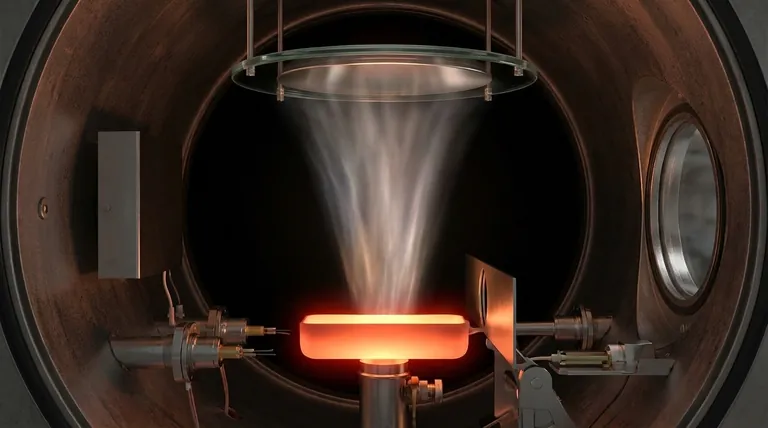
In essence, thermal evaporation in a vacuum is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique used to create extremely thin and pure films of a material. The process involves heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until its atoms sublimate or evaporate. These gaseous atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler substrate, forming a solid, uniform coating.
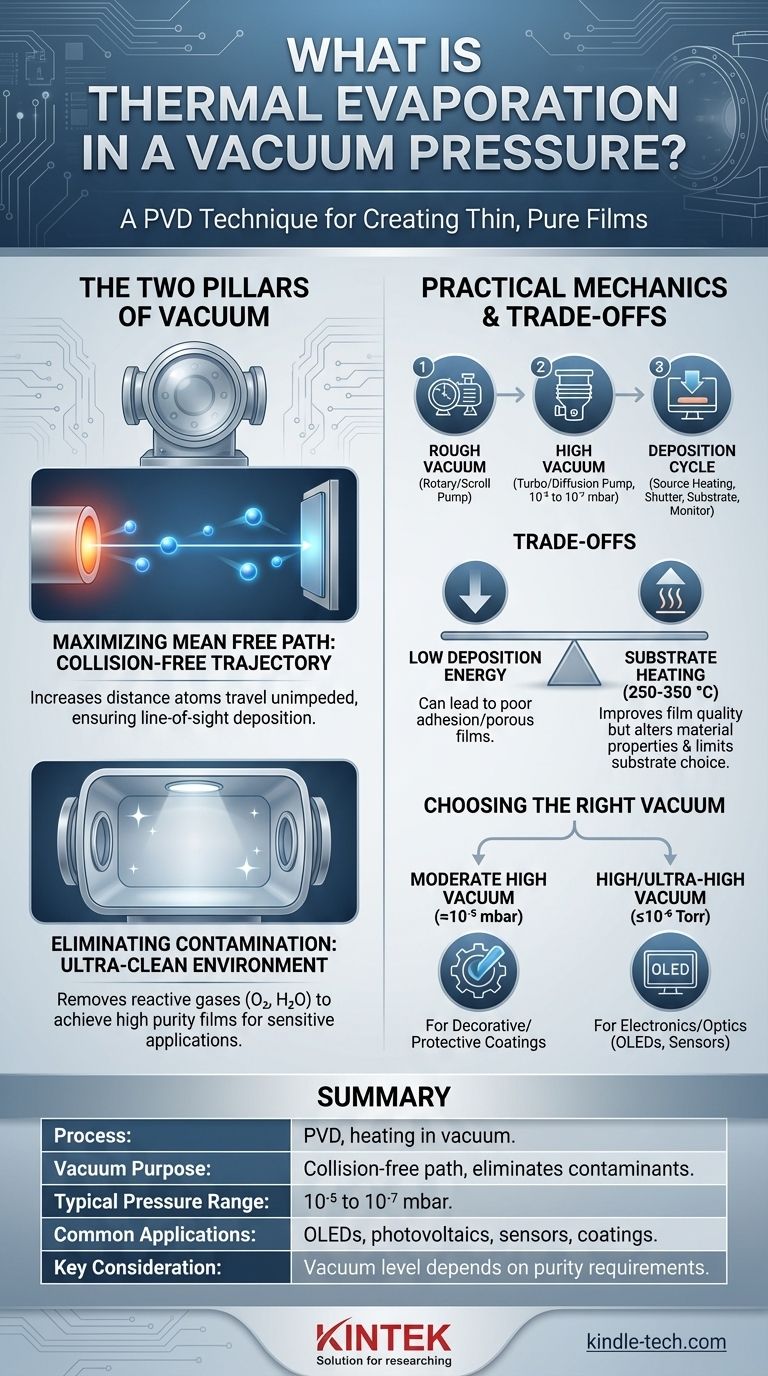
The core purpose of the vacuum is not merely to provide an empty space, but to actively control the deposition process. It serves two critical functions: it ensures evaporated atoms have a clear, collision-free path to the substrate and it eliminates gaseous contaminants to guarantee the purity of the resulting film.

