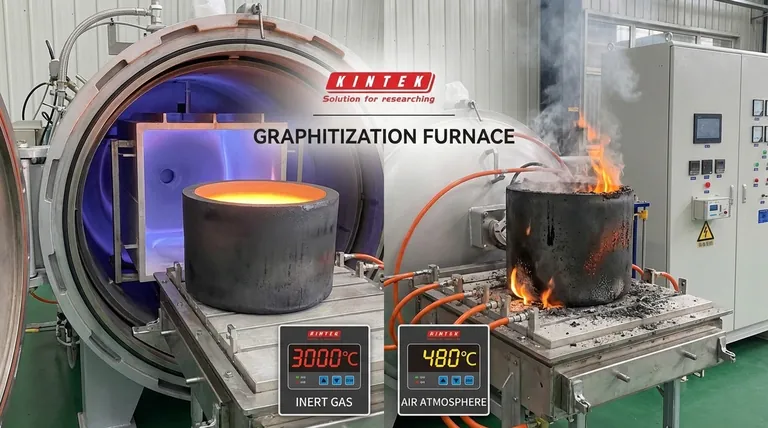
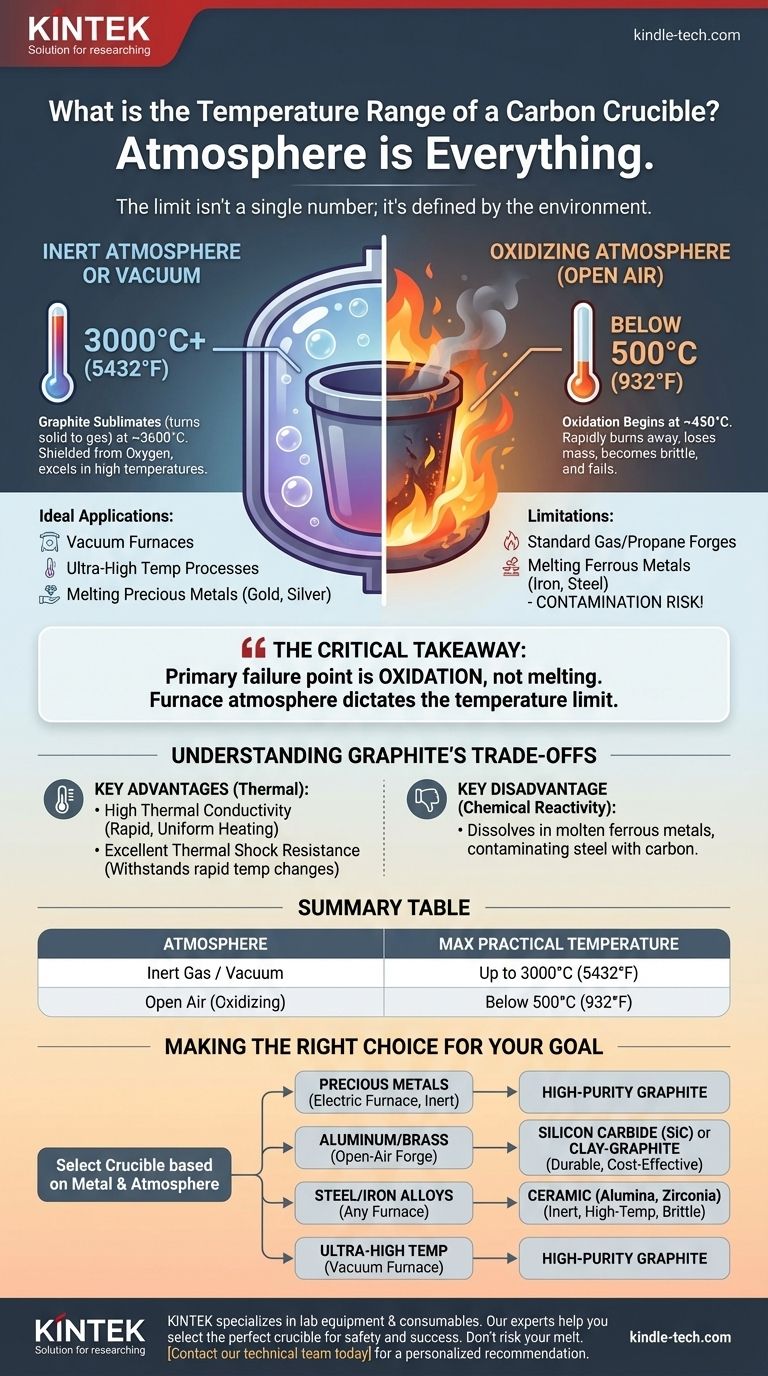
At its core, the temperature range of a carbon crucible is not a single number but is dictated entirely by its surrounding atmosphere. In a vacuum or inert gas environment, it can withstand temperatures exceeding 3000°C (5432°F), but in open air, its usefulness is severely limited to below 500°C (932°F) before it begins to rapidly burn away.
