A furnace is a precisely engineered system, not a single object. Its construction involves a range of specialized materials, from common steels for the exterior body to advanced ceramics and refractory metals for the high-temperature core. Key materials include stainless and low-carbon steel for the shell, alumina fiber for insulation, and elements like silicon carbide, molybdenum, or graphite for generating heat.
The selection of materials for a furnace is dictated entirely by function. Each component, from the outer shell to the internal heating element, uses a material with specific properties—like structural strength, heat insulation, or extreme temperature resistance—to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable operation.

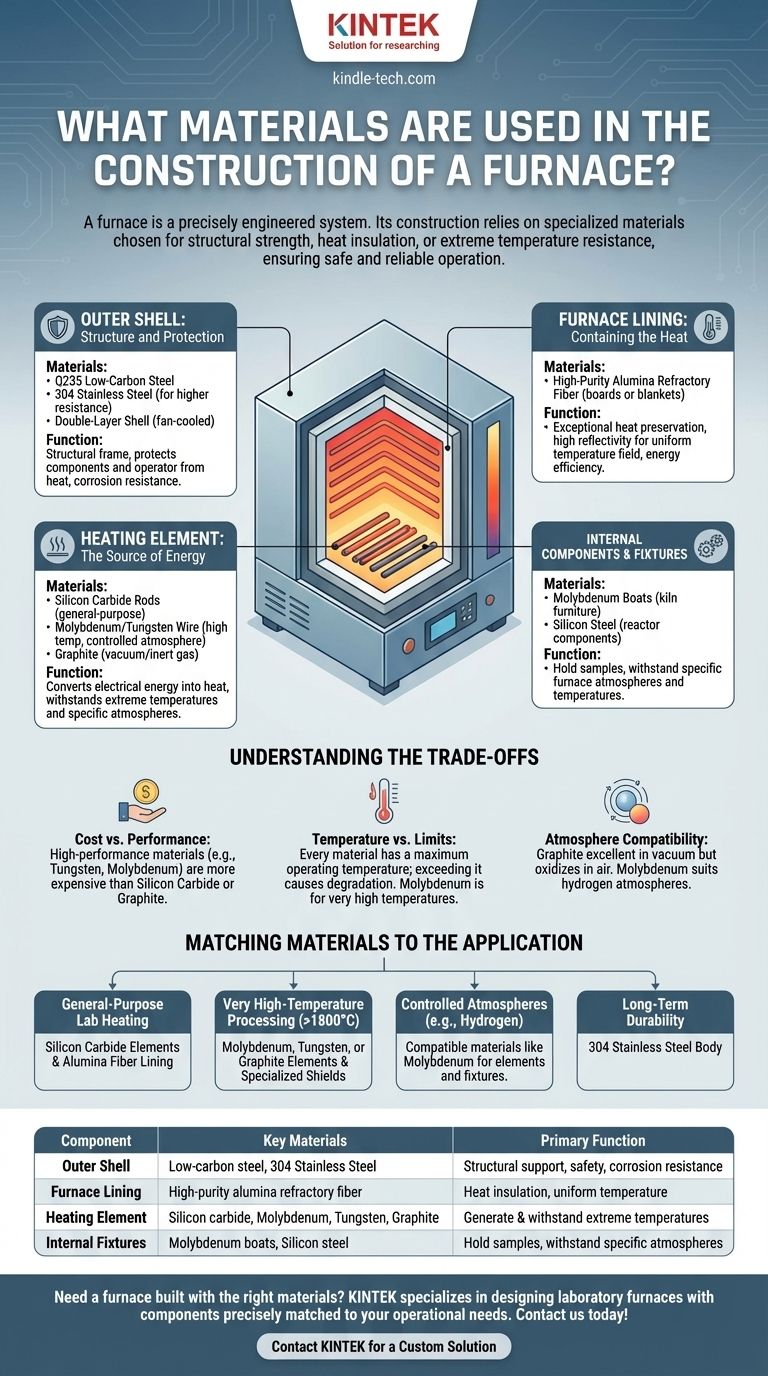
Deconstructing the Furnace: Key Components and Materials
A furnace is best understood by breaking it down into its core functional parts. Each part faces a different set of challenges, demanding a unique material solution.
The Outer Shell: Structure and Protection
The furnace shell provides the structural frame, houses the internal components, and protects the operator from the intense heat within.
