At its core, creating a lab diamond involves one of two primary technologies: High Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). These are not simply machines but sophisticated industrial processes designed to replicate the extreme conditions under which diamonds form, resulting in a product that is physically, chemically, and optically identical to a mined diamond.
The question isn't just about the machines, but the two fundamentally different philosophies they represent. One method simulates the brute force of nature, while the other builds a diamond with atomic precision, layer by layer.

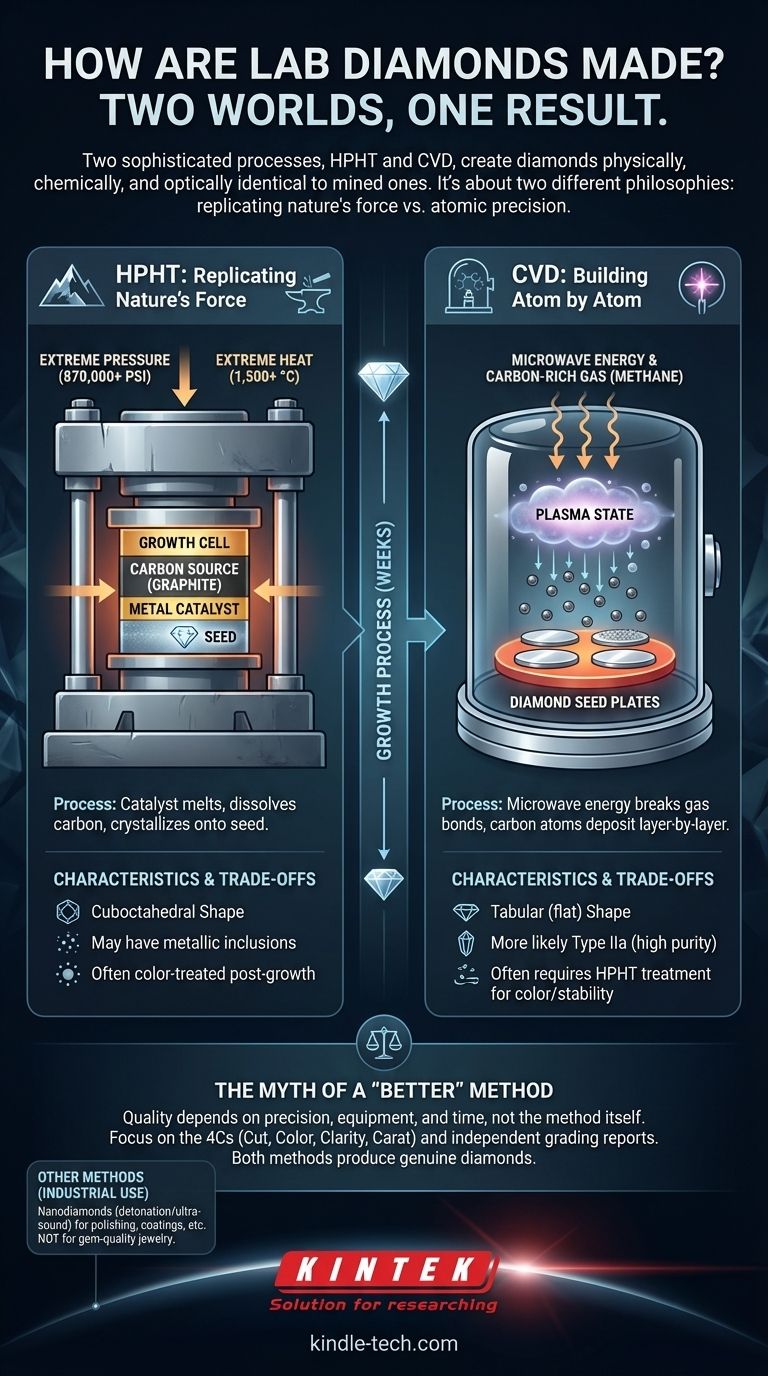
The Two Core Technologies for Gem-Quality Diamonds
For diamonds used in jewelry, the industry relies exclusively on two proven methods. Each process starts with a "seed"—a tiny, high-quality sliver of a previously grown diamond that acts as the template for new growth.
HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature): Replicating Nature's Force
The HPHT method is the original process for growing diamonds and directly mimics the conditions deep within the Earth's mantle.
