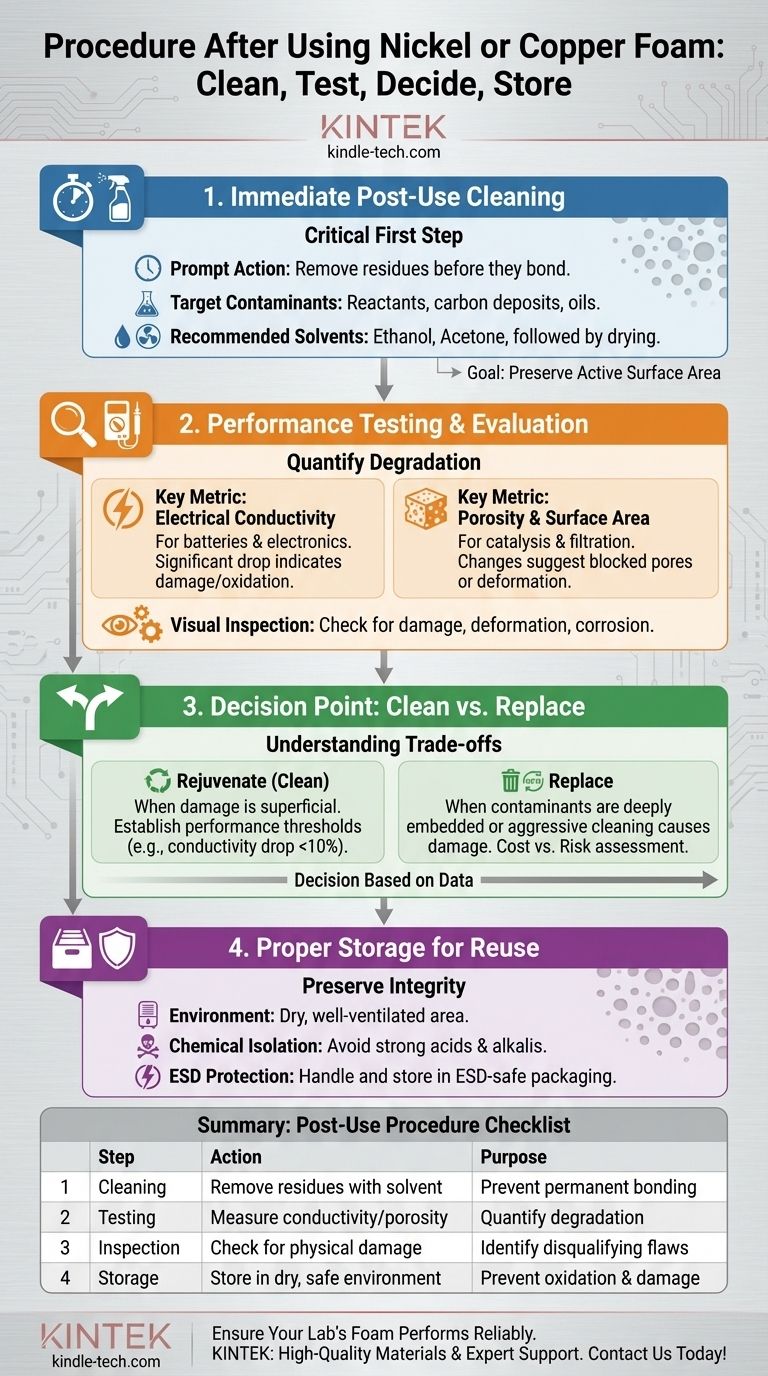
After using nickel or copper foam, you must follow a two-part procedure to ensure its integrity for future use. The first step is to promptly and thoroughly clean the foam to remove all surface residues from the application. The second is to conduct performance tests to quantify any degradation, which provides the data needed to decide if the material can be reliably reused or must be replaced.
The core principle of post-use care is not just cleaning, but systematically evaluating the foam's condition. This data-driven approach prevents future failures and ensures consistent performance in sensitive applications like catalysis or electronics.
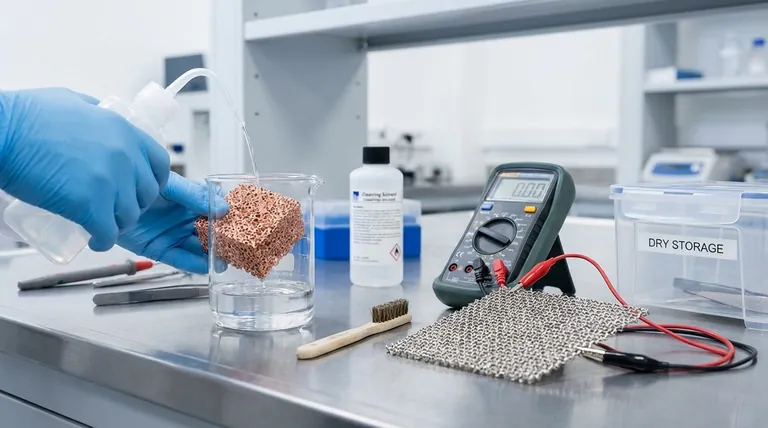

The Critical First Step: Immediate Post-Use Cleaning
Proper cleaning is the foundation of material longevity. Delaying this step can allow contaminants to bond permanently to the foam's intricate structure, rendering it unusable.