The most critical takeaway is that a carbon crucible's primary failure point is not melting, but oxidation. Your choice of furnace atmosphere—inert gas versus open air—is more important than the target temperature itself when deciding if a carbon crucible is the right tool for the job.
The Critical Factor: Atmosphere Defines the Limits
The question of a carbon crucible's temperature range can only be answered by first defining the environment where it will be used. These two scenarios have drastically different outcomes.
In an Inert Atmosphere or Vacuum
This is the environment where carbon (graphite) crucibles truly excel. Shielded from oxygen in a vacuum furnace or an argon/nitrogen atmosphere, graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure but sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at an exceptionally high temperature, around 3600°C (6500°F).
For practical purposes in these controlled environments, high-purity graphite crucibles are routinely used for processes requiring temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F).
In an Oxidizing Atmosphere (Open Air)
This is the single greatest limitation of a carbon crucible. When heated in the presence of oxygen, graphite begins to oxidize and literally burn, converting the solid carbon into CO and CO2 gas.
This process begins slowly around 450°C (842°F) and accelerates rapidly as temperature increases. The crucible will lose mass, become brittle, and ultimately fail. This makes pure carbon crucibles a very poor choice for high-temperature work in a standard, air-breathing propane or gas forge.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Graphite
Beyond temperature, a material's inherent properties determine its suitability for a specific task. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for preventing costly failures and contaminated melts.
Key Advantage: Thermal Properties
Graphite has extremely high thermal conductivity. This means it transfers heat very efficiently, allowing for rapid and uniform heating of the material inside.
It also possesses excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning it can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, a common failure point for many ceramic materials.
Key Disadvantage: Chemical Reactivity
Carbon is not inert. When melting ferrous metals like iron or steel, the molten metal will dissolve carbon directly from the crucible. This contaminates the melt, turning your steel into a high-carbon cast iron and simultaneously destroying the crucible.
For this reason, carbon crucibles are generally restricted to melting non-ferrous metals like gold, silver, copper, brass, and aluminum.
Comparing Common Crucible Alternatives
- Clay-Graphite: A mix of clay and graphite, these are a common and affordable choice for hobbyists. They offer better oxidation resistance than pure graphite but have a lower maximum working temperature, typically around 1550°C (2822°F).
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): More expensive than clay-graphite but significantly more durable and resistant to both oxidation and thermal shock. They are the workhorse for many non-ferrous foundries and serious hobbyists.
- Ceramic (Alumina, Zirconia): These are required for melting steel, platinum, and other high-temperature or reactive metals. They are inert and can withstand extreme temperatures even in air, but are typically more brittle and susceptible to thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is a foundational step for safety and success. Base your decision on the metal you are melting and the equipment you are using.
- If your primary focus is melting precious metals (gold, silver) in an electric furnace: A pure graphite crucible is the ideal choice due to its thermal efficiency and clean melting properties.
- If your primary focus is melting aluminum or brass in an open-air propane forge: A more durable silicon carbide (SiC) or a cost-effective clay-graphite crucible is the correct and safer choice.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or iron alloys: You must use a ceramic crucible (like alumina) to withstand the temperature and prevent carbon contamination of your metal.
- If your primary focus is specialized, ultra-high temperature melting in a vacuum furnace: A high-purity graphite crucible is one of the few materials capable of performing this task.
Ultimately, matching your crucible material to your metal, temperature, and atmosphere is the key to a safe and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere | Maximum Practical Temperature | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas / Vacuum | Up to 3000°C (5432°F) | Sublimation (not melting) |
| Open Air (Oxidizing) | Below 500°C (932°F) | Rapid oxidation and burnout |
Need the Right Crucible for Your Specific Application?
Choosing the correct crucible is critical for the safety and success of your melting process. The wrong material can lead to contamination, crucible failure, and wasted materials.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible—whether it's high-purity graphite for precious metals in a controlled furnace or durable silicon carbide for open-air forging—ensuring optimal performance for your specific metal, temperature, and atmosphere.
Don't risk your melt. Contact our technical team today for a personalized recommendation and get the right tool for the job!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does graphite thermal decompose? The Critical Role of Atmosphere
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere



















