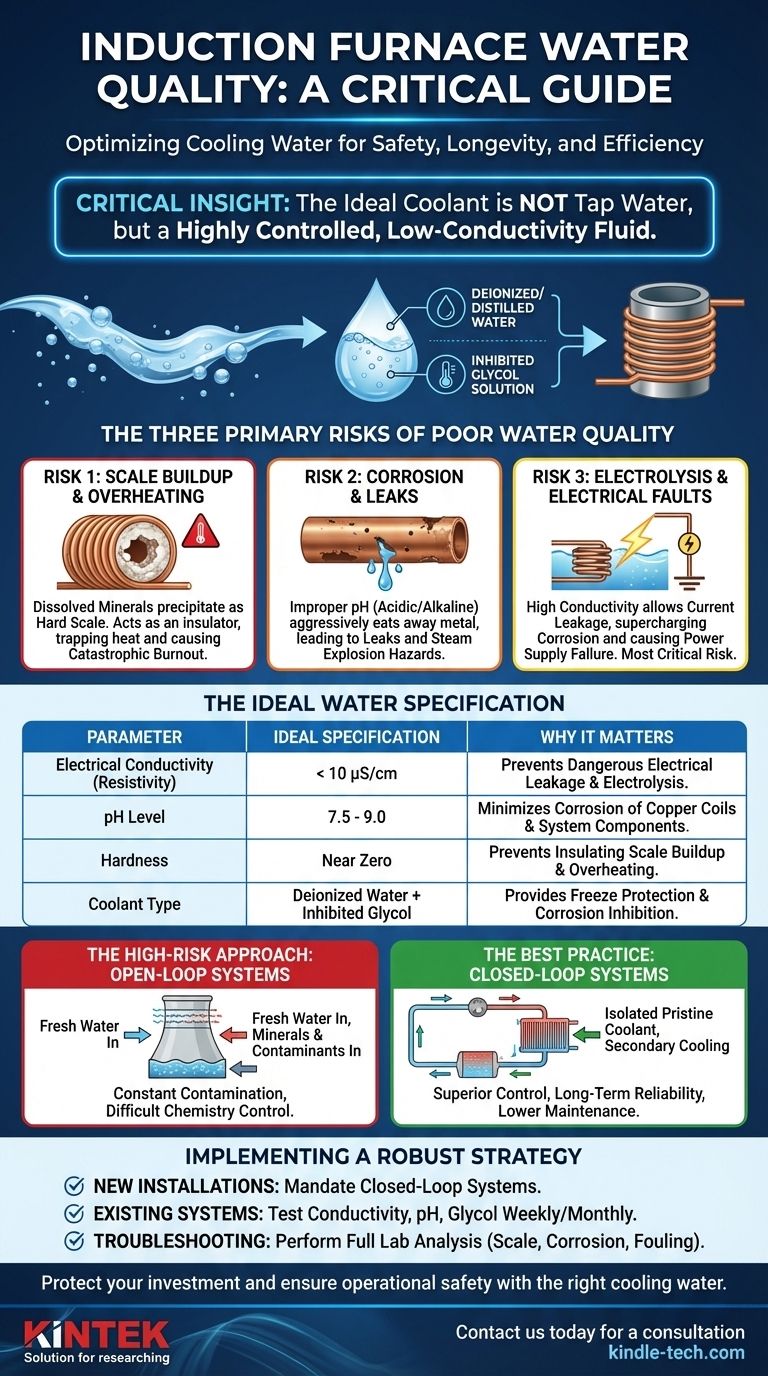
For an induction furnace, the ideal cooling water is not tap water, but a highly controlled fluid, typically a mixture of deionized or distilled water and an inhibited glycol solution. The single most important property is low electrical conductivity to prevent dangerous electrical faults, followed by a stable pH and near-zero hardness to stop corrosion and scale buildup. Neglecting these parameters risks catastrophic equipment failure.
The water in your induction furnace's cooling system is not just a utility—it is a critical, engineered component. Treating it as such by controlling its electrical and chemical properties is the most effective way to ensure operational safety, furnace longevity, and melting efficiency.

Why Water Quality is Mission-Critical
An induction furnace operates under extreme conditions, using immense electrical power to generate temperatures exceeding 1600°C (3000°F). The cooling system is the only thing preventing a multi-million dollar asset from self-destructing.
The Role of the Cooling System
The cooling water circulates through hollow copper induction coils and critical power supply components like thyristors or IGBTs. This system's job is to continuously remove enormous amounts of waste heat generated by electrical resistance and thermal radiation.
The High Cost of Failure
If cooling is compromised, the copper coil can overheat, soften, and rupture. A water leak inside a furnace filled with molten metal can cause a violent steam explosion, a life-threatening event that destroys the equipment and surrounding infrastructure.
The Three Primary Risks of Poor Water Quality
Simply ensuring water is flowing is not enough. The chemistry of the water presents three distinct threats to the integrity of your furnace.
Risk #1: Scale Buildup and Overheating
Untreated water contains dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium, which measure its "hardness." When heated, these minerals precipitate out and form a hard, insulating layer of scale on the inside of the copper coil.
