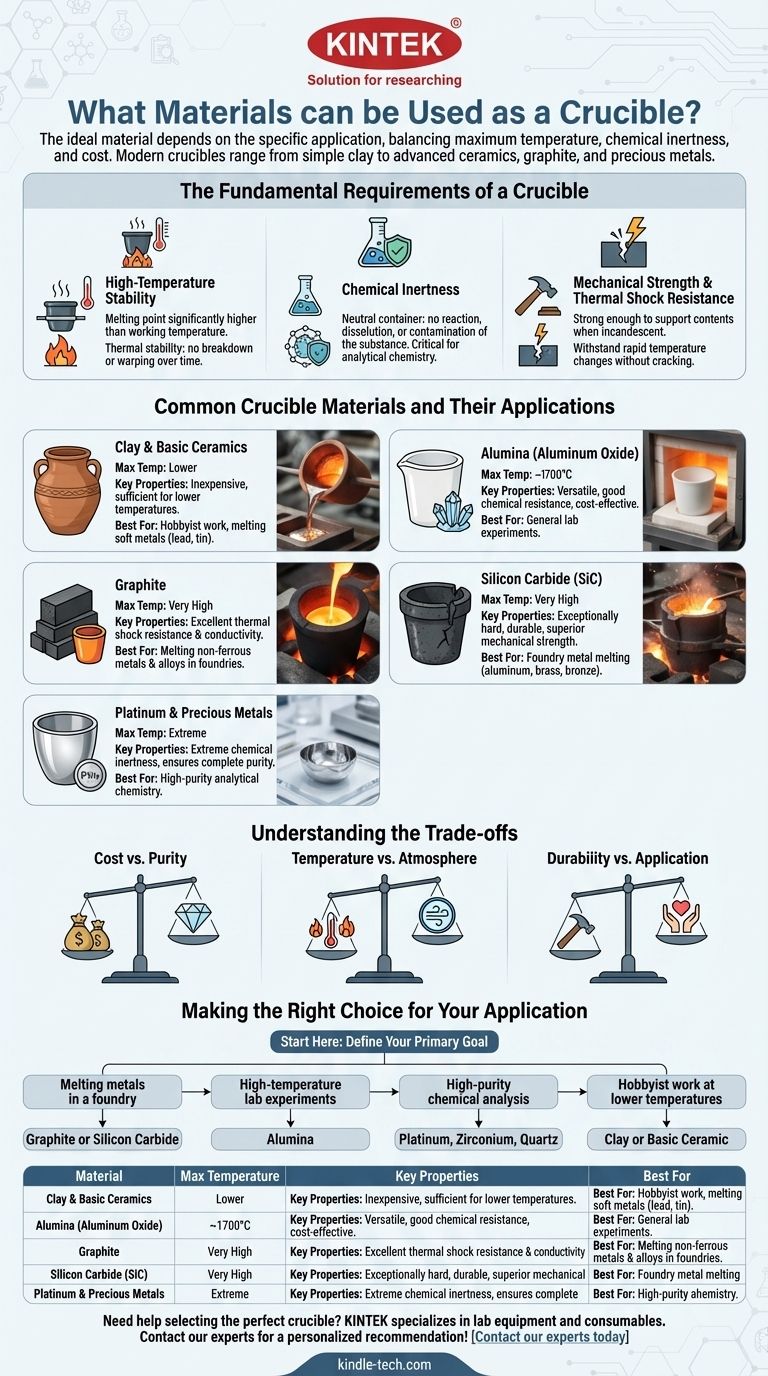
The ideal material for a crucible depends entirely on the specific application. While historically made from simple clay, modern crucibles are engineered from a variety of advanced materials including high-purity ceramics like alumina and zirconia, graphite, silicon carbide, and even precious metals like platinum. The correct choice is dictated by the maximum temperature required and the chemical reactivity of the substance being heated.
Selecting a crucible is not about finding a material that simply survives the heat. It is a critical decision that balances three factors: maximum temperature, chemical inertness with the substance being heated, and cost. The right material is the one that meets your thermal and chemical needs without failing or contaminating your sample.

