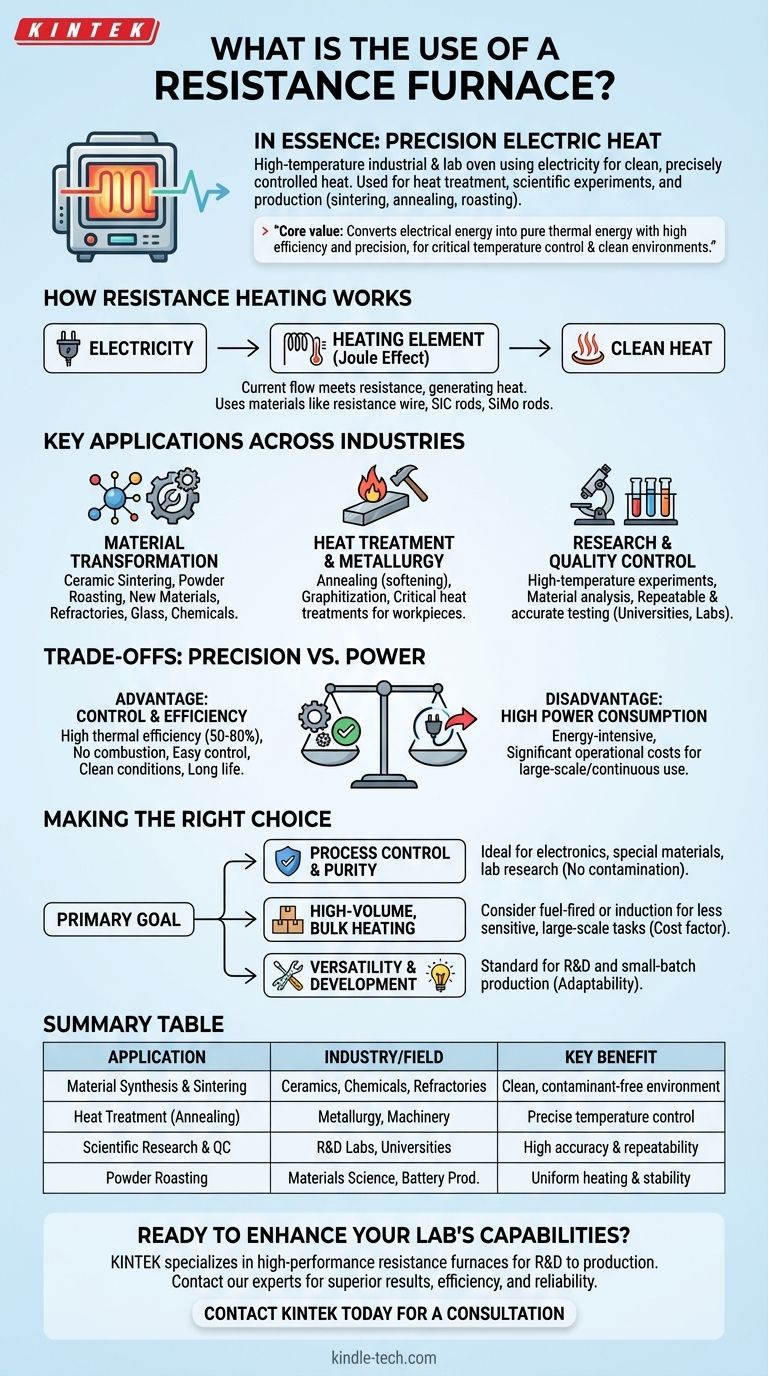
In essence, a resistance furnace is a high-temperature industrial and laboratory oven that uses electricity to generate clean, precisely controlled heat. Its primary uses are for the heat treatment of materials, high-temperature scientific experiments, and various production processes like sintering, annealing, and powder roasting across dozens of industries.
The core value of a resistance furnace lies in its ability to convert electrical energy into pure thermal energy with high efficiency and precision, making it indispensable for processes where temperature control and a clean environment are critical.

The Fundamental Principle: How Resistance Heating Works
A resistance furnace operates on a straightforward and reliable principle of physics. Understanding this is key to appreciating its role in modern industry and science.
Converting Electricity to Heat
The heat source is based on Joule heating. When an electric current is passed through a conductor, the material's natural resistance to the flow of electricity causes it to heat up. The furnace harnesses this effect by using specialized components that can withstand extreme temperatures.
The Role of Heating Elements
The furnace contains electric heating elements made from materials with high resistance and high melting points. Common materials include resistance wire, silicon carbide rods, and silicon molybdenum rods. The choice of element depends on the maximum temperature required for the specific application.
Key Applications Across Industries
The precise and clean nature of electric resistance heating makes this furnace a versatile tool used in nearly every field that requires high temperatures.
Material Transformation and Synthesis
Resistance furnaces are crucial for creating and modifying materials. This includes ceramic sintering, powder roasting, developing new materials, and processing refractories, glass, and chemicals.
Heat Treatment and Metallurgy
In metallurgy and machinery, these furnaces are used for processes that alter the physical properties of metals. Common applications include annealing (to soften metal), graphitization, and other critical heat treatments for demanding workpieces.
Research and Quality Control
Universities, scientific institutes, and industrial labs rely heavily on resistance furnaces. They are used for high-temperature experiments, material analysis, and quality control testing where repeatable and accurate temperature profiles are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Power
While incredibly useful, the resistance furnace is not the right tool for every job. Its selection involves a clear trade-off between operational benefits and costs.
The Advantage of Control and Efficiency
The greatest strength of a resistance furnace is its high thermal efficiency, often ranging from 50% to 80%. Because there is no combustion, the thermal system is easy to control, the working conditions are clean, and the furnace itself has a long operational life.
The Disadvantage of High Power Consumption
The primary drawback is its high power consumption. Converting electricity directly to heat is an energy-intensive process, which can lead to significant operational costs, especially for large-scale or continuous operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your primary goal. A resistance furnace excels in specific scenarios.
- If your primary focus is process control and material purity: The resistance furnace is ideal for applications in electronics, special materials, and laboratory research where contamination from combustion is unacceptable and temperature must be exact.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, bulk material heating: The high energy cost may make other technologies, such as fuel-fired or induction furnaces, a more economical choice for less sensitive, large-scale melting or heating tasks.
- If your primary focus is versatility and development: The resistance furnace is a standard for R&D and small-batch production due to its adaptability to different materials and processes.
Ultimately, a resistance furnace is the definitive tool when the precision and quality of the final product justify the cost of energy required to create it.
Summary Table:
| Application | Industry/Field | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Sintering | Ceramics, Chemicals, Refractories | Clean, contaminant-free environment |
| Heat Treatment (Annealing, etc.) | Metallurgy, Machinery | Precise temperature control for material properties |
| Scientific Research & Quality Control | R&D Labs, Universities | High accuracy and repeatability for experiments |
| Powder Roasting & Graphitization | Materials Science, Battery Production | Uniform heating and process stability |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, clean heat?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a wide range of resistance furnaces designed for your specific application—from R&D and material synthesis to quality control and production. Our experts can help you select the ideal furnace to achieve superior results, improve efficiency, and ensure process reliability.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in laboratory excellence!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















