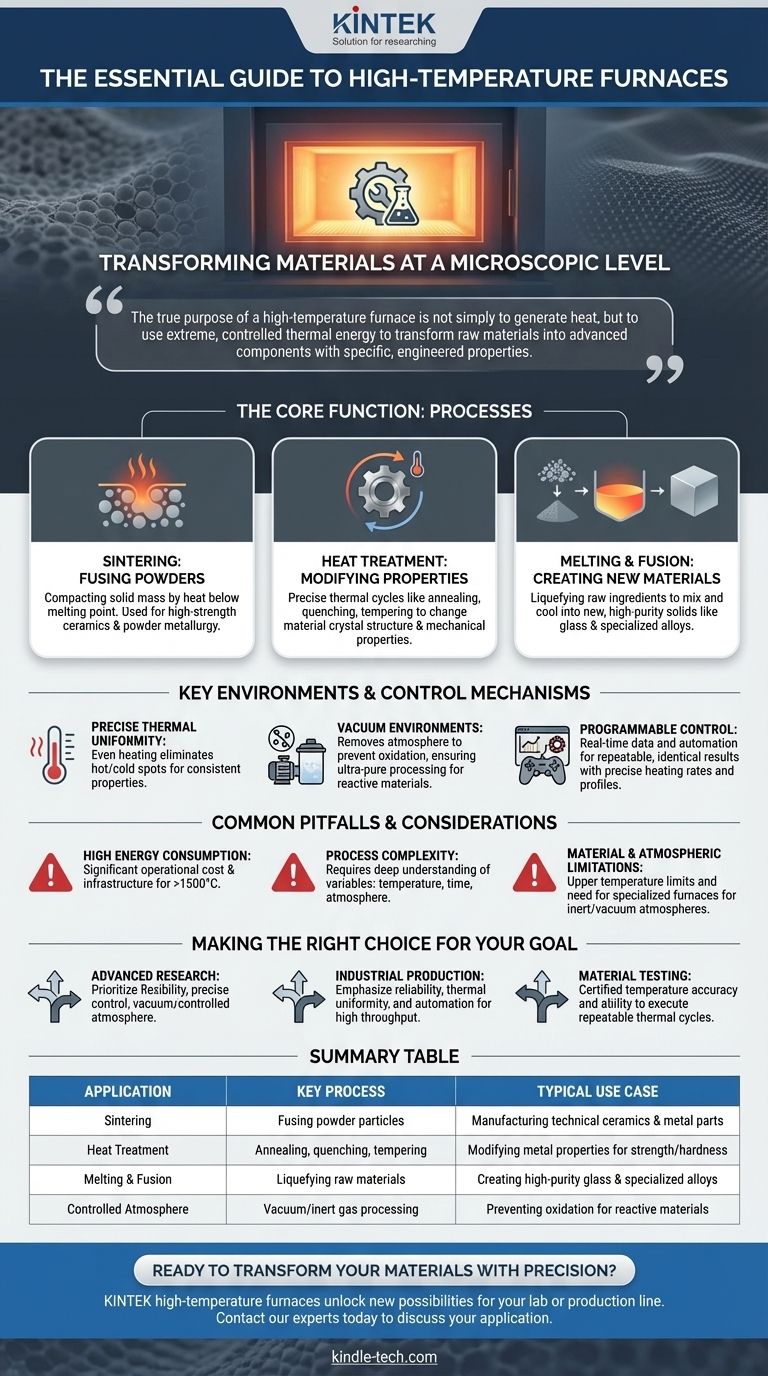
At its core, a high-temperature furnace is an essential tool for fundamentally altering the physical and chemical properties of materials. It is used across research and industry for processes like sintering technical ceramics, melting glass, and performing specific heat treatments on metals, all of which require a precisely controlled environment at temperatures often exceeding 1500°C.
The true purpose of a high-temperature furnace is not simply to generate heat, but to use extreme, controlled thermal energy to transform raw materials into advanced components with specific, engineered properties.

The Core Function: Transforming Materials at a Microscopic Level
The value of a high-temperature furnace lies in its ability to manipulate the internal structure of a material. This allows for the creation of components that are stronger, purer, or have unique characteristics unobtainable through other means.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into a Solid Mass
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
The intense heat causes the atoms in the powder particles to diffuse across the boundaries, fusing the particles together. This is a primary method for producing high-strength technical ceramics and parts via powder metallurgy.
Heat Treatment: Modifying Material Properties
Metals are often subjected to precise thermal cycles to change their mechanical properties.
Processes like annealing (softening and relieving stress), quenching (hardening), and tempering (reducing brittleness) all rely on a furnace's ability to achieve and hold specific temperatures to alter the material's crystal structure.
Melting and Fusion: Creating New Materials
For materials like glass or certain metal alloys, the furnace's role is to melt the raw ingredients completely.
This allows them to be mixed, purified, and then cooled into a new, homogenous solid form, from high-purity glass for labs to specialized metal alloys.
Key Environments and Control Mechanisms
Achieving these material transformations requires more than just raw heat. The process must be executed within a highly controlled environment to ensure quality and repeatability.
Achieving Precise Thermal Uniformity
For a part to have consistent properties, it must be heated evenly. High-temperature furnaces often position heating elements on multiple sides of the chamber to ensure there are no hot or cold spots.
This thermal uniformity is critical for reliable results in both scientific experiments and industrial production.
The Role of Vacuum Environments
Many materials, especially certain metals, will oxidize or become contaminated when heated in the presence of air.
A high-temperature vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere from the chamber. This creates an ultra-pure environment for processing reactive materials and achieving superior material quality.
Programmable Control for Repeatable Results
Modern furnaces use a thermocouple or other sensor to provide real-time temperature data to a controller.
This allows for high automation and programmable control, where an operator can define precise heating rates, hold times, and cooling profiles. This ensures that every production run or experiment is identical.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, these furnaces are specialized instruments with distinct operational challenges. Understanding them is key to successful application.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures of 1500°C and beyond requires a tremendous amount of electrical energy. This represents a significant operational cost and infrastructure requirement.
Process Complexity
Effective use requires a deep understanding of material science. Simply heating a material is not enough; the specific temperature, time, and atmosphere are all critical variables that must be controlled to achieve the desired outcome.
Material and Atmospheric Limitations
The furnace itself, and the materials being processed, have upper temperature limits. Furthermore, a standard muffle furnace is not suitable for processes that require an inert or vacuum atmosphere, which necessitates a more specialized and expensive vacuum furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace configuration depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is advanced research: Prioritize a furnace with maximum flexibility, highly precise programmable control, and the option for a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: Emphasize reliability, thermal uniformity, and automation to ensure high throughput and consistent quality for a specific, repeated process.
- If your primary focus is material testing: You need a furnace certified for its temperature accuracy and ability to execute repeatable thermal cycles according to industry standards.
Ultimately, a high-temperature furnace is an indispensable tool for pushing the boundaries of material science and manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Fusing powder particles | Manufacturing technical ceramics & metal parts |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, quenching, tempering | Modifying metal properties for strength/hardness |
| Melting & Fusion | Liquefying raw materials | Creating high-purity glass & specialized alloys |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Vacuum/inert gas processing | Preventing oxidation for reactive materials |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? A high-temperature furnace from KINTEK can unlock new possibilities for your laboratory or production line. Whether you are sintering advanced ceramics, performing critical heat treatments on metals, or melting specialized alloys, our lab equipment delivers the precise temperature control, thermal uniformity, and atmosphere management you need for repeatable, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace solution for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















