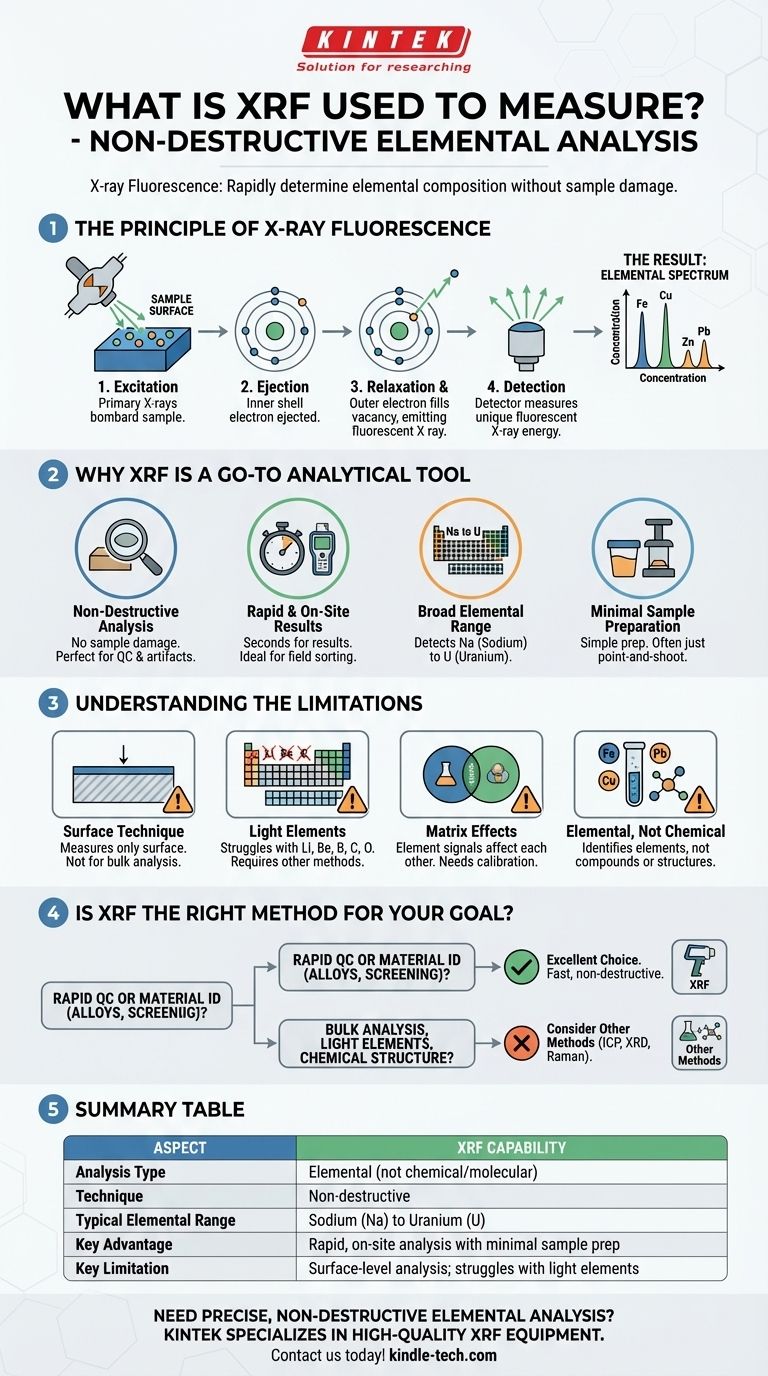
At its core, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a widely used analytical technique to determine the elemental composition of a material. It is a powerful, non-destructive method that bombards a sample with X-rays and then measures the unique secondary X-rays that are "fluoresced" or emitted back from the sample. Each element emits X-rays at a characteristic energy, allowing the instrument to identify precisely which elements are present and in what quantity.
The central takeaway is that XRF provides rapid, non-destructive elemental analysis, making it an invaluable tool for everything from quality control in manufacturing to analyzing precious artifacts. However, it is fundamentally a surface-level technique and has limitations in detecting very light elements.
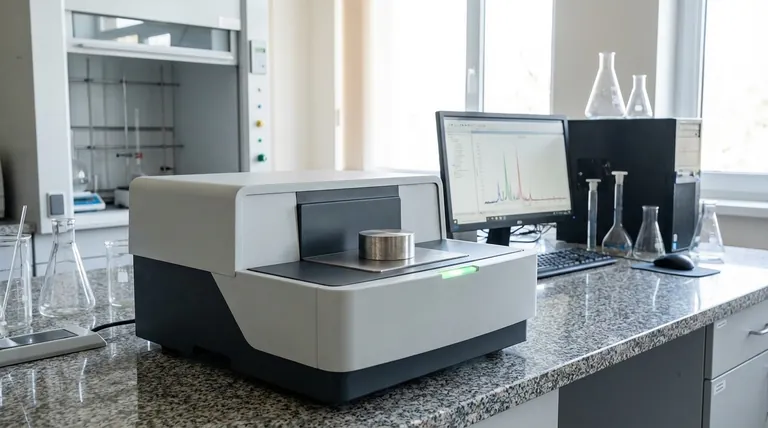

The Principle of X-ray Fluorescence
Understanding how XRF works reveals both its strengths and its limitations. The process is a sequence of events at the atomic level, triggered by an initial X-ray beam.
