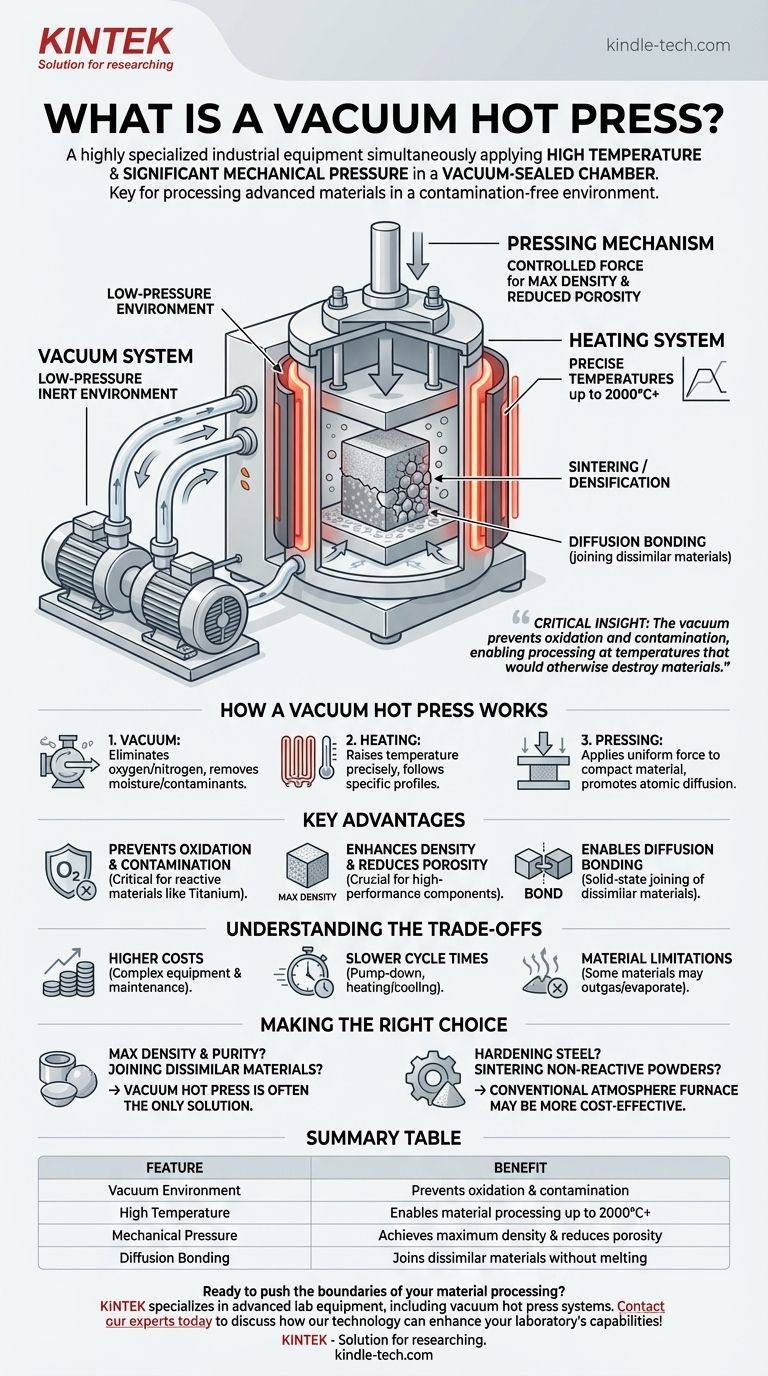
At its core, a vacuum hot press is a highly specialized piece of industrial equipment that simultaneously applies high temperature and significant mechanical pressure to a material inside a vacuum-sealed chamber. This unique combination allows for the processing, bonding, and densification of advanced materials in a precisely controlled, contamination-free environment that would be impossible to achieve in open air.
The critical insight is that the vacuum is not merely an accessory; it is the enabling factor. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, the hot press prevents oxidation and contamination, allowing materials to be bonded and formed at temperatures that would otherwise destroy them.

How a Vacuum Hot Press Works
A vacuum hot press integrates three distinct systems—vacuum, heating, and pressing—into a single, synergistic process. Understanding how these components interact is key to understanding the machine's capabilities.
The Vacuum System: Creating the Inert Environment
The process begins by placing materials inside a sealed chamber. Powerful pumps then remove the air, creating a low-pressure, or vacuum, environment.
This step is fundamental. It eliminates atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen, which would aggressively react with and degrade most materials at high temperatures. It also removes moisture and other volatile contaminants.
The Heating System: Achieving Precise Temperatures
Once the vacuum is established, heating elements—often made of graphite or refractory metals—raise the temperature inside the chamber.
These systems are designed for extreme precision, allowing operators to follow specific temperature profiles, or "recipes," that are critical for achieving the desired material properties. Temperatures can often exceed 2000°C (3632°F).
The Pressing Mechanism: Applying Controlled Force
While the material is at its target temperature, a hydraulic or electromechanical press applies a controlled, uniform force.
This pressure compacts the material, squeezing out internal voids (porosity) and promoting atomic diffusion between surfaces. The force is carefully managed to avoid damaging the material while achieving maximum density.
The Key Advantages of Processing in a Vacuum
The decision to use a vacuum hot press is driven by the need to solve specific material science challenges that conventional furnaces cannot address.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the primary benefit. For materials like titanium, refractory metals, and certain ceramics, even trace amounts of oxygen at high temperatures can form brittle oxide layers, ruining the component's structural integrity. The vacuum ensures the material's surface chemistry remains pure.
Enhancing Density and Reducing Porosity
The combination of heat and pressure effectively consolidates powdered materials or eliminates microscopic gaps in solid parts. This process, known as sintering or densification, is crucial for creating high-performance components with superior mechanical strength and reliability.
Enabling Diffusion Bonding
A vacuum hot press is one of the few methods capable of diffusion bonding. This is a solid-state joining process where two dissimilar materials are pressed together at high temperatures. The vacuum ensures the surfaces are perfectly clean, allowing atoms from each material to intermingle and form a permanent bond without melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not a universal solution. The complexity of the system introduces specific operational considerations.
Higher Equipment and Maintenance Costs
Vacuum hot presses are significantly more complex and expensive than standard atmosphere furnaces. The high-performance pumps, seals, and control systems require specialized maintenance and skilled operators.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum (a very low pressure) can be time-consuming, a phase known as "pump-down." The heating and cooling cycles within a vacuum are also often slower than in a gas-filled furnace, leading to longer overall processing times per part.
Material Limitations
Not all materials are suitable for a vacuum. Materials that have a high vapor pressure can "outgas" or evaporate under vacuum at high temperatures, which can contaminate the chamber and alter the material's composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing method depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and purity for reactive materials like advanced ceramics or superalloys: A vacuum hot press is often the only viable solution.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or non-weldable materials with a seamless bond: Diffusion bonding in a vacuum hot press is the industry-standard approach.
- If your primary focus is simply hardening steel or sintering non-reactive powders: A more cost-effective conventional atmosphere furnace is likely the better tool for the job.
Ultimately, a vacuum hot press is a powerful tool for engineers and scientists pushing the boundaries of what materials can do.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
| High Temperature | Enables material processing up to 2000°C+ |
| Mechanical Pressure | Achieves maximum density and reduces porosity |
| Diffusion Bonding | Joins dissimilar materials without melting |
Ready to push the boundaries of your material processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum hot press systems designed for superior densification and bonding of reactive materials. Our solutions help researchers and engineers achieve contamination-free results with precise temperature and pressure control. Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hot press technology can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results



