This scale layer acts like a blanket, preventing the water from effectively removing heat. The coil temperature rises, efficiency drops, and the risk of a catastrophic burnout increases dramatically.
Risk #2: Corrosion and Leaks
The water's pH level determines its acidity or alkalinity. If the water is too acidic (low pH) or too alkaline (high pH), it will aggressively corrode the copper coil and other metallic components in the system.
This corrosion thins the coil walls from the inside out, eventually leading to pinhole leaks that can grow into a major rupture.
Risk #3: Electrolysis and Electrical Faults
This is the most critical and unique risk for induction systems. The induction coil carries thousands of amps of alternating current. If the water used for cooling is electrically conductive (due to dissolved minerals and ions), it provides a path for this current to leak to ground.
This electrical leakage, known as electrolysis, supercharges corrosion and rapidly eats away at the coil, causing deep pitting and premature failure. High conductivity can also cause electrical faults in the power supply.
Defining the Ideal Water Specification
To mitigate these risks, the cooling water must be treated as a precise dielectric and coolant fluid. While you should always follow your furnace manufacturer's specific guidelines, the industry standards are clear.
Electrical Conductivity (Resistivity)
This is the paramount specification. The goal is to use water that is a poor conductor of electricity. We measure this as conductivity (in microsiemens, μS) or its inverse, resistivity (in megohm-cm).
The ideal fluid is deionized (DI) or distilled water, which has nearly all conductive ions removed. A typical target is a conductivity of less than 10 μS/cm.
pH Level
The pH must be maintained in a narrow, non-corrosive range, typically between 7.5 and 9.0. Pure DI water can be slightly acidic and corrosive, which is why inhibitors are essential.
Hardness and Dissolved Solids
To prevent scale, water hardness should be virtually zero. Using DI or distilled water inherently solves this problem, as the process removes the minerals that cause hardness.
Additives: Glycol and Inhibitors
A mixture of DI water and ethylene or propylene glycol is the standard solution. The glycol provides freeze protection, while a package of chemical inhibitors mixed in with it serves to buffer the pH and passivate metal surfaces to prevent corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs: System Design
The type of cooling system you use has the single biggest impact on your ability to maintain proper water quality.
The High-Risk Approach: Open-Loop Systems
An open-loop system uses an evaporative cooling tower and continuously circulates "fresh" water. While cheap to install, this design is highly problematic. It constantly introduces minerals, oxygen, and biological contaminants, making it a constant, expensive battle to control water chemistry with chemical treatments.
The Best Practice: Closed-Loop Systems
A closed-loop system uses a sealed circuit of high-quality water/glycol solution that is cooled by a secondary heat exchanger (like a water-to-air chiller).
Although the initial investment is higher, this approach isolates the pristine coolant from contamination. It provides vastly superior control, safety, and long-term reliability, dramatically reducing the risk of failure and lowering maintenance costs.
Implementing a Robust Water Management Strategy
Proactive management of your furnace's cooling water is a non-negotiable part of a safe and profitable melting operation.
- If your primary focus is a new installation: Mandate a closed-loop cooling system from the start and charge it with the correct mixture of deionized water and inhibited glycol specified by the furnace OEM.
- If your primary focus is managing an existing system: Immediately test your water for conductivity, pH, and glycol concentration, and establish a weekly or monthly monitoring schedule to track trends and catch deviations early.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting cooling issues: Look beyond clogged filters or flow switches. Send a water sample to a lab for a full analysis to diagnose the root cause, whether it's scale, corrosion, or biological fouling.
Ultimately, viewing your cooling water as a critical machine component—and maintaining it accordingly—is the best investment you can make in your furnace's long-term health and safety.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Ideal Specification | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | < 10 μS/cm | Prevents dangerous electrical leakage and electrolysis. |
| pH Level | 7.5 - 9.0 | Minimizes corrosion of copper coils and system components. |
| Hardness | Near Zero | Prevents insulating scale buildup that causes overheating. |
| Coolant Type | Deionized Water + Inhibited Glycol | Provides freeze protection and corrosion inhibition. |
Protect your investment and ensure operational safety. The right cooling water is critical for your induction furnace's performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the correct coolant and maintenance strategy for your specific furnace model. Contact us today for a consultation and ensure your melting operations run safely and efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
People Also Ask
- How does induction furnace work? Achieve Fast, Clean, and Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the limitations of induction brazing? High Costs, Geometric Constraints, and More
- What are the requirements for induction heating? Achieve Fast, Precise, and Clean Heat
- What are the advantages of induction melting furnace? Achieve Purity, Efficiency, and Safety
- What role does a Vacuum Induction Melting furnace play in 12% Cr martensitic steel? Achieve Ultra-Pure Alloy Control
- How is the VIDP furnace designed to improve production efficiency? Maximize Uptime for Large-Scale Metal Production
- What is the difference between flame brazing and induction brazing? Precision vs. Flexibility for Your Brazing Needs
- What is induction furnace used for? Achieve Fast, Clean Metal Melting and Heat Treatment













