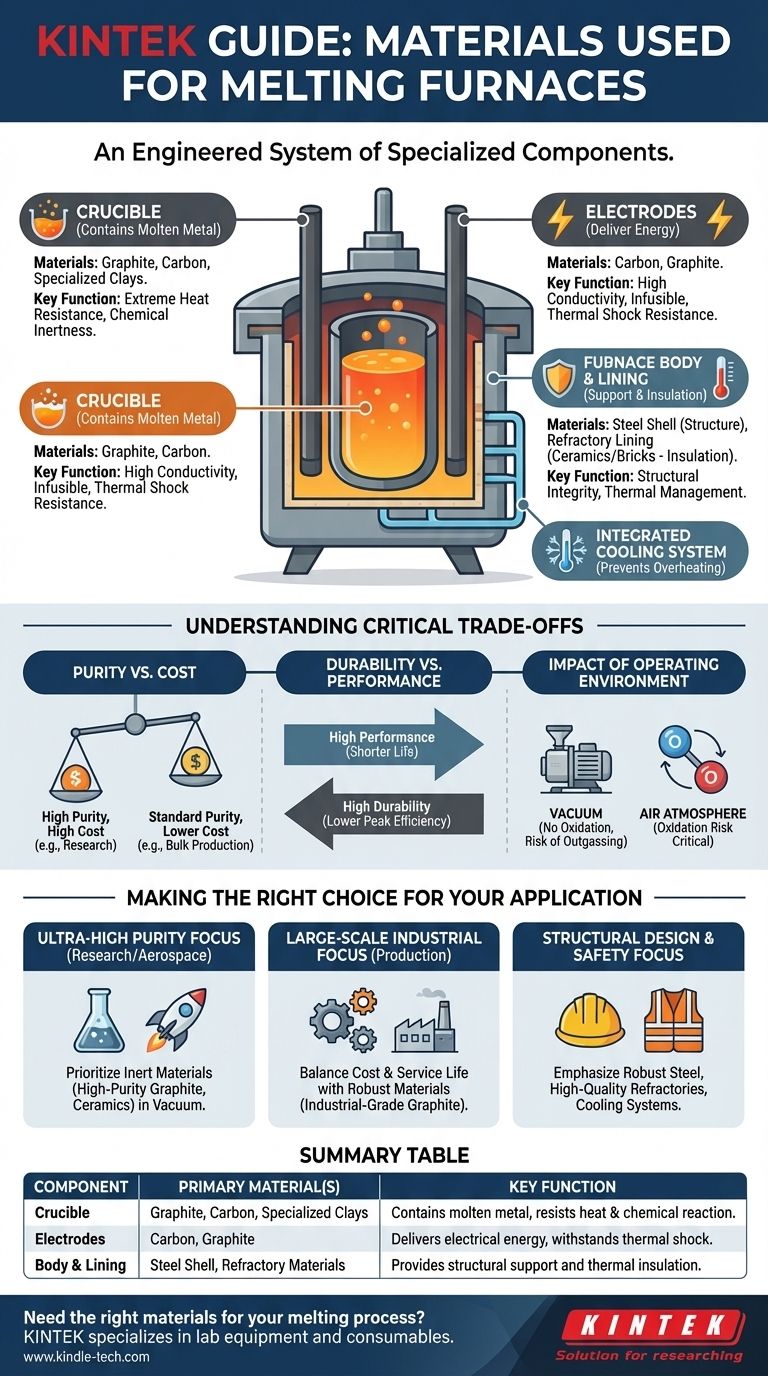
Critically, a melting furnace is not made of a single material. It is an engineered system where different materials are selected for specific roles based on extreme temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and electrical properties. The core components that contact molten metal, like the crucible, are typically made of graphite, carbon, or specialized clays, while energy-delivery components like electrodes are made of highly conductive carbon or graphite.
The choice of material for a melting furnace is dictated entirely by the function of each specific component. The goal is to create a system that can safely contain extreme heat, deliver energy efficiently, and avoid contaminating the final product.

The Anatomy of a Furnace: A System of Materials
Thinking of a furnace as a single object is a common misconception. In reality, it's an assembly of distinct parts, each with a job to do and a material perfectly suited for that task. The primary components are the crucible, the electrodes (in some designs), and the structural body and lining.
The Crucible: Containing the Molten Metal
The crucible is the vessel that directly holds the molten material. Its job is to remain stable and inert at temperatures that would vaporize most other substances.
For this reason, materials like graphite carbon and specialized clays are the most common choices. They possess an extremely high melting point and are chemically resistant, which prevents them from dissolving into or reacting with the molten metal, ensuring purity.
The Electrodes: Delivering the Energy
In arc furnaces, massive amounts of energy are delivered through electrodes to melt the material. These components require a unique combination of properties.
They are made from carbon or graphite because these materials are excellent electrical conductors. Crucially, they are also infusible (they don't melt) and can withstand severe thermal shock—the rapid temperature changes that would crack lesser materials.
The Furnace Body and Lining
The outer structure of a furnace provides support and containment. This is typically a steel shell, which offers mechanical strength but has no significant heat resistance.
To protect the steel shell, the interior is lined with refractory materials (not explicitly mentioned in the references, but a fundamental part of any furnace). These are heat-resistant ceramics or bricks that act as the primary thermal insulation, keeping the intense heat inside and protecting the outer structure. A cooling system is often integrated to prevent overheating in key structural areas.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting materials for a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. The perfect material rarely exists, so engineers must make informed compromises.
Purity vs. Cost
High-purity metals and advanced alloys, such as those melted in a vacuum furnace, require crucibles made from very pure, inert materials to avoid contamination. These high-grade materials are significantly more expensive.
For bulk melting of common metals, a more cost-effective clay-graphite composite may be sufficient, even if it introduces trace impurities that would be unacceptable in a high-tech application.
Durability vs. Performance
Some materials may offer superior performance—for instance, higher electrical conductivity in an electrode—but may have a shorter operational life due to erosion or oxidation.
This creates a trade-off between the furnace's peak efficiency and its maintenance costs and downtime. Choosing a slightly less performant but more durable material is often the more practical economic decision.
The Impact of the Operating Environment
The environment inside the furnace dramatically changes material requirements. A vacuum induction furnace, for example, eliminates the risk of oxidation.
However, in a vacuum, a different problem emerges: outgassing, where the furnace materials themselves can release trapped gases and contaminate the melt. In a standard air-atmosphere furnace, oxidation resistance is a far more critical property.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal material choice is always tied to the specific goal of the melting process.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity for research or aerospace: Prioritize inert crucible materials like high-purity graphite or ceramics and use a vacuum furnace to eliminate environmental contamination.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: Balance material cost and service life by using robust materials like industrial-grade graphite electrodes and durable clay-graphite crucibles.
- If your primary focus is structural design and safety: Emphasize a robust steel frame combined with high-quality refractory linings and an integrated cooling system to ensure thermal management and structural integrity.
Ultimately, understanding that a furnace is a system of specialized parts is the key to selecting the right materials for the job.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material(s) | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible | Graphite, Carbon, Specialized Clays | Contains molten metal, resists heat & chemical reaction |
| Electrodes | Carbon, Graphite | Delivers electrical energy, withstands thermal shock |
| Body & Lining | Steel Shell, Refractory Materials | Provides structural support and thermal insulation |
Need the right materials for your melting process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the optimal furnace components—whether for high-purity research or industrial production—to ensure efficiency, safety, and product integrity. Contact us today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube facilitate fractional condensation in a horizontal tube vacuum gasification furnace? Expert Guide



















