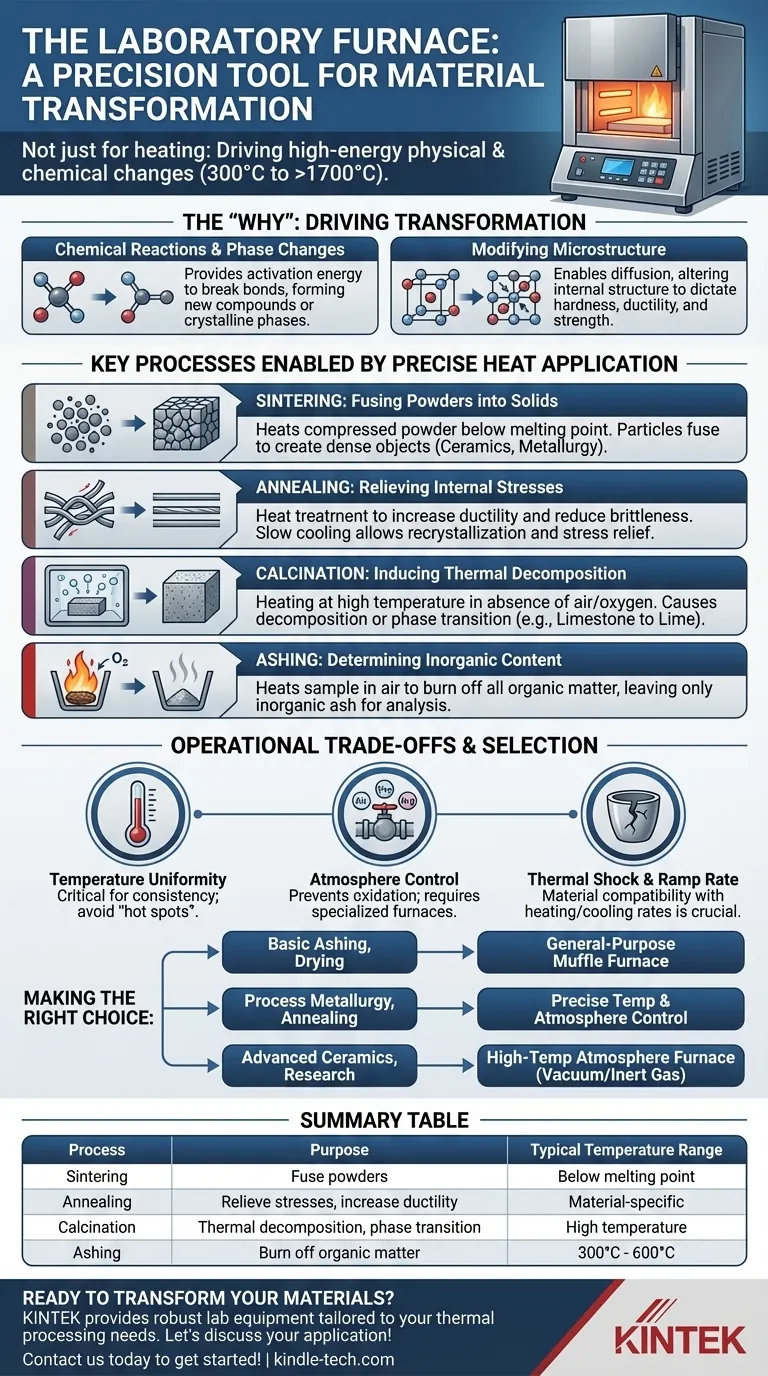
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing device used to fundamentally alter the physical and chemical properties of materials. Unlike a simple oven, a furnace operates at temperatures typically ranging from 300°C to over 1700°C to perform specific material transformations such as sintering, annealing, and ashing under highly controlled conditions.
A laboratory furnace is not merely for heating. It is a precision instrument for driving specific, high-energy transformations within a material's structure, enabling the creation of new materials and the analysis of existing ones.