Materials like Q235 low-carbon steel are often used for their strength and cost-effectiveness. They are typically coated to resist corrosion and static.
For applications requiring higher corrosion resistance or a more refined finish, 304 stainless steel is the material of choice for the shell, flanges, and various access ports.
Modern designs often feature a double-layer shell with a fan-cooled air gap. This engineering detail keeps the outer surface temperature low, ensuring operator safety.
The Furnace Lining: Containing the Heat
The lining, or hearth, is the critical insulation layer that contains the extreme temperatures and prevents heat from escaping.
The most common material is high-purity alumina refractory fiber, sometimes referred to as polycrystalline fiber. This material is vacuum-formed into rigid boards or used as a soft blanket.
Its primary benefits are exceptional heat preservation and high reflectivity, which helps create a balanced and uniform temperature field inside the furnace. This directly translates to energy efficiency and consistent heating of the material being processed.
The Heating Element: The Source of Energy
The heating element is the heart of the furnace, converting electrical energy into heat. The choice of material here is critical and depends entirely on the required operating temperature and internal furnace atmosphere.
For general-purpose furnaces, silicon carbon rods are a common and reliable choice.
For very high-temperature applications, especially in controlled atmospheres, refractory metals are used. Molybdenum wire, with a melting point of 2630°C, and tungsten wire are frequently used in hydrogen furnaces.
In vacuum or inert-gas furnaces, graphite is often used for the heating elements, the furnace chamber, and even the insulation due to its excellent high-temperature stability.
Internal Components and Fixtures
Beyond the main sections, various internal components also require specialized materials.
Fixtures used to hold samples inside the furnace, known as "kiln furniture," must also withstand extreme heat. In hydrogen furnaces, molybdenum boats are commonly used.
In some specialized furnace reactors, silicon steel is a key material. It is critical to use new, high-quality silicon steel to ensure the reactor operates efficiently and avoids failures associated with recycled materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing furnace materials is a constant balance between performance requirements, operating conditions, and cost. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance materials come at a high price. Tungsten and molybdenum offer incredible temperature resistance but are significantly more expensive than silicon carbide or graphite elements. Similarly, a full stainless steel shell is more costly than a coated low-carbon steel one.
Temperature vs. Material Limits
Every material has a maximum operating temperature. Pushing a material beyond its limit will lead to rapid degradation and furnace failure. Molybdenum is chosen for its high melting point, making it suitable for processes that other elements cannot handle.
Atmosphere Compatibility
The chemical environment inside the furnace is a critical factor. Graphite is an excellent heating element in a vacuum, but it will quickly oxidize and burn away in the presence of air. Molybdenum is particularly well-suited for hydrogen atmospheres where other materials might become brittle.
Matching Materials to the Application
Your specific goal determines the ideal combination of furnace materials.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating: A furnace with silicon carbon heating elements and an alumina fiber lining provides an excellent balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is very high-temperature processing (above 1800°C): Look for furnaces built with molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite heating elements and specialized heat shields.
- If your primary focus is working with controlled atmospheres (e.g., hydrogen): The furnace must use compatible materials like molybdenum for its heating elements and internal fixtures to prevent chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and corrosion resistance: A furnace constructed with a 304 stainless steel body for the shell, flanges, and ports is the superior choice.
Ultimately, a furnace's performance and reliability are defined by the intelligent selection and combination of these specialized materials.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Low-carbon steel, 304 Stainless Steel | Structural support, safety, and corrosion resistance |
| Furnace Lining | High-purity alumina refractory fiber | Heat insulation and uniform temperature distribution |
| Heating Element | Silicon carbide, Molybdenum, Tungsten, Graphite | Generate and withstand extreme temperatures |
| Internal Fixtures | Molybdenum boats, Silicon steel | Hold samples and withstand specific furnace atmospheres |
Need a furnace built with the right materials for your specific application?
The materials used in a furnace are critical to its performance, safety, and lifespan. At KINTEK, we specialize in designing and supplying laboratory furnaces with components precisely matched to your operational needs—whether you require high-temperature processing, controlled atmospheres, or general lab heating.
We provide expert guidance to ensure you get a furnace that delivers reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let our specialists help you select the ideal equipment.
Contact KINTEK for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- When we heat a metal ring it gets expand or compressed? The Hole Gets Bigger, Not Smaller
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in lab? Ensuring Sample Purity Through Complete Isolation



