The Two Pillars of Vacuum in Thermal Evaporation
To understand why the vacuum is non-negotiable, you must grasp the two fundamental problems it solves: atomic collisions and chemical contamination.
Maximizing the Mean Free Path
The mean free path is the average distance an atom can travel before it collides with another particle.
In normal air pressure, this distance is incredibly short. An evaporated atom would collide with air molecules billions of time per second, scattering it and preventing it from ever reaching the target substrate in a straight line.
A high vacuum dramatically increases the mean free path. By removing nearly all residual gas molecules, the vacuum ensures the distance between particles is much greater than the distance from the evaporation source to the substrate.
This creates a "line-of-sight" trajectory, allowing the evaporated atoms to travel unimpeded and deposit evenly onto the substrate.
Eliminating Film Contamination
The second critical function of the vacuum is to create an ultra-clean environment.
Gases that we consider harmless in the atmosphere, like oxygen and water vapor, are significant contaminants at the atomic scale. These molecules can become trapped in the growing film or chemically react with it.
This contamination can severely degrade the film's electrical, optical, or mechanical properties. For sensitive applications like organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) or photovoltaics, even trace amounts of oxygen can "quench" the active material, destroying its function.
To achieve high purity, the partial pressure of these reactive gases must be reduced to a minimal level, often below 10⁻⁶ Torr.
The Practical Mechanics of the Process
A thermal evaporation system is a precise combination of vacuum technology and heating elements designed for controlled deposition.
Achieving the Necessary Vacuum
Creating the required vacuum is a multi-stage process. A system typically uses a rotary vane or scroll pump to remove the bulk of the air from the chamber.
Once this "rough vacuum" is achieved, a turbomolecular or diffusion pump takes over to remove the remaining molecules, bringing the chamber pressure down to the high-vacuum range required for deposition, typically between 10⁻⁵ and 10⁻⁷ mbar.
The Deposition Cycle
Inside the chamber, the source material is placed in a crucible, often made of a refractory material like tungsten or molybdenum. A high electrical current is passed through the crucible, heating it until the source material evaporates.
A shutter is typically positioned between the source and the substrate. This allows the operator to stabilize the evaporation rate before opening the shutter to begin coating the substrate.
The thickness of the deposited film is monitored in real-time using a thin film monitor, such as a quartz crystal microbalance, which provides precise control over the final layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not without its limitations. The physics of the process introduces specific trade-offs that engineers must manage.
Low Deposition Energy
The atoms leaving the heated source do so with relatively low thermal energy. They arrive at the substrate without the high kinetic energy seen in other PVD processes like sputtering.
This low energy can sometimes result in a film with poor adhesion or an undesirable, porous microstructure.
The Need for Substrate Heating
To counteract the low deposition energy and improve film quality, the substrate is often heated to several hundred degrees Celsius (e.g., 250-350 °C).
This added thermal energy gives the arriving atoms more mobility on the substrate surface, allowing them to settle into a denser, more stable film structure.
However, this necessary heating means the resulting film's microstructure and properties can be significantly different from the bulk material that was evaporated. It also makes the process unsuitable for temperature-sensitive substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The required vacuum level is dictated entirely by the desired purity and properties of your final film.
- If your primary focus is a simple metallic coating for decorative or protective purposes: A moderate high vacuum (around 10⁻⁵ mbar) is often sufficient to ensure good adhesion and coverage.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity film for electronics or optics (OLEDs, sensors): A high or ultra-high vacuum (10⁻⁶ Torr/mbar or lower) is non-negotiable to prevent performance-killing contamination.
- If your primary focus is controlling the film's crystal structure or density: Your attention must be on balancing the vacuum pressure with precise control over the substrate temperature and deposition rate.
Ultimately, mastering thermal evaporation requires treating the vacuum not as a passive backdrop, but as the primary variable controlling the purity and integrity of your deposited material.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | A PVD technique where a material is heated in a vacuum to evaporate and condense on a substrate. |
| Vacuum Purpose | Ensures a collision-free path for atoms and eliminates contaminants for film purity. |
| Typical Pressure Range | 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ mbar (Torr). |
| Common Applications | OLEDs, photovoltaics, sensors, optical coatings, and decorative/metallic layers. |
| Key Consideration | Vacuum level is critical and depends on the required film purity and application. |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity thin films for your laboratory?
Thermal evaporation is a cornerstone technique for creating the advanced materials that power modern technology. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master this process, from robust vacuum systems to durable evaporation sources.
Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, optical components, or specialized coatings, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for reliable and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thermal evaporation requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition



