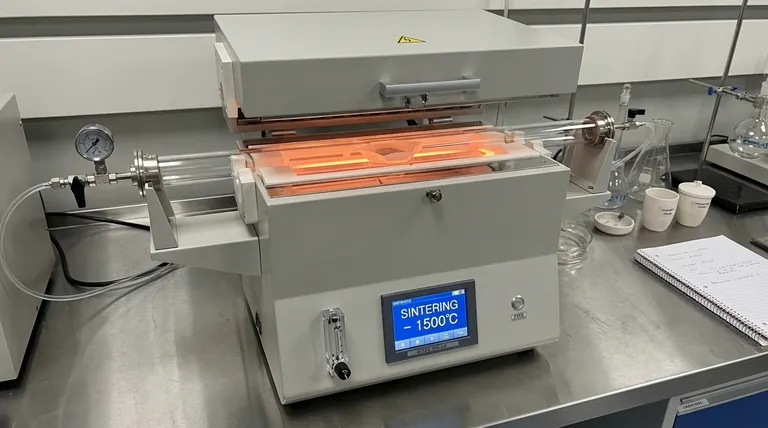

The Furnace as a Tool for Material Transformation
To understand the furnace's role, you must first understand why high heat is a critical variable in material science. Heat is a form of energy that can initiate or accelerate changes that would not otherwise occur at room temperature.
Driving Chemical Reactions and Phase Changes
High temperatures provide the necessary activation energy for many chemical reactions. This energy allows atomic bonds to break and reform, leading to the creation of entirely new compounds or different crystalline phases of the same compound.
Modifying Material Microstructure
Heat allows the atoms within a solid material to move and rearrange. This process, known as diffusion, can alter a material's internal structure—or microstructure—which directly dictates its physical properties like hardness, ductility, and strength.
Key Processes Enabled by a Laboratory Furnace
The general principles of heat application translate into several key laboratory and industrial processes. A furnace provides the controlled environment needed to execute them reliably.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into a Solid Mass
Sintering involves heating a compressed powder to a temperature below its melting point. The heat provides enough energy for the individual particles to fuse together, creating a solid, dense object. This is a foundational process in ceramics, metallurgy, and powder-based manufacturing.
Annealing: Relieving Internal Stresses
Annealing is a heat treatment that alters a material's properties to make it more ductile and less brittle. The material is heated to a specific temperature and held there before being cooled slowly. This process allows the microstructure to recrystallize, relieving internal stresses that may have built up during manufacturing.
Calcination: Inducing Thermal Decomposition
Calcination involves heating a material to a high temperature in the absence of air or oxygen. The goal is not to melt it, but to cause thermal decomposition, remove a volatile fraction, or induce a phase transition. A common example is converting limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide).
Ashing: Determining Inorganic Content
In analytical chemistry, ashing is used to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. A furnace heats the sample to a high temperature in the presence of air, burning off all organic matter and leaving only the inorganic ash for gravimetric analysis.
Understanding Operational Trade-offs
While powerful, a furnace is not a one-size-fits-all tool. Its effectiveness depends on understanding its limitations and selecting the right type for the job.
Temperature Uniformity and Control
The most critical factor is the ability to maintain a precise and uniform temperature throughout the chamber. Inexpensive furnaces may have "hot spots" that lead to inconsistent results, which is unacceptable for sensitive processes like annealing.
Atmosphere Control
Many advanced material processes require a specific atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation. Basic muffle furnaces operate in ambient air, while more advanced atmosphere furnaces allow for processing under a vacuum or in a controlled flow of inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
Thermal Shock and Material Compatibility
Not all materials or crucibles can withstand rapid temperature changes. The rate at which the furnace heats up and cools down (its ramp rate) is a crucial parameter. Subjecting an incompatible material to rapid heating can cause it to crack or shatter due to thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific scientific or industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is basic ashing, drying, or binder burnout: A simple, general-purpose muffle furnace with reliable temperature control is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is process metallurgy or annealing metals: You need a furnace with very precise temperature programming and, potentially, atmosphere control to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or materials research: A high-temperature atmosphere furnace with programmable ramp rates and the ability to operate under vacuum or inert gas is essential.
By understanding these core processes, you can utilize a laboratory furnace not just as a heat source, but as a powerful and precise instrument for material analysis and creation.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Fuse powders into solid objects | Below melting point |
| Annealing | Relieve internal stresses, increase ductility | Material-specific |
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition, phase transition | High temperature |
| Ashing | Burn off organic matter for analysis | 300°C - 600°C |
Ready to Transform Your Materials with Precision?
Choosing the right laboratory furnace is critical for achieving consistent, high-quality results in sintering, annealing, calcination, or ashing. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific thermal processing needs.
Our experts can help you select a furnace with the precise temperature control, atmosphere management, and ramp rates your research demands. Let's discuss your application and find the perfect solution to enhance your lab's capabilities.
Contact us today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















