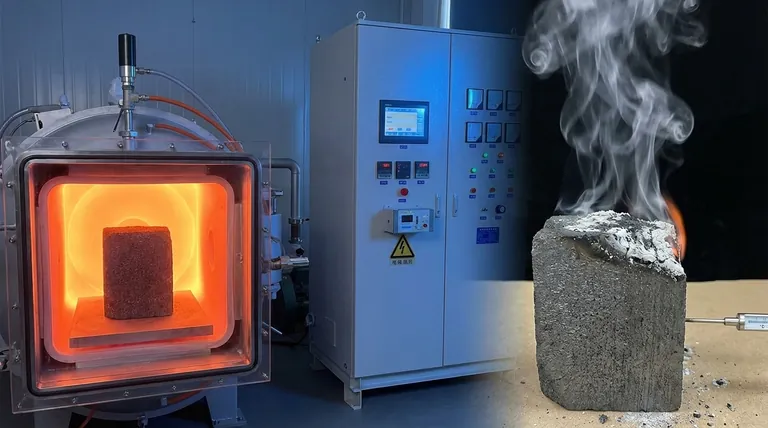
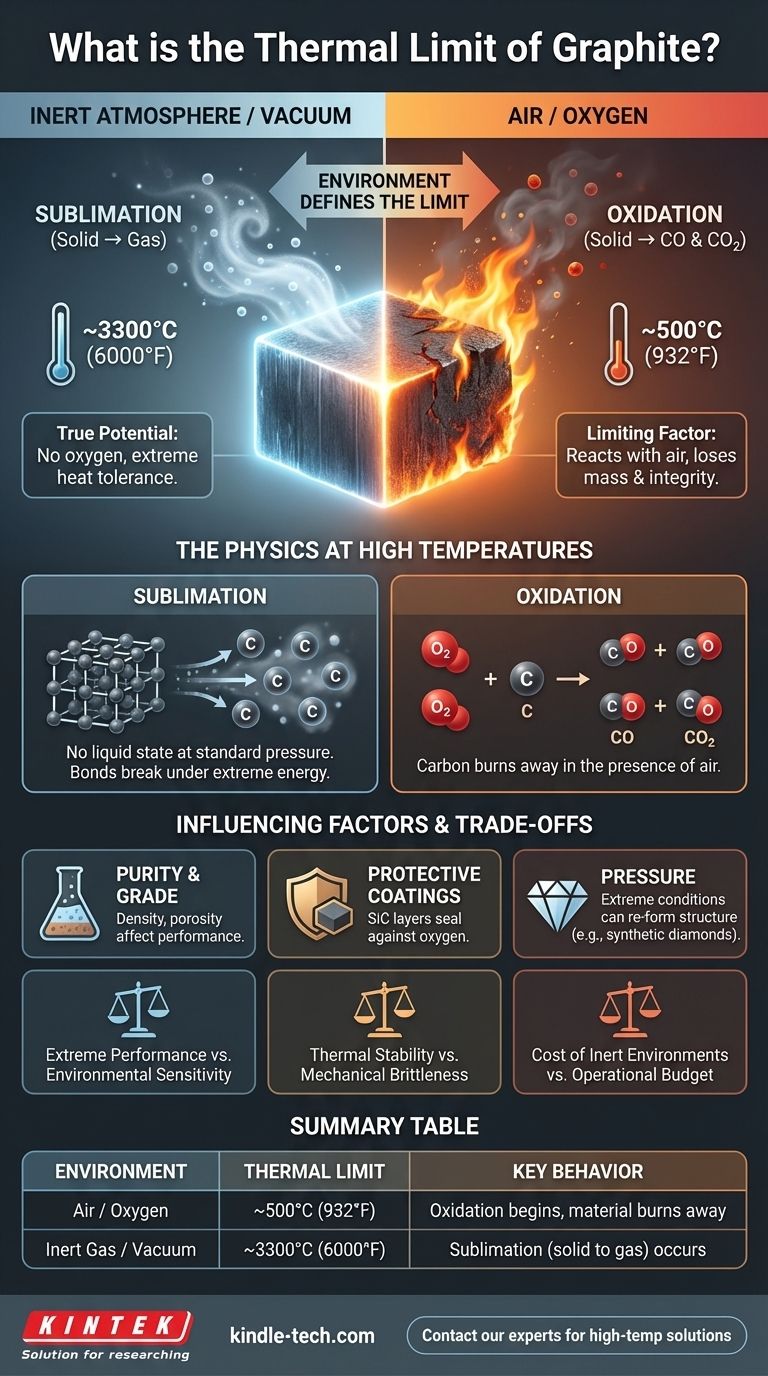
The thermal limit of graphite is not a simple melting point, as it behaves differently from most materials under heat. In an inert atmosphere or vacuum, pure graphite does not melt but instead sublimates—turning directly from a solid to a gas—at approximately 3300°C (6000°F). However, this impressive number changes drastically in the presence of oxygen.
