At its core, heat treating steel involves two primary components: a specialized furnace for precise temperature control and a carefully managed atmosphere or quenching medium to direct the steel's transformation. The furnace provides the necessary thermal energy, while the surrounding environment—be it specific gases, liquids, or even a vacuum—controls the chemical reactions and cooling rate that ultimately define the steel's final properties.
The crucial insight is that heat treatment is not simply about heating and cooling steel. It is a highly controlled process of manipulating steel's internal crystalline structure through precise thermal cycles and chemical environments to achieve specific, predictable outcomes like enhanced hardness, softness, or durability.

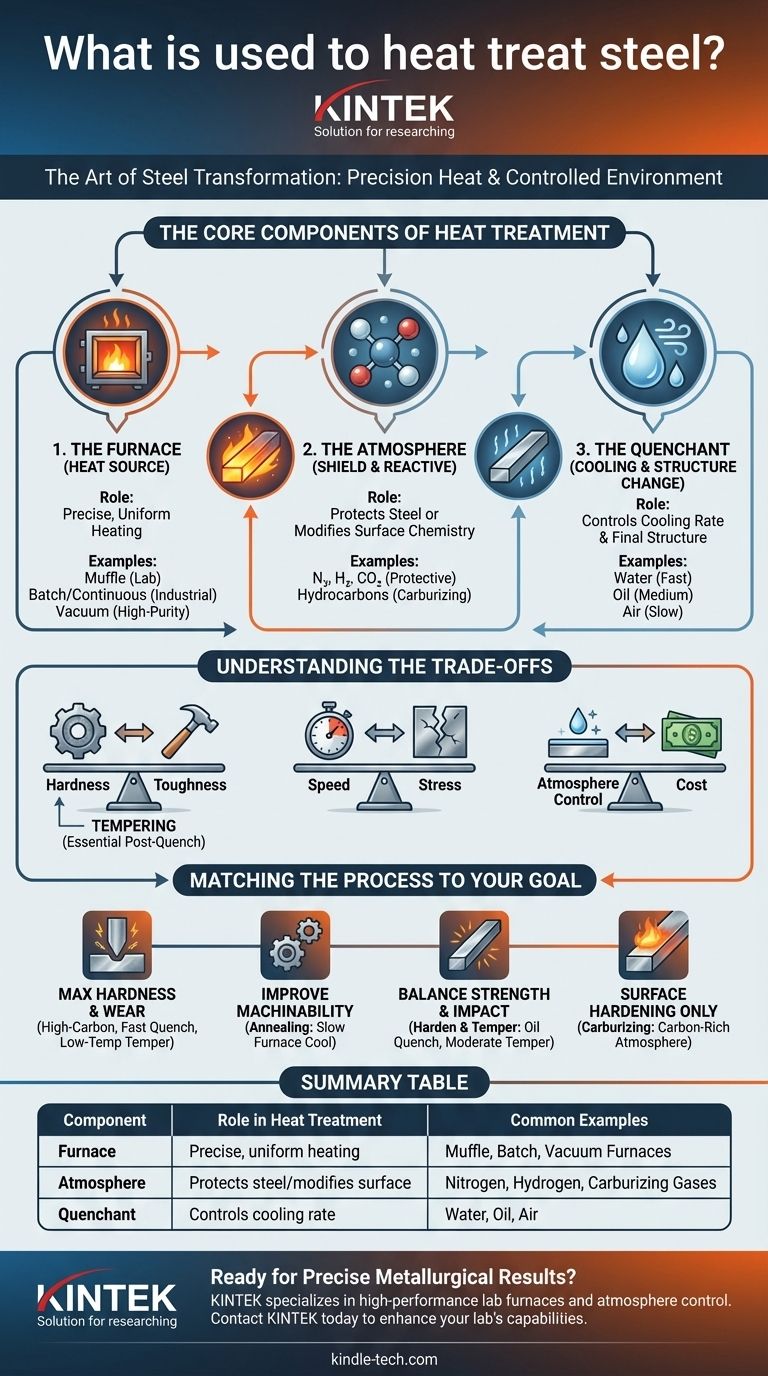
The Core Components of Heat Treatment
To understand the process, we must look at the three critical elements used to transform steel: the heat source, the protective atmosphere, and the cooling medium. Each plays a distinct role in the final result.