The Fundamental Requirements of a Crucible
Before examining specific materials, it's essential to understand the non-negotiable properties a crucible must possess. The choice of material is a direct response to these three demands.
High-Temperature Stability
The most obvious requirement is that the crucible must have a melting point significantly higher than your working temperature.
Equally important is thermal stability. The material cannot break down, warp, or degrade when held at high temperatures for extended periods.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible must act as a neutral container. It should not react with, dissolve into, or otherwise contaminate the substance it holds.
This is especially critical in analytical chemistry, where even trace amounts of contamination from the crucible can render an experiment's results invalid.
Mechanical Strength & Thermal Shock Resistance
The material must be strong enough to hold its shape and support the weight of its contents, even when incandescent.
It must also withstand thermal shock—the stress created by rapid changes in temperature. A material with poor thermal shock resistance can easily crack if heated or cooled too quickly.
Common Crucible Materials and Their Applications
Each material offers a unique profile of temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and cost, making it suitable for different tasks.
Clay and Basic Ceramics
Historically, clay was the most common material for crucibles. It is inexpensive and sufficient for lower-temperature applications, such as melting soft metals like lead or tin.
Modern industrial ceramics are far more robust. Alumina (aluminum oxide) is a versatile workhorse, offering excellent high-temperature performance (up to ~1700°C) and good chemical resistance for a reasonable cost. Zirconia offers a higher temperature ceiling and enhanced stability.
Graphite
Graphite crucibles are the standard for melting non-ferrous metals and alloys in foundries. Their primary advantage is outstanding thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock.
This allows for very rapid heating and cooling cycles without the risk of cracking, making them highly efficient for production environments.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Often used in a composite with graphite, silicon carbide is an exceptionally hard and durable material.
These crucibles provide superior mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. They are ideal for melting and holding non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze.
Precious Metals and High-Purity Materials
For the most demanding applications in analytical chemistry, crucibles are made from materials like platinum and zirconium.
Their extreme chemical inertness ensures that the sample remains completely pure, which is paramount for accurate elemental analysis. Their high cost makes them unsuitable for anything but this specialized, high-purity work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" crucible material. Your choice will always involve balancing competing priorities.
Cost vs. Purity
A basic clay crucible might cost a few dollars, while a platinum one can cost thousands. You are paying for purity. For general melting, contamination from an alumina crucible is negligible. For trace metal analysis, it is unacceptable.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere
Graphite has a phenomenal temperature resistance, but it will rapidly oxidize and burn away in an oxygen-rich atmosphere at high temperatures. Ceramic crucibles like alumina do not have this limitation and are stable in air.
Durability vs. Application
A silicon carbide crucible is extremely durable and built for the rough environment of a foundry. A thin-walled platinum crucible, while chemically superior, is delicate and must be handled with care.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, start by defining your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is melting metals in a foundry: You will likely need a graphite or silicon carbide crucible for its excellent thermal shock resistance and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature lab experiments: An alumina crucible is often the most cost-effective and reliable choice for general use.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical analysis: You must invest in a platinum, zirconium, or high-purity quartz crucible to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist work at lower temperatures: A simple and affordable clay or basic ceramic crucible is often sufficient.
Choosing the correct crucible is the first step toward ensuring the integrity and success of your high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | ~1700°C | Good chemical resistance, cost-effective | General lab experiments |
| Graphite | Very High | Excellent thermal shock resistance, conductive | Melting non-ferrous metals |
| Silicon Carbide | Very High | High strength, abrasion resistant | Foundry metal melting |
| Platinum | Extreme | Ultimate chemical purity, inert | High-purity chemical analysis |
| Clay/Ceramic | Lower | Inexpensive, basic use | Hobbyist or low-temp work |
Need help selecting the perfect crucible for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to ensure your high-temperature processes are efficient, contamination-free, and cost-effective. Whether you're in a research lab, foundry, or analytical setting, our range of crucibles—from durable alumina to high-purity platinum—is designed to meet your exact needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized recommendation and enhance the integrity of your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container



