Step 1: Excitation
A primary X-ray beam, generated by an X-ray tube inside the analyzer, is directed at the surface of the sample.
Step 2: Ejection
When a primary X-ray strikes an atom in the sample, it can transfer enough energy to knock an electron out of one of its inner orbital shells (most commonly the K or L shell).
Step 3: Relaxation & Fluorescence
The atom is now unstable with a vacancy in its inner shell. To regain stability, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell immediately drops down to fill the empty spot.
As this electron moves to a lower energy state, it releases its excess energy in the form of a secondary X-ray. This emission is called X-ray fluorescence.
Step 4: Detection
The energy of this fluorescent X-ray is unique to the element from which it was emitted. It acts as an elemental "fingerprint." An X-ray detector in the analyzer measures the energy and intensity of all the fluorescent X-rays coming from the sample.
The Result: An Elemental Spectrum
The analyzer's software processes these signals to create a spectrum. This spectrum displays peaks at specific energy levels, which identify the elements present, while the intensity (height or area) of each peak corresponds to the concentration of that element in the sample.
Why XRF is a Go-To Analytical Tool
The principles behind XRF give it several key advantages that make it indispensable across numerous industries, from mining and metallurgy to environmental science and art conservation.
Non-Destructive Analysis
This is arguably XRF's most significant benefit. You can analyze a sample without altering or damaging it in any way. This is critical for quality control of finished products, testing precious metals, or examining priceless historical artifacts.
Rapid and On-Site Results
Handheld XRF analyzers can provide a comprehensive elemental breakdown in just a few seconds. This speed makes it ideal for fieldwork like sorting scrap metal, screening soil for contaminants, or checking consumer goods for restricted substances.
Broad Elemental Range
XRF is effective for detecting a wide range of elements, typically from sodium (Na) up to uranium (U) on the periodic table. This covers the majority of elements relevant to industrial and scientific applications.
Minimal Sample Preparation
For many applications, particularly with handheld analyzers, you can simply point the device at the material and get a reading. For more precise laboratory analysis, samples might be ground into a powder and pressed into a pellet, but this is still far less intensive than methods that require dissolving the sample.
Understanding the Limitations of XRF
No technique is perfect. Being an effective advisor means understanding where a tool is not the right fit. The limitations of XRF are a direct consequence of its underlying physics.
Primarily a Surface Technique
The primary X-rays only penetrate a very shallow depth into the material—typically from a few micrometers to a few millimeters, depending on the sample's density. This means XRF only measures the composition of the surface. If the sample is not homogeneous, the surface reading may not represent the bulk material's true composition.
Difficulty with Light Elements
XRF struggles to detect very light elements (those with an atomic number lower than sodium, such as lithium, beryllium, boron, and carbon). The fluorescent X-rays emitted by these elements are very low in energy and are easily absorbed by the air or even the detector window before they can be measured.
Matrix Effects
The signal from one element can be enhanced or suppressed by the other elements present in the sample (the "matrix"). Accurate quantitative analysis requires careful calibration with standards that closely match the sample's matrix or the use of sophisticated software corrections to account for these effects.
It's Elemental, Not Chemical
XRF tells you what elements are present and in what amounts. It does not provide information about the chemical state or molecular structure. For example, it can tell you the percentage of iron (Fe) in a sample of rust, but it cannot distinguish between different iron oxides like FeO and Fe₂O₃.
Is XRF the Right Method for Your Goal?
Choosing the correct analytical method depends entirely on the question you need to answer.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or material identification: XRF is an excellent, often unbeatable choice for its speed and non-destructive nature, especially for metal alloys, minerals, and regulatory compliance screening.
- If your primary focus is analyzing the bulk composition of a coated or non-uniform material: You must recognize that XRF will only measure the surface; for bulk analysis, the sample must be homogenized or a different, penetrative technique is required.
- If your primary focus is detecting light elements like lithium, carbon, or oxygen: XRF is not the right tool; you should consider techniques like Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) or Combustion Analysis.
- If your primary focus is identifying chemical compounds or crystal structures: You need a different method, such as X-ray Diffraction (XRD) or Raman Spectroscopy, which provide molecular and structural information.
XRF provides powerful, fast, and non-destructive elemental analysis, making it an indispensable tool when its surface-level nature and elemental focus are aligned with your analytical objective.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | XRF Capability |
|---|---|
| Analysis Type | Elemental (not chemical/molecular) |
| Technique | Non-destructive |
| Typical Elemental Range | Sodium (Na) to Uranium (U) |
| Key Advantage | Rapid, on-site analysis with minimal sample prep |
| Key Limitation | Surface-level analysis; struggles with light elements (e.g., Li, C, O) |
Need precise, non-destructive elemental analysis for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality XRF equipment and consumables to meet your specific lab needs. Whether you're in quality control, mining, or research, our solutions deliver the speed, accuracy, and reliability you require.
Let our experts help you choose the right tool for your goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your analytical capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials



