The "machine" is a massive mechanical press capable of generating immense force and heat. These presses subject a carbon source, like purified graphite, to pressures over 870,000 pounds per square inch and temperatures above 1,500°C (2,732°F).
Inside the press, the carbon source and a diamond seed are placed in a growth cell with a metal catalyst. The intense heat melts the catalyst, which dissolves the carbon source. This dissolved carbon then crystallizes onto the diamond seed, growing a new, larger rough diamond over several weeks.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Building Atom by Atom
The CVD method is a newer technique that builds a diamond in a way more analogous to 3D printing, but on an atomic scale.
The machine for this process is a vacuum chamber. Diamond seed plates are placed inside, and the chamber is filled with carbon-rich gases, typically methane.
High-power microwave energy is used to heat the gases into a plasma state. This breaks the molecular bonds of the gas, freeing carbon atoms. These atoms then "rain down" and deposit onto the cooler diamond seed plates, growing the diamond crystal one layer at a time. This process can also take several weeks to produce a sizeable gem.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While both methods produce genuine diamonds, the different growth environments can leave behind subtle tell-tale signs, or "growth habits," that gemological labs can detect.
The Impact on Diamond Characteristics
HPHT diamonds grow in a cuboctahedral shape. Due to the metal catalyst used, they can sometimes have tiny metallic inclusions. Many HPHT diamonds undergo a post-growth treatment to improve their color.
CVD diamonds grow in a flatter, tabular shape. They are more likely to be Type IIa diamonds, a classification that is very rare in nature and denotes exceptional chemical purity. However, many CVD diamonds also require post-growth treatment (often using the HPHT process) to enhance their color and stability.
The Myth of a "Better" Method
Neither HPHT nor CVD is inherently superior. The final quality of any lab-grown diamond is determined by the precision of the manufacturer, the quality of their equipment, and their commitment to slow, stable growth.
A high-quality diamond from a top-tier CVD grower will be far superior to a low-quality diamond from a rushed HPHT process, and vice-versa. The growth method is a manufacturing detail, not a final indicator of quality.
What About Other Methods?
You may encounter mentions of other diamond-creation techniques, such as detonation synthesis or ultrasound cavitation.
Nanodiamonds for Industrial Use
These methods are not used for creating gem-quality diamonds. Instead, they produce vast quantities of microscopic diamond dust, or nanodiamonds.
These tiny diamonds are used for industrial purposes, such as in polishing slurries, engine oil additives, and advanced coatings. For the purpose of jewelry, these methods are irrelevant.
How This Informs Your Choice
Understanding how lab diamonds are made empowers you to focus on what truly matters: the final product's quality, not its specific manufacturing journey.
- If your primary focus is technology: You might find the story behind either the nature-mimicking HPHT process or the atom-by-atom CVD process more compelling.
- If your primary focus is quality and value: Ignore the growth method entirely and concentrate on the independent grading report, which details the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat).
Ultimately, the machine is just the tool; the true measure of any diamond is its certified quality and brilliance.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Process Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) | Uses massive presses to replicate Earth's mantle conditions with extreme pressure and heat. | Grows cuboctahedral crystals; may have metallic inclusions; often color-treated post-growth. |
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Builds diamonds layer-by-layer in a vacuum chamber using carbon-rich gas and microwave energy. | Produces tabular-shaped crystals; often Type IIa (high purity); may require HPHT treatment for color. |
Ready to explore lab equipment for advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving researchers and manufacturers in need of reliable, precise tools for diamond growth and other advanced processes. Whether you're scaling up HPHT presses or optimizing CVD chambers, our expertise ensures you get the right solutions for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation with cutting-edge technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal chemical vapor deposition method? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Films
- What is the thin film production method? A Guide to Deposition Techniques
- What is chemical vapor deposition method of graphene? A Guide to Scalable, High-Quality Production
- Why vacuum is required in thin-film deposition? The Critical Role of Vacuum in Achieving Purity and Precision
- What methods are used to deposit thin films? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and ALD Techniques
- What technical advantages do single-source precursors offer in SiC CVD? Achieve Superior Stoichiometry and Low Defects
- What is physical Vapour deposition techniques? A Guide to Sputtering, Evaporation & More
- What are the advantages of using an externally heated tubular fluidized bed reactor? Achieve High-Purity Nickel CVD



















