification |
| Mid-Range | 800°C - 1200°C | Lime production (calcination), gypsum calcination |
| Low-Temperature | 200°C - 600°C | Drying bulk solids, thermal desorption of contaminants |
Need to define the perfect thermal profile for your material?
KINTEK specializes in designing and supplying robust rotary kilns and laboratory equipment to meet your precise thermal processing needs. Whether your goal is high-temperature sintering, mid-range calcination, or low-temperature drying, our solutions ensure precise temperature control, efficiency, and product quality.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your specific process goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research



















