At its core, vacuum deposition of aluminum is a high-tech manufacturing process where solid aluminum is vaporized inside a vacuum chamber and then allowed to condense onto a target object, forming an extremely thin and uniform metallic film. This technique is the foundation for creating everything from the reflective layer in your car's headlights to the protective barrier inside a bag of potato chips.
The critical insight is that using a vacuum is not just an incidental detail—it is the key to the entire process. The vacuum removes air and other contaminants, allowing pure aluminum atoms to travel unimpeded and bond to a surface, creating a flawless film with properties unattainable through conventional methods like painting or plating.

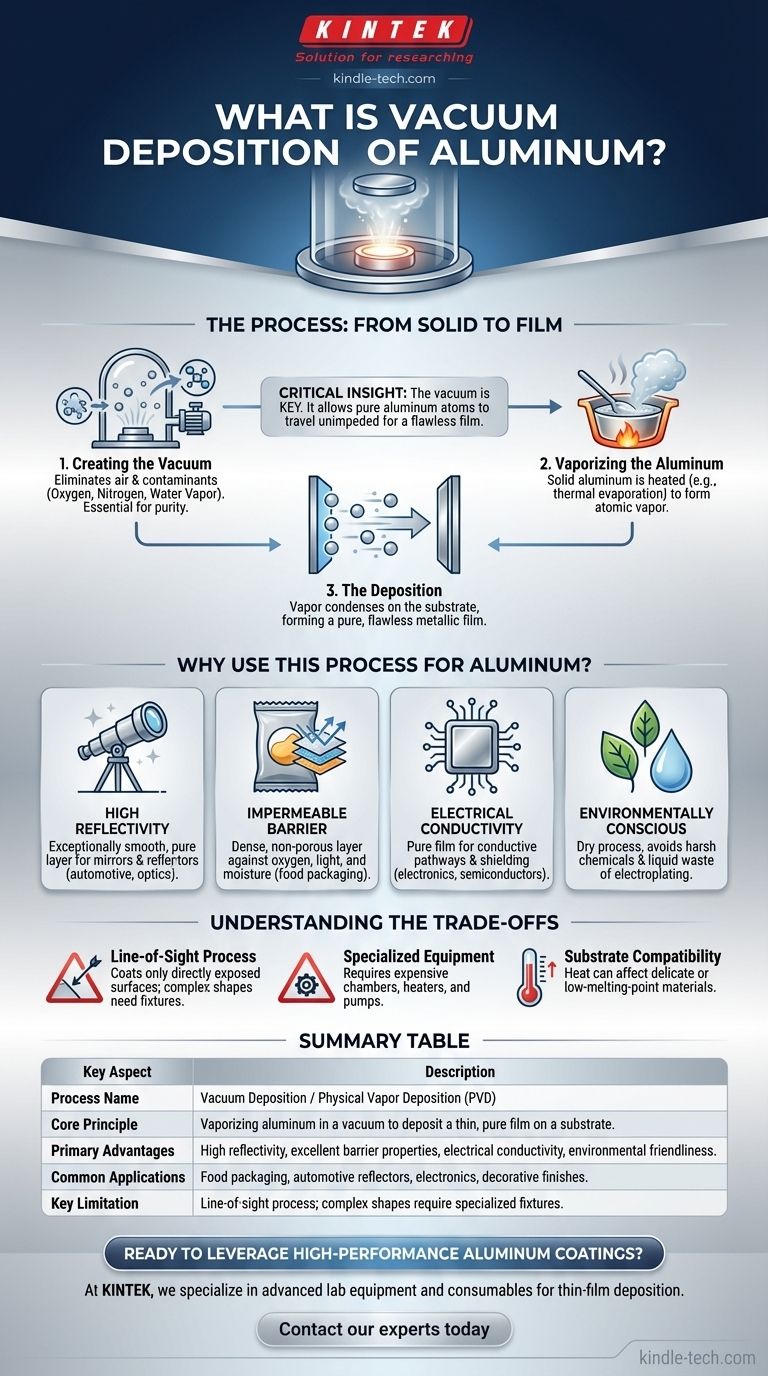
How the Process Works: From Solid to Film
Vacuum deposition, sometimes called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), is a precisely controlled, multi-stage process. Each step is critical to achieving a high-quality final coating.
Stage 1: Creating the Vacuum
The first step is to place the aluminum source and the object to be coated (the substrate) inside a sealed chamber. Almost all the air is then pumped out, creating a near-vacuum environment.
This step is crucial because it eliminates particles like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor that could otherwise react with the hot aluminum vapor, causing impurities and defects in the final film.
