In the world of metallurgy, annealing is a critical heat treatment process used to intentionally reduce a metal's hardness and increase its ductility. This is achieved by heating the material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly, which alters its internal microstructure to make it more formable and less prone to fracture.
The core purpose of annealing is not simply to make a metal "softer." It is a strategic process used to reset a material's internal structure, relieving stresses and removing the brittleness induced by previous work, thereby preparing it for subsequent manufacturing operations.

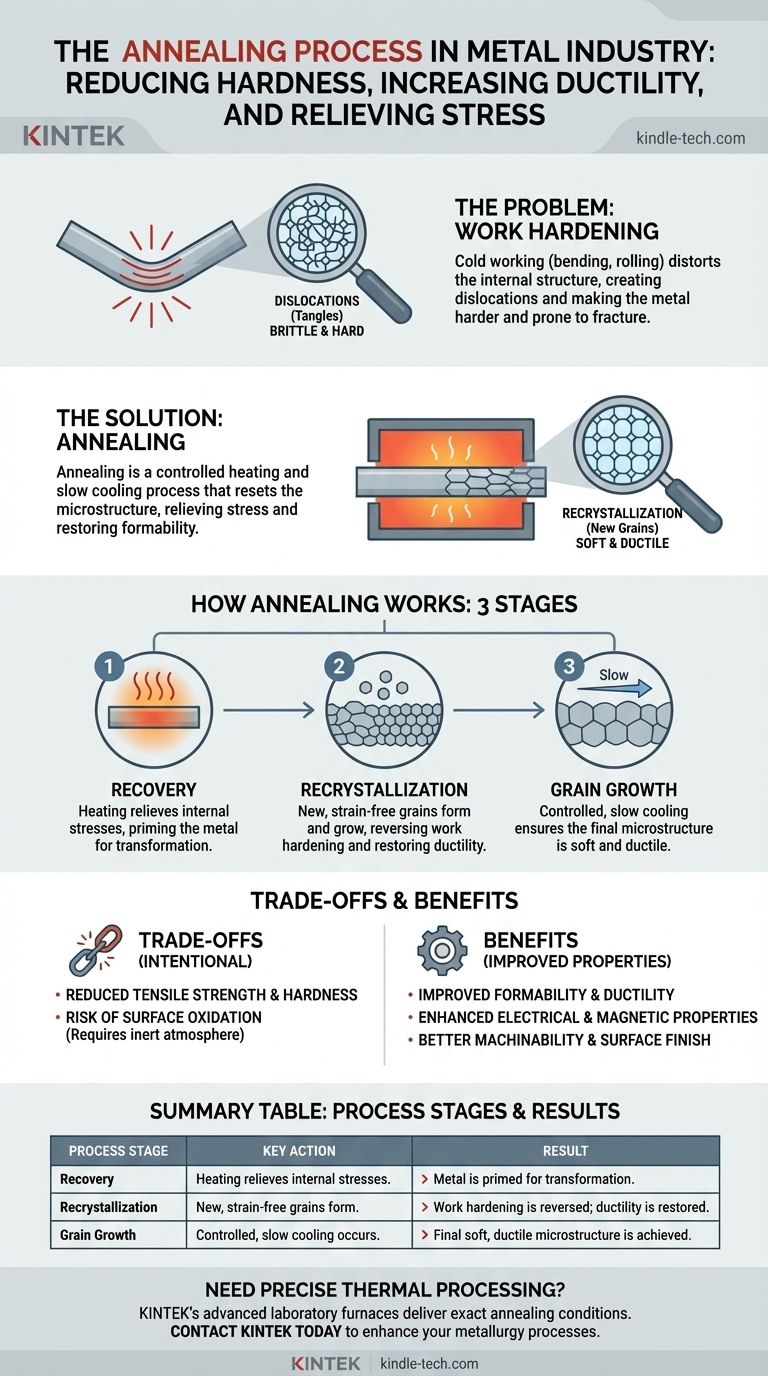
The Core Problem Annealing Solves: Work Hardening
To understand annealing, you must first understand the problem it is designed to fix. When metal is bent, stretched, rolled, or hammered at room temperature (a process known as cold working), it becomes progressively harder, stronger, and more brittle.