Why Immediate Cleaning is Non-Negotiable
After use, especially in high-temperature or reactive environments, residues can begin to chemically bond with or physically embed into the metal surface. Immediate cleaning minimizes this effect, preserving the foam's active surface area and properties.
Common Contaminants to Address
The specific contaminants depend entirely on the application. For catalysis, this often includes reactant residues and carbon deposits. In other uses, it could be oils, electrolytes, or other environmental particulates.
Recommended Cleaning Protocols
Select a solvent that effectively dissolves the specific contaminants without reacting with the nickel or copper base metal. Common choices for general cleaning include ethanol or acetone to remove oils and organic films, followed by a thorough drying process.
Assessing Material Integrity Through Performance Testing
Cleaning restores the surface, but testing reveals the true health of the material. This evaluation quantifies degradation that may not be visible to the naked eye.
The Purpose of Post-Use Evaluation
The goal is to gather objective data on the foam's key properties. Comparing these post-use measurements to the material's baseline specifications provides a clear basis for deciding on maintenance, reuse, or replacement.
Key Metric: Electrical Conductivity
For applications in batteries, electronics, or sensors, electrical conductivity is paramount. A significant drop in conductivity indicates internal structural damage, oxidation, or stubborn contamination, signaling that the foam may no longer meet performance requirements.
Key Metric: Porosity and Surface Area
In catalysis, filtration, and battery electrodes, the foam's high porosity is its most critical feature. A change in porosity suggests that pores have been blocked by residue or that the internal structure has been physically deformed or corroded.
Visual Inspection for Physical Damage
Before any quantitative testing, perform a careful visual inspection. Look for signs of damage, deformation, or corrosion that would immediately disqualify the material from further use.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Clean vs. Replace
Reusing material can be cost-effective, but not if it introduces risk into your process. Understanding the limits of rejuvenation is crucial.
The Limits of Cleaning
Aggressive cleaning can sometimes cause more damage than the initial use. If contaminants are deeply embedded or have chemically altered the foam, no amount of cleaning will restore its original properties.
Performance Thresholds for Replacement
Establish clear failure points before you begin. For example, you might decide to replace the foam if its electrical conductivity drops by more than 10% or if its porosity changes significantly. This removes guesswork from the decision-making process.
The Cost of Reuse vs. The Risk of Failure
Consider the full cost. The labor and equipment time for cleaning and testing must be weighed against the cost of a new piece of foam. More importantly, evaluate the risk and cost of a process failure if a degraded piece of foam is reused.
Proper Storage Protocols for Future Use
If the foam is deemed suitable for reuse, proper storage is essential to preserve its condition until the next application.
Environmental Control
Store the cleaned and dried foam in a dry, well-ventilated environment. Moisture is a primary driver of oxidation and corrosion for both nickel and copper, rapidly degrading their performance.
Avoiding Chemical Corrosion
Isolate the foam from all corrosive substances. This is especially true for strong acids and strong alkalis, which will aggressively attack the metal and destroy the delicate foam structure.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Given the high conductivity of these materials, they must be handled and stored with electrostatic protection in ESD-sensitive environments. This prevents static discharge from damaging the foam or nearby electronic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your post-use protocol should be directly aligned with your application's most critical performance metric.
- If your primary focus is reusability in catalysis: Prioritize thorough cleaning to remove all residues and validate the foam's porosity and surface area before reuse.
- If your primary focus is consistent electrical performance: Make conductivity testing the centerpiece of your evaluation and enforce strict ESD-safe handling and storage.
- If your primary focus is long-term material longevity: Emphasize immediate cleaning after every use and meticulous, moisture-free storage away from all potential chemical contaminants.
By implementing this systematic clean-and-verify procedure, you transform material care from a chore into a strategic process that ensures reliability and extends the useful life of your metal foam.
Summary Table:
| Procedure Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Cleaning | Remove residues with solvents like ethanol or acetone. | Prevent permanent bonding of contaminants and preserve surface area. |
| Performance Testing | Measure electrical conductivity and porosity. | Quantify degradation and decide on reuse or replacement. |
| Visual Inspection | Check for physical damage, deformation, or corrosion. | Identify obvious flaws that disqualify reuse. |
| Proper Storage | Store in a dry, well-ventilated area away from corrosive substances. | Prevent oxidation and maintain material integrity for future use. |
Ensure your lab's metal foam performs reliably every time. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including nickel and copper foam tailored for catalysis, electronics, and energy storage. Our experts can help you select the right materials and implement best practices for cleaning, testing, and storage—maximizing your ROI and minimizing downtime. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let KINTEK support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Foam
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
People Also Ask
- What electrostatic protection measures should be taken when using nickel and copper foam? Essential ESD Safety Protocols
- Is copper foam safe? Discover the facts about its antimicrobial and cooling benefits
- What are the proper storage conditions for nickel and copper foam? A Guide to Preserving Performance
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage



