The true thermal limit of graphite is defined by its environment. While it can withstand over 3000°C in a vacuum, its practical limit in open air is dictated by oxidation, which begins around 500°C (932°F).

The Physics of Graphite at High Temperatures
To properly leverage graphite, one must understand how it behaves under thermal stress. The distinction between its performance in a vacuum versus in air is the most critical factor for any application.
Sublimation, Not Melting
At standard atmospheric pressure, graphite has no liquid state. Instead of melting, its carbon atoms gain enough energy to break their bonds and escape directly into a gaseous phase. This process, known as sublimation, occurs at an exceptionally high temperature.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The 3300°C figure is only achievable in a controlled, inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) or a vacuum. In these conditions, there is no oxygen to react with the carbon atoms, allowing the material to reach its true thermal potential.
Oxidation: The Real-World Limiting Factor
When heated in the presence of air, graphite's performance is severely limited. Around 500°C (932°F), it begins to react with oxygen. This oxidation process converts the solid carbon into carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas, causing the material to literally burn away and lose mass and structural integrity.
Factors Influencing Graphite's Performance
The theoretical sublimation point is a baseline. In practice, several other variables can influence how graphite behaves at high temperatures.
Purity and Grade
Different manufacturing processes produce various grades of graphite, such as isostatic or extruded. While the fundamental chemical limits remain the same, factors like density, porosity, and grain size can affect the rate of oxidation and overall performance.
Protective Coatings
To overcome the limitation of oxidation, graphite components can be treated with protective coatings. Materials like silicon carbide (SiC) can form a protective layer, sealing the graphite from oxygen and dramatically increasing its usable temperature range in air.
Pressure
Under conditions of extremely high pressure and high temperature, graphite's carbon structure can re-form. This is the process used to create synthetic diamonds, highlighting how environmental conditions can completely transform the material's properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Graphite's remarkable thermal properties come with practical considerations that are crucial for successful implementation.
Extreme Performance vs. Environmental Sensitivity
The primary trade-off is clear: you gain one of the highest temperature resistances of any common material, but only if you can shield it from oxygen. This makes it ideal for vacuum furnaces but challenging for open-air applications.
Thermal Stability vs. Mechanical Brittleness
While thermally robust, graphite is a brittle material. It is susceptible to mechanical shock and can crack under rapid temperature changes (thermal shock), especially in complex geometries. Its structural strength must be considered alongside its thermal limit.
Cost of Inert Environments
Achieving the full potential of graphite requires creating a vacuum or an inert gas environment. The equipment and operational costs associated with maintaining this environment are a significant factor in a project's overall budget and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting graphite requires matching its unique properties to the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is vacuum or inert gas applications (e.g., vacuum furnaces, rocket nozzles): Graphite is an exceptional choice capable of performing reliably up to its sublimation point of ~3300°C.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature use in air (e.g., casting crucibles, brake linings): Unprotected graphite is limited to around 500°C; you must consider specialized grades or protective coatings for higher temperatures.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity at extreme heat: You must evaluate not just the sublimation temperature but also the material's mechanical properties and resistance to thermal shock in your specific design.
Understanding the environmental context is the key to successfully harnessing graphite's remarkable thermal capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Thermal Limit | Key Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Air / Oxygen | ~500°C (932°F) | Oxidation begins, material burns away |
| Inert Gas / Vacuum | ~3300°C (6000°F) | Sublimation (solid to gas) occurs |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab?
Graphite's performance is highly dependent on the right equipment and environment. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—from high-temperature furnaces to protective crucibles—that enable you to safely leverage graphite's extreme thermal capabilities.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you select the right materials and equipment for your specific high-temperature applications, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab



