What is Work Hardening?
As metal is deformed, its internal crystal structure becomes distorted and stressed. This phenomenon, known as work hardening or strain hardening, makes further shaping of the metal increasingly difficult.
Eventually, a work-hardened metal will reach a point where any additional attempt to form it will cause it to crack or fracture.
The Microscopic View: Crystal Dislocations
At a microscopic level, metals are made of crystalline grains. Cold working creates and tangles imperfections in this crystal lattice, known as dislocations.
These tangled dislocations act like internal roadblocks, preventing the layers of atoms from sliding past one another. This resistance to atomic movement is what we perceive as increased hardness and brittleness.
How Annealing Reverses Work Hardening
Annealing is a controlled thermal process that systematically erases the effects of work hardening. It typically involves three distinct stages.
Stage 1: Recovery
As the metal is heated, it first enters the recovery stage. Here, the heat provides enough energy to relieve some of the internal stresses locked within the material. The primary crystal structure does not yet change, but the metal is primed for the next, more transformative stage.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature continues to rise, the process of recrystallization begins. This is the heart of annealing. New, strain-free grains begin to form and grow, consuming and replacing the old, deformed grains that were full of dislocations.
This fundamental change in the microstructure is what eliminates the brittleness from work hardening and restores the metal's ductility.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
After the new grains have fully replaced the old ones, a controlled cooling process begins. The rate of cooling is critical, as it influences the final size of the crystal grains. Slow cooling prevents the re-introduction of stress and ensures the metal remains soft and ductile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Annealing is a powerful tool, but it involves clear and intentional trade-offs. The decision to use it depends entirely on the desired final properties of the component.
The Intentional Loss of Strength
The primary trade-off of annealing is a reduction in tensile strength and hardness. The very process that makes the metal ductile also makes it weaker and less resistant to wear.
For this reason, annealing is the direct opposite of hardening processes, which are used to make components more durable. A part is annealed for formability, not for final in-service strength.
The Risk of Oxidation
Heating metal to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen will cause it to oxidize, forming a layer of scale on the surface. This scale can be detrimental to the part's finish and dimensions.
To prevent this, annealing is often performed in a controlled, inert atmosphere. Furnaces are purged with gases like nitrogen to displace oxygen and protect the metal's surface during the heating cycle.
Improved Secondary Properties
By creating a more uniform and perfect crystal structure, annealing can also improve other properties. For many metals, this refined structure enhances electrical conductivity and can optimize magnetic properties, making it a valuable step in producing components for the electrical industry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process is about aligning the material's properties with its intended function.
- If your primary focus is complex forming or deep drawing: Annealing is essential to increase ductility and prevent the material from cracking during the manufacturing operation.
- If your primary focus is improving the machinability of a work-hardened material: Annealing can dramatically reduce tool wear and improve surface finish by making the metal softer and less abrasive to cut.
- If your primary focus is maximizing final strength and wear resistance: You should avoid a full anneal and instead investigate hardening and tempering processes for the finished part.
By understanding annealing, you gain precise control over a material's properties, enabling more ambitious and reliable designs.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery | Heating relieves internal stresses. | Metal is primed for transformation. |
| Recrystallization | New, strain-free grains form. | Work hardening is reversed; ductility is restored. |
| Grain Growth | Controlled, slow cooling occurs. | Final soft, ductile microstructure is achieved. |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
KINTEK's advanced laboratory furnaces and controlled atmosphere systems are engineered to deliver the exact annealing conditions your metals require. Whether you're relieving stress in work-hardened parts or preparing materials for complex forming, our equipment ensures consistent, reliable results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our lab equipment solutions can enhance your metallurgy processes and improve your manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What temperature does titanium vaporize at? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Resistance for Aerospace
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the challenges of welding stainless steel? Overcome Warping, Sensitization, and Contamination



















