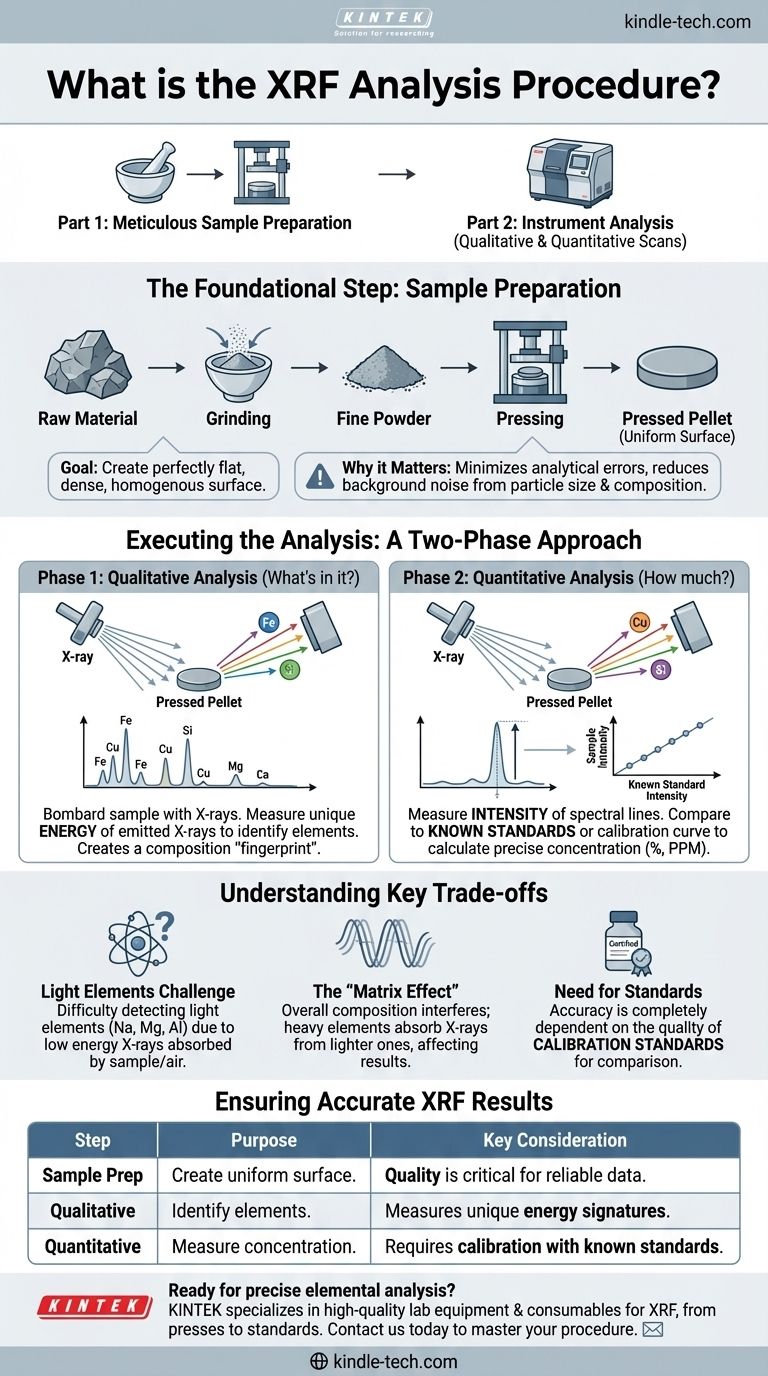
At its core, the X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis procedure is a two-part process for determining a sample's elemental composition. First, the material is meticulously prepared to ensure a uniform surface. Then, the instrument performs a qualitative scan to identify which elements are present, followed by a quantitative scan to measure how much of each element exists.
The accuracy of any XRF analysis depends less on the instrument itself and more on the quality of the sample preparation. A poorly prepared sample will yield unreliable data, regardless of the sophistication of the machine.