Stage 2: Vaporizing the Aluminum
Once the vacuum is established, the solid aluminum is heated until it evaporates, turning directly into a gas. This is typically done using methods like thermal evaporation, where the aluminum is heated in a small crucible until it boils.
The result is a cloud of individual aluminum atoms ready to be deposited.
Stage 3: The Deposition
The vaporized aluminum atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber until they strike the cooler surface of the substrate.
Upon contact, they rapidly cool and condense back into a solid state, forming a thin, even, and highly pure layer of aluminum that conforms perfectly to the substrate's surface.
Why Use This Process for Aluminum?
While other methods can coat a surface, vacuum deposition is chosen when the specific properties of the aluminum film are paramount. The process delivers unique advantages rooted in its physics.
For Creating Highly Reflective Surfaces
Aluminum is naturally very reflective. The vacuum deposition process creates an exceptionally smooth and pure aluminum layer, maximizing this reflectivity without the hazing or impurities that can occur in open-air processes.
This is why it's the standard for coating telescope mirrors, automotive lighting reflectors, and decorative "chrome-look" plastics.
For Forming Impermeable Barrier Layers
A thin film of vacuum-deposited aluminum is an outstanding barrier against oxygen, light, and moisture. The process creates a dense, non-porous layer that is impossible to achieve with other methods.
This is essential in the food packaging industry—the shiny layer inside snack bags and coffee pouches is aluminum, preserving freshness and extending shelf life.
For Electrical Conductivity
The purity of the deposited aluminum film makes it an excellent electrical conductor. It's used in electronics to create thin conductive pathways, capacitor layers, and shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
An Environmentally Conscious Choice
As noted in industrial analyses, vacuum deposition is considered a "dry process." It avoids the harsh chemicals and liquid waste associated with traditional electroplating methods for materials like chromium and cadmium.
This makes it an attractive alternative for companies seeking to reduce their environmental impact while achieving a durable, metallic finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Understanding the limitations of vacuum deposition is key to using it effectively.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the aluminum atoms travel in a straight line, they can only coat surfaces that have a direct "line of sight" to the vapor source.
Coating complex, three-dimensional shapes with hidden surfaces requires sophisticated rotating fixtures to expose all areas, which can add complexity and cost.
It Requires Specialized Equipment
Vacuum chambers, high-power heating sources, and powerful pumps are complex and expensive pieces of industrial equipment. This makes the process less accessible for small-scale or low-cost applications.
Substrate Compatibility Matters
The deposition process, particularly the heat from the vapor source, can affect the substrate. While ideal for metals, glass, and many high-temperature plastics, it requires careful control when coating delicate or low-melting-point materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use aluminum vacuum deposition depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product.
- If your primary focus is high reflectivity: This process is the industry standard for creating brilliant, mirror-like finishes on glass, metal, and plastic.
- If your primary focus is creating a protective barrier: It is the superior choice for flexible packaging and electronics where blocking moisture, oxygen, or light is critical.
- If your primary focus is a chrome-like decorative finish: It provides a durable and environmentally friendlier alternative to traditional chrome electroplating.
- If your primary focus is thin-film conductivity: It is a reliable method for applying pure, conductive aluminum layers in semiconductor and electronics manufacturing.
By controlling matter at the atomic level in a vacuum, this process delivers a level of purity and performance that turns a common material like aluminum into a high-performance coating.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Name | Vacuum Deposition / Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Vaporizing aluminum in a vacuum to deposit a thin, pure film on a substrate. |
| Primary Advantages | High reflectivity, excellent barrier properties, electrical conductivity, environmental friendliness. |
| Common Applications | Food packaging, automotive reflectors, electronics, decorative finishes. |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-sight process; complex shapes require specialized fixtures. |
Ready to leverage high-performance aluminum coatings for your products?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials research and development, including solutions for thin-film deposition processes. Whether you are developing new packaging, refining electronic components, or creating specialized optics, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's innovation in coating technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does the vacuum pump system influence magnesium morphology? Control Pressure for High-Purity Crystallization
- Why is a vacuum annealing furnace required for Inconel 713LC & 738? Ensure Peak Superalloy Performance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Purity and Precision for High-Performance Metals
- What changes in the annealing process? A Guide to the 3 Key Microstructural Stages
- What do you understand by intermittent and continuous furnaces? Optimize Your Industrial Heating Process
- Why is a vacuum furnace used for degassing Al-4Cu alloy powders? Ensure Maximum Density and Material Integrity
- What is a resistance heating furnace? Achieve Precise, Clean High-Temperature Processing
- What is catalytic fast pyrolysis process? The Key to Upgrading Bio-Oil for Clean Fuel



