The Furnace: The Source of Heat
The furnace is the heart of the operation, responsible for bringing the steel to a specific temperature and holding it there uniformly. The type of furnace depends on the scale and goal of the process.
A common type for lab work or small parts is a muffle furnace. This design isolates the steel from the direct flame, allowing for clean heating and better control over the immediate environment.
For larger industrial applications, batch furnaces (like box or pit furnaces) or continuous furnaces (where parts move through on a conveyor) are used for high-volume production. Vacuum furnaces represent a high-purity option, removing all atmospheric gases to prevent any surface reactions.
The Atmosphere: The Protective and Reactive Shield
Heating steel to high temperatures (often above 1,500°F / 815°C) makes it highly reactive with oxygen in the air, causing undesirable scale and decarbonization. To prevent this, a controlled atmosphere is used.
The gases mentioned—nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide—are the building blocks of these atmospheres. Nitrogen is often used as an inert base gas to displace oxygen.
In some cases, the atmosphere is intentionally reactive. Hydrocarbons (like methane or propane) are introduced in a process called carburizing to diffuse carbon into the surface of low-carbon steel, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer case.
The Quenchant: The Catalyst for Structural Change
The rate at which steel is cooled from its treatment temperature is just as important as the heating itself. This rapid cooling, known as quenching, locks the steel's internal structure into a hard state called martensite.
Common quenching mediums, or quenchants, include water, brine (saltwater), various oils, and even air. The choice of quenchant determines the cooling speed. Water provides a very fast, severe quench, while oil is slower and less harsh.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of equipment and process parameters is a balancing act. Every decision involves a trade-off between desired properties, cost, and potential risks.
Hardness vs. Toughness
The fundamental trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and toughness. A process that creates extreme hardness (like a rapid water quench) also tends to make the steel brittle and susceptible to cracking.
This is why a secondary process called tempering is almost always performed after hardening. Tempering involves reheating the steel to a much lower temperature to relieve stress and sacrifice a small amount of hardness in exchange for a significant gain in toughness.
Speed vs. Stress
The speed of the quench directly correlates to the amount of internal stress induced in the part. A faster quench creates more hardness but also more stress.
Using a slower quenchant like oil can reduce the risk of distortion or cracking, especially in complex shapes or high-carbon steels, but may not achieve the absolute maximum possible hardness.
Atmosphere Control vs. Cost
Using a sophisticated controlled atmosphere or a vacuum furnace produces superior results, with clean, scale-free parts that require less post-treatment finishing.
However, this equipment is significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than a simple air-fired furnace. For applications where surface finish is not critical, heating in air may be a more economical choice, accepting that some surface scaling will occur.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right heat treatment method is entirely dependent on what you need the steel to do.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use a high-carbon steel, heat it to its critical temperature, and quench it rapidly in water or brine, followed by a low-temperature temper.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Use an annealing process, which involves heating the steel and then letting it cool very slowly inside the furnace to make it as soft as possible.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength and impact resistance: Use a standard harden and temper process, quenching in a medium like oil and then tempering at a moderate temperature to achieve a tough, durable structure.
- If your primary focus is hardening only the surface: Use a case-hardening process like carburizing, which uses a carbon-rich atmosphere to create a hard shell on a softer, tougher core.
Ultimately, the tools of heat treatment are chosen to precisely guide steel toward its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Heat Treatment | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Provides precise, uniform heating | Muffle, Batch, Vacuum Furnaces |
| Atmosphere | Protects steel or modifies surface chemistry | Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Carburizing Gases |
| Quenchant | Controls cooling rate to set final structure | Water, Oil, Air |
Ready to achieve precise metallurgical results in your lab? The right heat treatment equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, atmosphere control systems, and consumables tailored for laboratory applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect setup for processes like annealing, hardening, or tempering. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific steel treatment needs and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