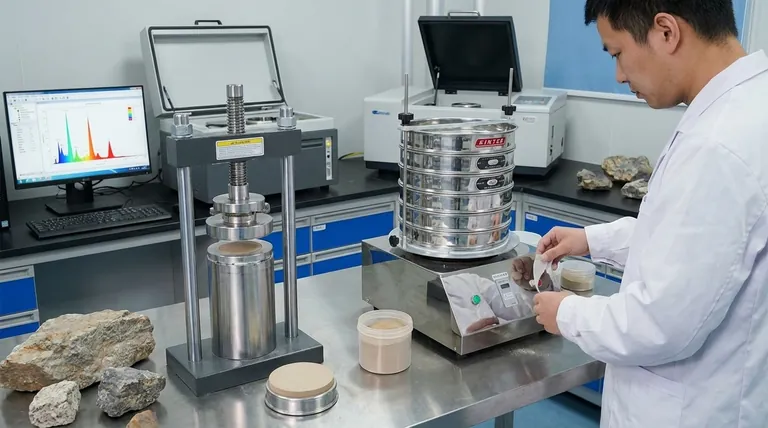

The Foundational Step: Meticulous Sample Preparation
The goal of sample preparation is to create a perfectly flat, dense, and homogenous surface to present to the X-ray beam. This minimizes analytical errors caused by the physical characteristics of the sample.
Why Sample Form Matters
The instrument's X-rays interact with the sample's surface. Factors like particle size, mineral composition, and particle density can scatter the X-ray beam inconsistently, creating background noise that hides the signals you want to measure.
The Standard Preparation Method
For most solid materials, the standard procedure involves grinding the sample into a very fine powder. This powder is then pressed under high pressure to form a smooth, solid disc known as a pressed pellet.
The Goal: Reducing Signal "Noise"
This process ensures that the X-ray beam interacts with a uniform surface. Grinding and pressing reduce background scattering, which makes the faint emission peaks from each element easier to detect and measure accurately.
Executing the Analysis: A Two-Phase Approach
Once the sample is prepared, the analysis itself happens in two distinct phases inside the spectrometer.
Phase 1: Qualitative Analysis (What's in the Sample?)
The instrument bombards the sample with high-energy X-rays, causing the atoms within to emit their own fluorescent X-rays. Each element emits X-rays at a unique, characteristic energy level.
By measuring the specific energy of the X-rays coming from the sample, the system can definitively identify every element present, creating a "fingerprint" of the material's composition.
Phase 2: Quantitative Analysis (How Much Is There?)
After identifying the elements, the instrument measures the intensity of the characteristic spectral lines for each one. A more intense signal corresponds to a higher concentration of that element.
To determine the exact concentration, the intensity of the sample's signal is compared to the intensity from a known standard or a pre-loaded calibration curve. This comparison allows the software to calculate the precise percentage or parts-per-million (PPM) of each element.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
XRF is powerful, but it's essential to be aware of its inherent limitations to interpret results correctly.
The Challenge of Light Elements
XRF has difficulty detecting very light elements (like sodium, magnesium, or aluminum). The characteristic X-rays they emit have very low energy and are often absorbed by the sample itself or the air before they can reach the detector.
The "Matrix Effect"
The overall composition of the sample—the "matrix"—can interfere with results. For example, a heavy element like iron can absorb the X-rays emitted by a lighter element like silicon, making the silicon concentration appear lower than it actually is. This is another reason why uniform sample preparation is so critical.
The Need for Standards
Quantitative analysis is fundamentally a process of comparison. Therefore, the accuracy of your results is completely dependent on the quality of the calibration standards you use. Without proper standards, concentration measurements are merely estimates.
How to Ensure Accurate XRF Results
Use these principles to guide your analytical approach based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is simple identification: A qualitative scan is sufficient, but remember that poor preparation can still mask the presence of trace elements.
- If your primary focus is precise concentration: Your process must include rigorous, repeatable sample preparation and the use of certified reference standards for calibration.
- If you are analyzing a complex material: Be aware of potential matrix effects and consider specialized sample preparation techniques, like fusion, to create a homogenous glass disc that eliminates these interferences.
By mastering sample preparation and understanding the two phases of analysis, you can reliably leverage XRF as a powerful tool for elemental determination.
Summary Table:
| Step | Purpose | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Create a uniform, flat surface for analysis. | Quality is critical for reliable data. |
| Qualitative Analysis | Identify which elements are present. | Measures unique energy signatures. |
| Quantitative Analysis | Measure the concentration of each element. | Requires calibration with known standards. |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable elemental analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your XRF analysis needs. From robust presses for creating perfect pellets to reliable calibration standards, our products are designed to ensure your sample preparation and analysis are accurate and efficient.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements and help you master the XRF procedure.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution



















